
Lingen Bio's cooperative customer: The team of Mr. Cui Kangping from Hefei University of Technology used the solution of Lingen Bio's metagenomic resistance gene research to study gadolinium (Gd(III)) and the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in the activated sludge of sewage treatment plants ) was investigated, emphasizing the influence of Gd(III) and SMX alone and coexistence on the denitrification mechanism as well as ARGs and MGEs. The research results were published in the environmental journal "Process Safety and Environmental Protection" (IF=7.926).

1. Research background
Hospital MRI detection and clinical treatment of bacterial infections lead to gadolinium and antibiotics entering wastewater treatment plants (WWTP). However, information on the combined contamination of gadolinium and antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants is still missing.
2. Experimental design
In this study, 50 μg/L gadolinium (Gd(III)) and 500 μg/L sulfamethoxazole (SMX) were selected to study their effects on biological nitrogen removal performance, microbial community structure, antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and mobile genetic elements (MGEs).
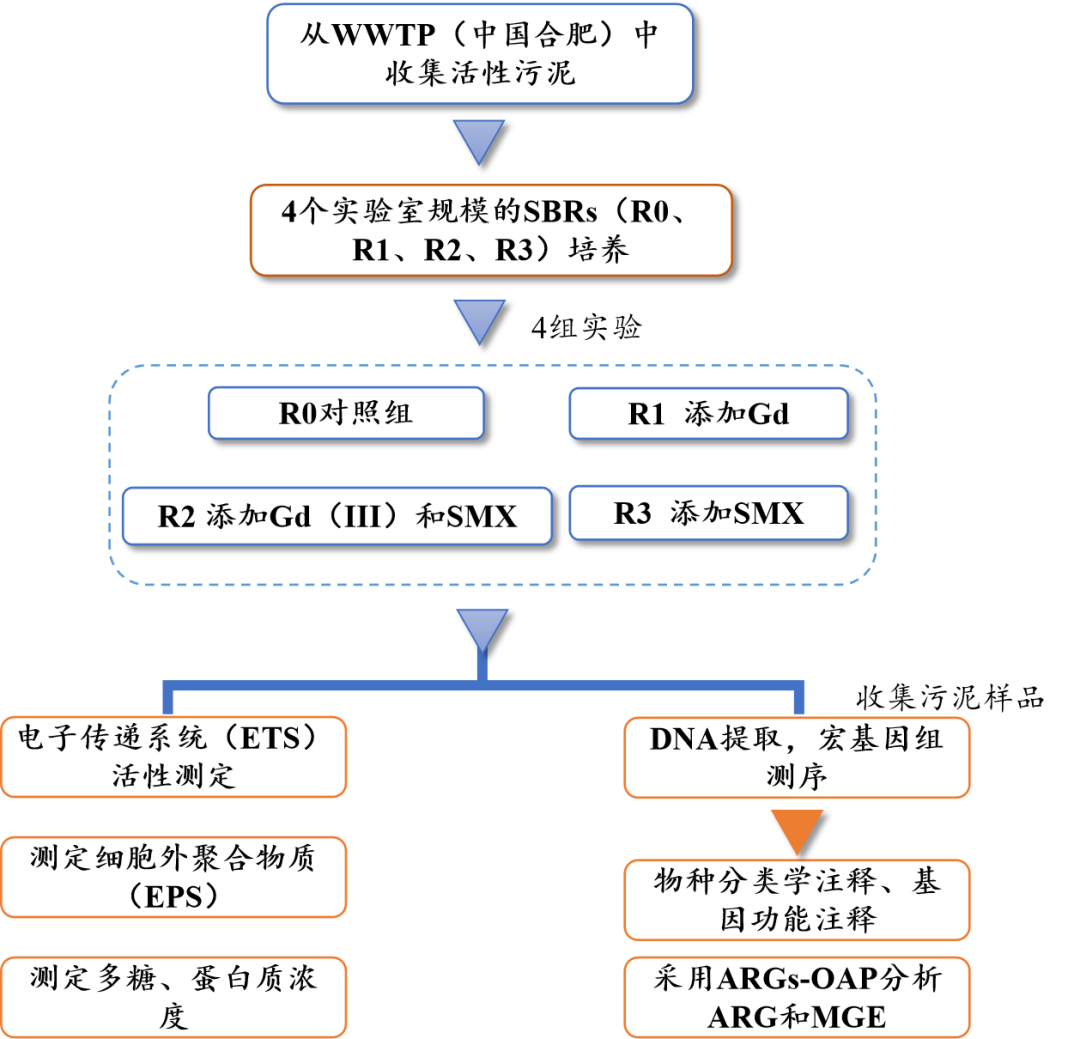
Figure 1 Overview of the study area and experimental design
3. Research conclusion
