Users at home and abroad are using cloud-native technology to improve application development efficiency and manageability. Many users use the open source Harbor product warehouse to manage images of cloud-native applications in the agile software supply chain, including image storage, image scanning, and image Signature and other functions.
Harbor already provides some advanced security features, such as scanning images to find potential security issues. Harbor's image scanning function is essentially a static scan, that is, through Trivy, Clair, Arksec and other vulnerability scanners (scanners), the image is scanned by events or periodically. Static scanning can detect potential threats in image files, but some risky images may still pass the scanner's detection and be deployed to the Kubernetes cluster, thus introducing runtime risks.
For example, Harbor scans a mirror, and the detection result shows that the mirror reaches a certain security level, allowing it to go online. After a while, a new CVE vulnerability was discovered, which happened to be included in the image, and Harbor no longer allowed the image to go online until the vulnerability was fixed. But for images that are already running, Harbor can't do anything.
Given that Harbor focuses on the static security protection of cloud-native applications, facing the increasingly serious risk of "supply chain attacks", users need to improve another security capability, namely dynamic security protection (runtime security protection).
To this end, we have launched a new open source project CNSI, Cloud Native Security Inspector (Cloud Native Security Inspector) , project code name: Narrows . Based on Harbor, Narrows has enhanced dynamic security capabilities, which allow users to conduct runtime security posture assessments on Kubernetes clusters and workloads in them. The images in the mirror warehouse can be scanned when they are introduced into the Kubernetes cluster, and the configuration and status of the Kubernetes cluster itself are scanned together and a security report is generated. This allows administrators to discover and mark security vulnerabilities in the cluster and isolate vulnerable workloads.
The runtime dynamic security scanning capability brought by Narrows is very critical. It helps administrators have better control and awareness of the security status of Kubernetes clusters and workloads on them, rather than just focusing on the life cycle of workloads.
Capabilities provided by Narrows include:
· Dynamic detection and perception of runtime vulnerabilities
· Discover misconfigurations of Kubernetes clusters
· Stop attacks in progress while the workload is running
· Summarize, aggregate and analyze scan reports and provide an open API interface
· Seamless integration with Harbor. Mirrors in external public mirror warehouses can be automatically synchronized to Harbor to generate secure data.
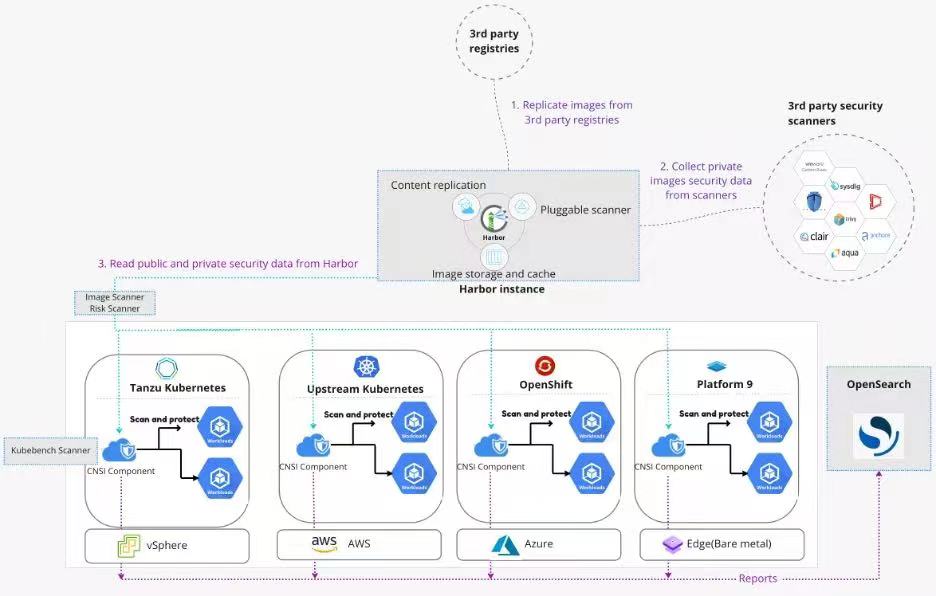
Narrows is integrated with Harbor, as shown above. Narrows allows users to define security expectations for workloads in Kubernetes clusters through a simple interface, and scans workloads based on user-specified scanners and scan cycles. Isolate workloads that do not meet security requirements.
The current version of Narrows supports three scanners, namely:
1.Image scanner (mirror scanner)
Comparing the security vulnerability level of the image in the Kubernetes cluster with the user's expected security vulnerability level can isolate workloads that do not meet security expectations.
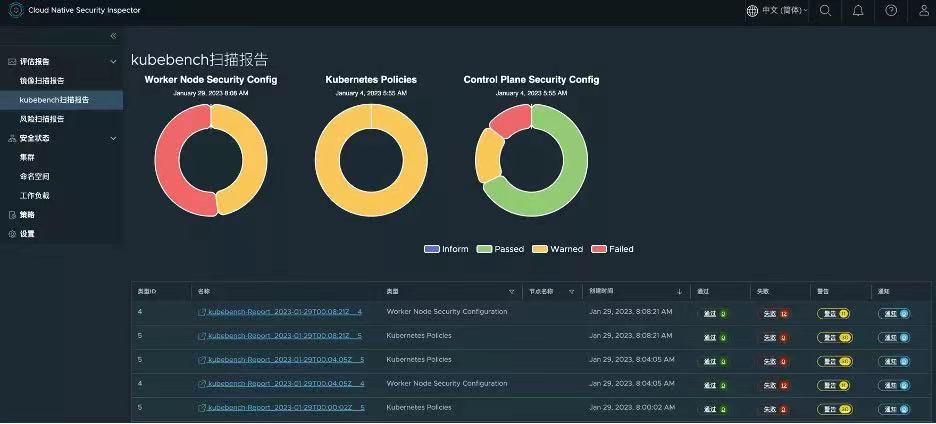
2. Kubebench scanner (Kubebench scanner)
Use kubebench to scan the configuration of the Kuberentes cluster, find unreasonable configuration items and provide suggestions for modification.
3.Risk scanner (run risk scanner)
Scans the software packages included in the workload and provides the corresponding CVE details.
We plan to enhance Narrows' detection capabilities by accessing new security data sources and introducing new scanners. At the same time, we will further in-depth research and expand the ability to handle security holes and insecure payloads. In the part of security data analysis and insight, we expect to be able to comprehensively summarize multi-dimensional security data, and perform security risk sorting, screening, and result presentation according to different scenarios and user preferences.
Narrows has been open sourced by VMware, using the commercially friendly Apache 2.0 software license, which is convenient for users to expand and innovate. In terms of the community, Arksec contributed a sorting function in the latest release of Narrows, which can be combined with container runtime scanning to prioritize security vulnerabilities. Yake Cloud will also continue to participate in the Narrows project and plans to contribute a number of security capabilities.
Narrows has been open sourced, and the Github address of the project is:
https://github.com/vmware-tanzu/cloud-native-security-inspector
Users are welcome to participate in our open source projects, and look forward to your use and feedback. If you are interested in the Narrows open source project, would like to work more closely with us, or would like to do testing and trials, suggestions or bugs, please email [email protected].
Content Source|Public Account: VMware China R&D Center