1. A brief introduction to the development pattern of the privacy track
The blockchain is the bottom layer for building various ecologies. In the early days, after the Bitcoin and Ethereum public chains determined an early outline, the subsequent public chain systems basically retained the characteristics of openness and transparency. They mainly adopted their own system architecture, Mechanism changes for better performance. This means that most of the applications built on it do not have privacy features, and every transaction can be tracked on the chain through the blockchain browser, and all transaction information can be seen at a glance. As DeFi ushered in an explosion and established a fundamental for the development of other tracks, more and more funds and users poured into it, and more and more users said that the overall openness and transparency made them feel uneasy , They don't want every transaction of theirs to be "monitored" by everyone.
From another perspective, when encrypted assets are used as a means of commercial payment, overall openness and transparency will definitely cause some problems, such as wage payment, settlement between commercial companies, etc., so cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology, etc. Privacy remains essential for further large-scale commercial adoption.
From the early days of the industry, the world of privacy encryption has been exploring, such as the early Zcash, Monero, and Dash, etc., which do not support anonymous systems with programmable extensions, but we have seen that they have considerable limitations and have not been accepted. further adoption. With the development of the industry, more and more teams have begun to use encryption protocols to achieve anonymity through emerging mechanisms, such as the currency mixing protocol Tornado Cash on Ethereum, the multi-chain currency mixing protocol Onion Mixer, and the whirlwind protocol on IoTeX Among them, because Tornado Cash is often used as a "whitewashing" pool after hackers steal assets, it was recently included in the sanction list by the U.S. regulatory agency OFAC for strict supervision, and many account addresses associated with it were frozen by relevant agreements, triggering industry heated discussion. Related anonymous encrypted assets such as Zcash, Monero, and Dash have previously been removed from the shelves of many encrypted asset trading platforms due to regulatory and compliance issues. narrow.
With the high development of DeFi, it has laid the foundation for the development of various sectors, and the blockchain application layer has gradually ushered in an explosion. Around the construction of privacy solutions for Web3 applications, Findora, Oasis Protocol and Secret Network are the mainstays. Several major privacy public chains mainly represented are building a new industry structure.
However, compared to the other two privacy ecosystems that rely on TEE (hardware) to achieve privacy and security, Findora has always been "unique" and insists on using cryptography as the basis to achieve privacy and ensure security, and supports regulatory agencies to audit data to meet Compliance means that the Findora development team has better cryptography skills and has received high attention and recognition from the industry.
Last year, the Findora Beta main network was launched, and in the second half of last year, Findora opened a multi-chain architecture, which consists of a UTXO-based blockchain (the original chain, used for privacy and scalability), and a newly launched account-based Composed of EVM-compatible blockchains (for programmability, interoperability, and composability), it provides comprehensive support for all EVM developers and opens up a new ecology. The upgraded Findora ecosystem aims to further expand the privacy of Ethereum and build privacy functions for all EVM compatible chains.
This article will give an all-round detailed explanation of the Findora ecosystem to further deepen readers' knowledge and understanding of the Findora privacy system.

2. Features of Findora Privacy System
double chain structure
Different from other blockchain architectures, after launching the EVM compatible chain last year, Findora uniquely built a multi-chain system, that is, a UTXO-based blockchain (the original chain of Findora) Findora OG, and an EVM compatible chain.
Findora implements a hybrid model that allows users to store assets in the form of UTXO or balance (account model). Relatively speaking, the UTXO model itself is more secure than the account model in terms of asset storage, and can be further based on its own on the Findora OG chain Cryptography technology to achieve privacy, while EVM compatible chain allows developers to develop various applications (Findora can provide Findora X development kit support), such as using ERC-20 compatible tokens to issue and trade, using Solidity to write Ethereum intelligence Contracts, using Ethereum and ERC-20 compatible networks to build cross-chain bridges, and using ERC-721 standards to create non-homogeneous tokens (NFTs) using tools, etc.

The architecture is optimized for ZK integration and cross-chain compatibility, with both local settlement capabilities and general programmability. Although transaction data, such as token quantity, token type, and wallet address, can be hidden on the Findora chain, it is not For compliance purposes, regulators can still audit these data (auditability and acceptance of supervision are the future privacy trend), and the UTXO model of Findora OG chain is expected to further improve the transaction concurrency of the DeFi protocol. In addition, in Findora's multi-chain architecture, internal connections are made through an untrustworthy atomic swap protocol called Prism to ensure the synchronization of system transaction information.