1. Gd(III) (50μg/L) alone and in combination can significantly inhibit denitrification, because Gd(III) can effectively inhibit the expression of nirD , nirB , napB and napA , in contrast, it has no effect on nitrification No noticeable effect. Gd(III) inhibits microbial activity, adversely affects EPS, and reduces the abundance of core ARGs host Streptomyces. Combined treatment significantly increased the abundance of ARGs and intl1 and promoted horizontal gene transfer (HGT) through MGEs, while combined treatment made ARGs highly correlated with MGEs. Studies also suggest that ARGs may repress denitrification genes.
2.Gd(III)抑制微生物活性,对EPS产生不利影响,降低核心ARGs宿主链霉菌的丰度。联合处理显著增加了ARGs和intl1的丰度,并通过MGEs促进了水平基因转移(HGT),同时联合处理使ARGs与MGEs高度相关。研究还表明ARGs可能抑制脱氮基因。
四、实验结果
1、Gd(III)和SMX单独或联合作用条件下脱氮性能的变化
4种序批式反应器(SBRs)的脱氮性能如图2所示。在45天的运行中,在4个反应器的出水中NH-N浓度都很低(图2(a))。
结果表明,在50μg/L Gd(III)和500μg/L SMX共存的作用下,SBR的反硝化性能受到抑制,但优于单独Gd(III)的作用,表明50μg/L Gd(III)在SBR中具有反硝化作用。
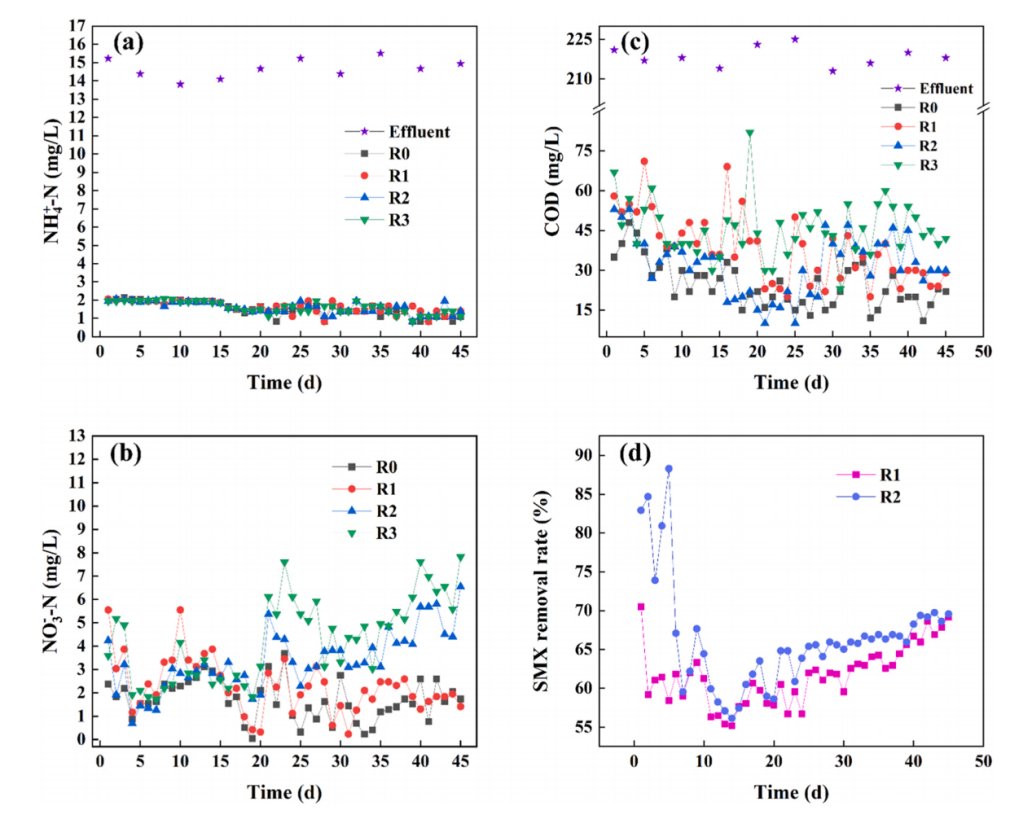
图2 四种序批式反应器(SBRs)的反应器性能(R0:对照,R1:单独添加SMX, R2: Gd(III)与SMX共存,R3:单独添加Gd(III))。
2、微生物群落的多样性和结构的变化
如图3(a)所示,α多样性分析结果表明,与对照组(R0)相比,R1和R3中Chao 1降低,而R2中显著升高。R1和R2的Shannon指数略有下降,而R3的指数有所升高。如图3(b)所示,在4个反应器中,变形菌门、放线菌门、拟杆菌门、厚壁菌门和亚硝化螺旋菌门均为优势门。
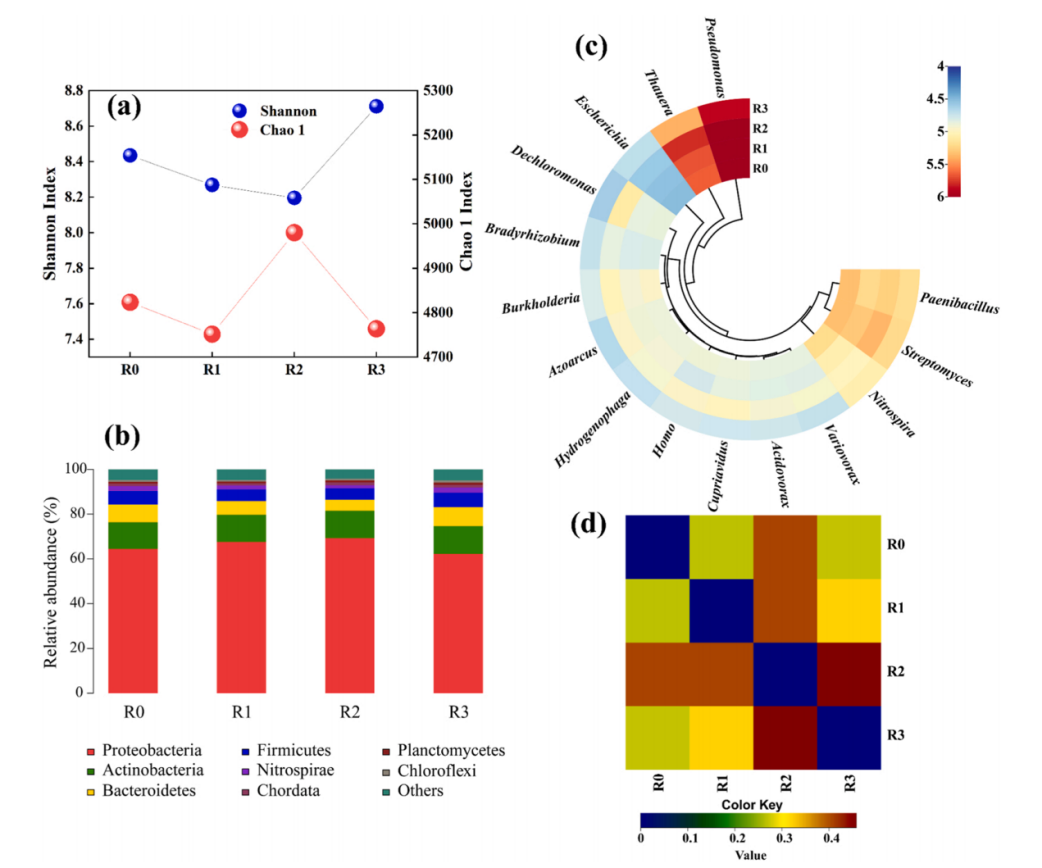
图3 (a)alpha多样性的变化。(b)门的相对丰度。(c)属水平微生物群落热图(log 10)(前15)。(d)距离热图中微生物群落的变异。