Although there is no attempt of this model in the industry so far, this innovative structure and mechanism is being verified and practiced.
Cryptography-Based Privacy
Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) is currently the best cryptographic scheme in the industry for building privacy and improving transaction efficiency. This scheme is initially based on ZK SNARK, which is a proof that requires two keys, one public key , a private key. The private key is used to generate the proof and the public key is used to verify the proof.
Findora, on the other hand, is based on several special ZKPs including Bulletproofs and Turbo Plonks (collectively referred to as Findora ZK) to support private transactions. Findora ZK is also an efficient, privacy-centric Ethereum Layer 2 solution that utilizes Ethereum for consensus and verification. All of Findora's ZK cryptography is stored in the Zei Library and is open source, and developers can find it and other open source documentation on Findora GitHub.

Bulletproofs are zero-knowledge proofs that do not require a trusted setup and have a small proof size. They were created in part by Findora researchers at Stanford University in 2018. Findora uses them to make blind asset records (BAR), based on Bulletproofs, Findora can mask the amount and token type involved in the transaction.
Turbo Plonks is a polynomial commitment system with sublinear size SNARKs. Turbo Plonks was created by Ethereum researcher Tim Ruffing in 2018. Turbo Plonks are specifically designed for verifiable state transitions in ZK-Rollup, a proof system that makes hash functions several times faster than before. Combining this with Proof of Carrying Data (PCD), Findora ZK can verify not only large amounts of private payments via ZK-Rollup, but also large amounts of more complex private computations. Additionally, Turbo Plonks allows wallet addresses involved in transactions to remain anonymous, and they convert BARs to ABARs or “Anonymous Blind Asset Records.
Therefore, Bulletproofs and Turbo Plonks are currently the main technical means for Findora to obtain privacy features, enabling transactions in Findora to selectively hide the amount and token type, and at the same time keep the address anonymous, which is not available in other privacy ecosystems. One of the characteristics possessed.
In addition to Bulletproofs and Turbo Plonks, another zero-knowledge proof is called ZK STARK, which is expected to be further introduced into Findora in the future. ZK STARK is also called zero-knowledge scalable and transparent knowledge proof, which is characterized by ZKP that does not require trusted settings. , is post-quantum secure, and the proof time is very short. This technology is expected to further enhance the security and efficiency of private transactions after being introduced into the system.
We have seen that Findora is currently a privacy chain using zero-knowledge proof technology. Although its original intention is cross-chain compatibility, the first focus is on chains compatible with Ethereum. However, in the future, it is expected to expand like more Layer 1 such as Solana, Aptos, etc. In addition to focusing on encrypted transactions, based on cryptography technology and a high degree of composability and compatibility, Findora is also expected to act as a general-purpose privacy tool for settlement transactions, such as providing native privacy for other projects and allowing them to use Findora's UTXO layer as a cross-all L1 A secret bridge to the network to issue privacy-preserving tokens.
FindoraX and FindoraCR
Findora X represents a series of complete toolkits, including Restful API, SDK and infrastructure. It is the ultimate privacy solution for all smart contract platforms. Any developer will be able to get technical support from Findora X. For example, bridging applications, assets, etc. through Findora X, creating DAPPs with optional privacy, etc. The Rust smart contract language supported by Findora X, as well as the low Gas of the Findora system itself, are further friendly to developers.

Findora CR allows organizations to issue credential tokens to identify individuals or institutions without revealing their specific identity. It's a way to gain privileges and permissions without revealing the recipient. By building on Findora's existing privacy protection blockchain, it is possible to further combine the decentralized identity (DID) management system to establish a Web3 credit infrastructure with privacy features, and obtain advanced zero-knowledge cryptography to protect the identity and identity on the chain. Support for credential data privacy.
Based on Findora CR, use cases based on real identity-related sectors, such as credit scores, personal healthcare data, and supply chain data related to specific companies, can be unlocked, which is expected to further promote the further development of the Web3 sector, and combine with the traditional world to integrate Web3 into the next stage of development.
3. Technical comparison between Findora and existing privacy systems
Zcash and Monero, etc., as privacy ecosystems that did not have programmability in the early days, are no longer competitive in this field. Oasis Protocol, Secret Network, and NYM are currently privacy ecosystems that also have potential, and are currently developing well.
Oasis Protocol and Secret Network
Oasis Protocol and Secret Network have similar technical principles, and they are mainly based on TEE technology to achieve privacy and security.
We see that in the traditional application field, TEE technology is mainly used for application protection on mobile phones and chip security protection, but currently, this technology is used to achieve privacy on the chain. For example, in Oasis Network, consensus and computing are separated into a consensus layer and a computing layer. The computing layer uses the TEE trusted execution environment to run smart contracts to build privacy for smart contracts. The TEE of Oasis Network uses Intel's SGX extended instruction set As a specific solution for its TEE trusted execution environment.
The Secret Network is a privacy-focused chain based on Cosmos. It compares itself to Ethereum smart contracts + Monero's default privacy protection + Cosmos' scalability and cross-chain, and programmable privacy. In fact, it is similar to Oasis Network The way to achieve privacy is similar, both are based on TEE, and the hardware support of TEE also comes from Intel SGX.
There are two main disadvantages of using TEE in a public permissionless blockchain. First, TEE requires validators to have specialized hardware, which further increases the threshold for ordinary users to join the network and reduces the decentralization of the blockchain network. network or "decentralization" and reduces the level of network security and trustworthiness. Second, a public blockchain network with hundreds of thousands of records is not the same as a cloud-based environment or a mobile computing environment, and TEE-based solutions are vulnerable to side-channel attacks. Decentralization of smart contracts to computing nodes that support the TEE trusted execution environment improves the overall performance of the network, but because the contracts are independent of each other and executed in parallel, it is difficult for the contracts to call each other. Therefore, Oasis Protocol and Secret Network rely too much on hardware, which may be a potential problem.
NYM
NYM is also one of the most popular anonymous systems in the industry. Its blockchain part is implemented based on the Cosmos SDK. The Nym hybrid network provides the privacy of the 0th layer, which provides a layer 1 (such as Bitcoin and Ethereum) and other blockchain and cryptocurrency projects at Layer 2 (including most DeFi projects) have added metadata protection.
NYM's hybrid network is a decentralized computer network arranged in a multi-layered format. Instead of sending messages directly over the Internet, users convert message packets into encrypted "Sphinx" packets on their devices. The "Sphinx" data packet format presents all data packets in a form of uniform size, making it impossible to track. At the same time, the order of information and data entering and leaving the network is disrupted through Mixnode (mixed network), so that the monitor cannot follow the order Timing of statistics and data input and output. In addition, when users use Mixnet, false cover information will be generated in the mixed network, and with the help of four types of nodes (service provider, mixing node, gateway and verification node), the monitor cannot know the time of information hiding .
NYM is based on the blockchain and is more of an incentive mechanism for Mixnet. It mainly pays more attention to off-chain privacy. It can only do private payment on the chain, and cannot achieve the programmable privacy of private public chains, versatility, The programmability is not strong, and it is similar to the anonymous currency on the whole.
Findora
Findora's ZKP-based zero-knowledge proof privacy scheme is a more friendly general-purpose computing (TurboPlonk and BulletProofs), which can be applied to blockchain networks with large-scale privacy requirements in a more decentralized form. Findora is a multi-chain system that integrates the UTXO model and the account model. The UTXO model has natural advantages in realizing the privacy/anonymity of tokens. This design enables applications on Findora to take advantage of both the privacy features of the UTXO ledger and the programmability of the EVM model. Therefore, Findora's privacy itself does not depend on trusted hardware, nor does it require encrypted input and output, and smart contracts with programmable privacy states. This is not possible in any other existing EVM-compatible blockchain, or TEE-based solutions.
The zero-knowledge proof based on cryptography further endows Findora with selective privacy features. It has selective privacy that other privacy ecology does not have, such as the ability to selectively hide the amount and token type, and at the same time keep the address anonymous. In addition, Findora's multi-chain structure ensures that it has better programmability, scalability, security, and perfect privacy support for other EVM Layer1 and Layer2.
As the Findora development team continues to optimize the network, the EVM in Findora has a relatively short block generation time during operation, which can reduce the waiting time for confirming each EVM transaction and bridge transmission operation, and improve the operating efficiency of the network. Findora's EVM solution is more efficient than some other alternatives. At present, Findora is superior in programmable privacy networks, and has the potential to be superior in the field of PriFi.
4. The development history of Findora
2017 - Findora researchers at Stanford contribute to the development of Bulletproofs.
2017-2020—Findora researchers and engineers aggregated their results into Zei Library, which is currently the industry's most advanced open source repository for ZK cryptography.
2020-2022 - Findora helps develop Turbo-Plonks, a lightweight ZKP for scaling, and transforms it from an academic exercise to a practical application.