3、氮功能基因的响应
本研究检测到6个硝化基因,如图4(a)所示。反硝化基因丰度变化更显著,13个反硝化基因如图4(b)所示,500μg/L SMX单独处理的反硝化基因变化与对照几乎相同,而50μg/L Gd(III)单独处理中,nirBDS和napAB的丰度显著降低。
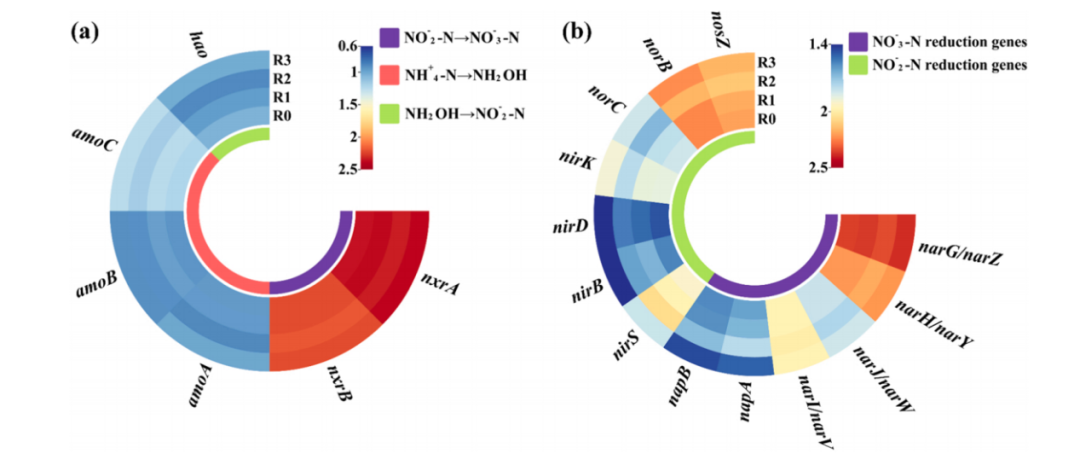
图4 4个SBRs中(a)硝化基因和(b)反硝化基因的相对丰度。
4、ARGs和MGEs的丰度和多样性分析
为了分析50μg/L Gd(III)和500μg/L SMX单独处理或联合处理的ARGs变化,通过宏基因组测序在样本中检测到20种ARGs,选择了前10个亚型,并显示在Circos中。耐药基因的主要类型是杆菌肽(bac)、SMX(sul)、氨基糖苷(aad)和多药(mex、omp、qac和multidrug_transporter)(图5(a))。R1和R2中SMX抗性基因(sul1和sul2)的丰度均高于对照,R1中sul1的丰度显著高于R2。结果表明,联合处理加速了细菌中优势ARGs的转移。
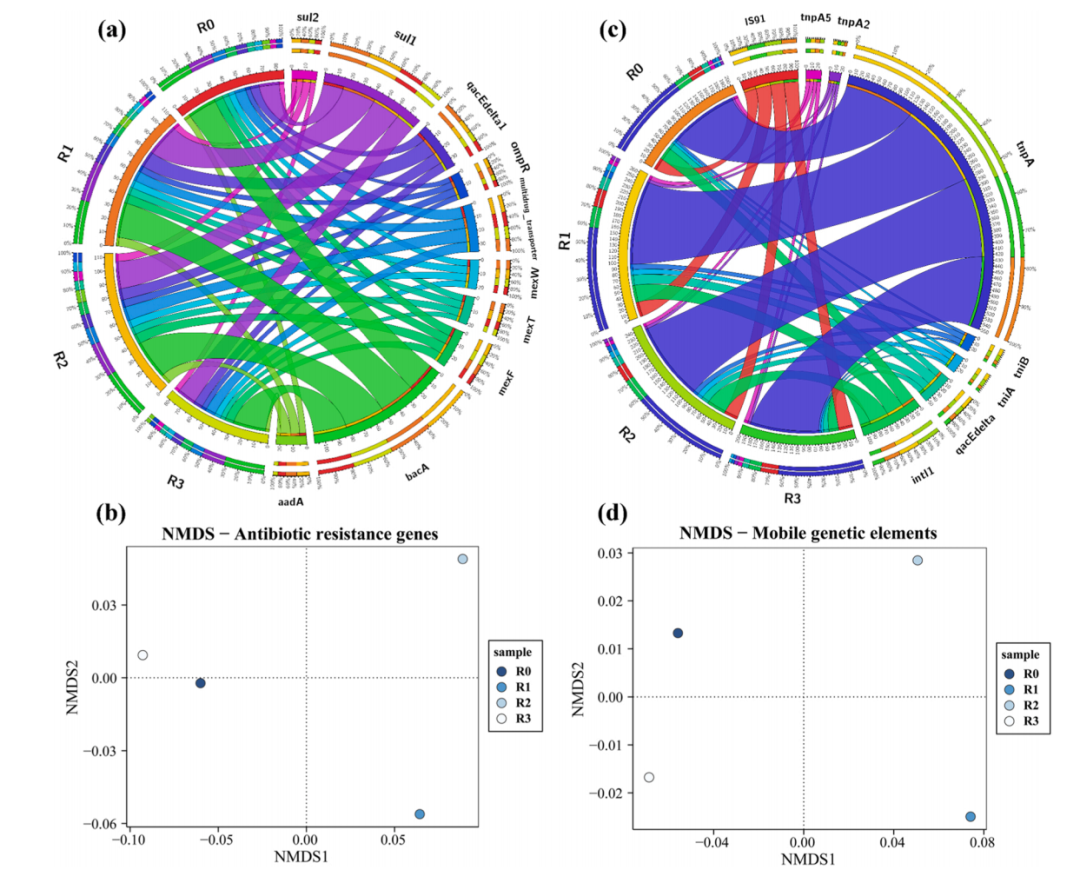
图5 Circos中(a)ARGs和(c)MGEs的相对丰度。(b)ARGs和(d)MGEs之间的NMDS的变化。
5、ARGs、MGEs和主要属之间的相关性
网络分析结果表明,ARGs与MGEs密切相关,且MGEs之间的相关性比ARGs之间的相关性更强(图6(a))。可以推断,Gd(III)和SMX的共存使MGEs在水平基因转移(HGT)中更加活跃。从图6(b)中可以看出,除Nitrospira外,其他属与前10个ARGs均呈正相关,说明Nitrospira中没有抗生素耐药性。
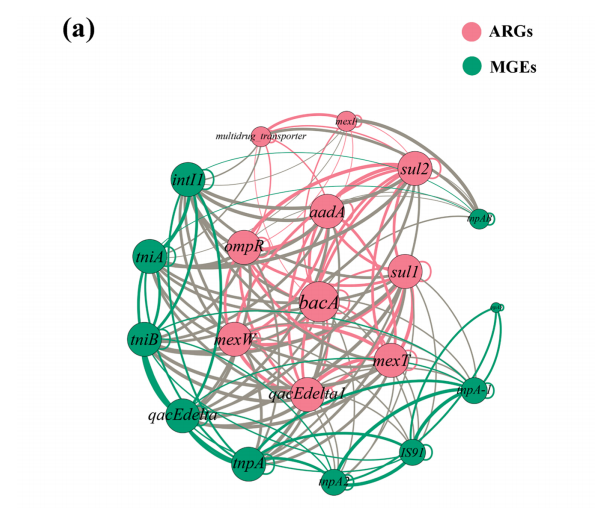

图6(a)ARGs与MGEs之间关系的网络分析。
6、ARGs与脱氮功能基因之间潜在的相互作用机制
采用Pearson相关系数分析ARGs与硝化和反硝化基因之间的关系(图7)。结果表明,除amoB外,大多数硝化基因与ARGs之间呈负相关,而反硝化基因与ARGs之间均存在正相关和负相关。在50μg/L的Gd(III)和500μg/L的SMX共存的条件下,ARGs的增加通常也会导致脱氮性能的下降。
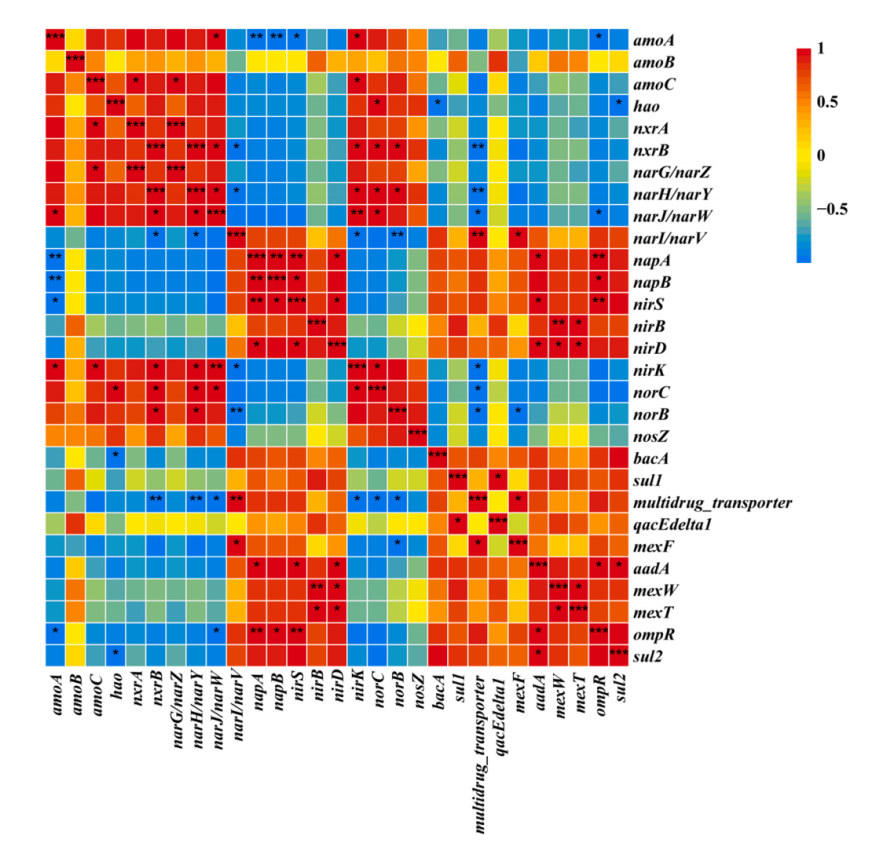
图7 脱氮功能基因与ARGs之间的距离热图。
参考文献
Deciphering the response of biological nitrogen removal to gadolinium and sulfamethoxazole combined pollution: Performance, microbial community, and antibiotic resistance genes. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022.
DOI:10.1016/j.psep.2022.09.030