March 2021—Findora Beta mainnet launch
July 2021—Testnet staking goes live
September 2021 - Findora adds EVM extensions and Ethereum compatibility via its own "Smart Chain".
October 2021 — Beta mainnet staking starts
October 2021 - Findora's $100M Ecosystem Fund launches to incubate projects and provide grants
2022 - Triple Masking (providing fully anonymous transaction transmission) goes live
5. Team and Community
The Findora Foundation is a non-profit entity that helps manage research and development grants for Findora. It is composed of several directors with decades of experience in building technology companies in Silicon Valley and is responsible for the promotion and strategy of the Findora ecosystem.
Discreet Labs as the main contributor to the development of Findora, the development team is the first company to receive funding from Findora. Discreet Labs currently has more than 60 employees on five continents, 80% of whom are engineers, designers, and product managers who work on Findora and other scalable privacy systems every day.
The Findora community mainly includes roles such as verifiers, developers, designers, operators, ambassadors, and evangelists. They are committed to spontaneously building various projects on Findora to promote the development of the Findora ecosystem. Projects include supporting platforms, DEXs, and DApps and DAO (some are currently live).
6. Ecological progress and activities
Ecological project
1. FairySwap
FairySwap is the first automated market maker (AMM) decentralized exchange (DEX) built on Findora undefined Utilizing Findora's EVM, FairySwap can provide extremely fast cross-chain exchanges with Layer 1 chains such as Ethereum while minimizing fees , Maximum efficiency, private transactions, cross-chain, etc. are its biggest features and advantages.
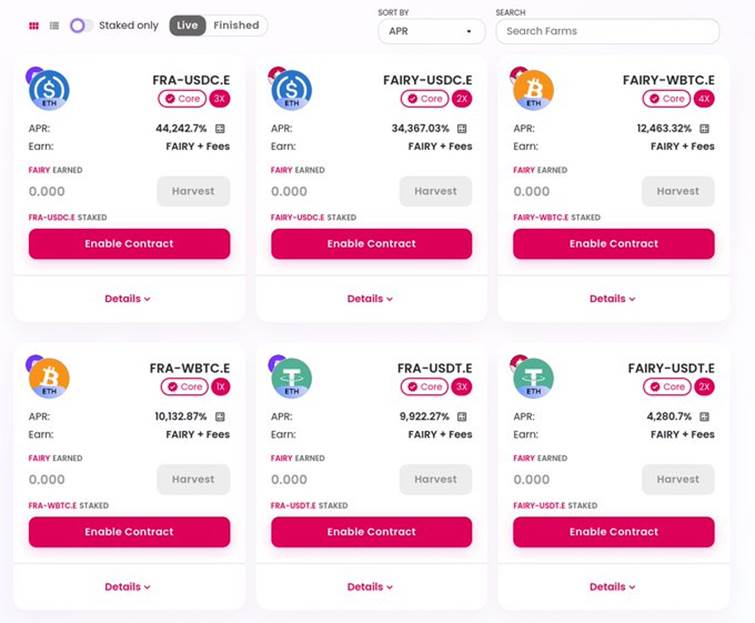
Currently, it integrates through the Rialto bridge (Findora ecological cross-chain bridge), and gradually realizes cross-chain conversion to obtain high returns and privacy protection on Findora. Currently, FairySwap is also developing the DEX NFT section, and NFT artists come from industry artists.
2.VeniceSwap
VeniceSwap is an early DEX in the Findora ecosystem. It uses Findora's zero-knowledge proof to provide traders with private transaction services and maximize their trading profits. VeniceSwap's Onion Transfer can automatically help users transfer user assets from traceable accounts to achieve anonymity. For example, it helps users send assets from KYC-enabled CEX accounts to an untraceable address to achieve transaction anonymity. In addition, users can also transfer from Venice Transparent accounts on other supported DeFi ecosystems, migrate and trade their assets to protect privacy.

VeniceSwap itself uses Findora ZK cryptography technology to protect users undefined from value extraction players and front-running trading attacks. At the same time, Venice will also provide traders with lightning-fast transaction speed, minimal slippage and maximum liquidity based on the bottom layer of Findora efficiency.
3.Poseidon
Poseidon is a cross-chain currency market protocol driven by Findora's ZKP technology. It has privacy features, but it can be audited and work within the scope of regulatory requirements. Poseidon enables users to control transaction information in multiple blockchain ecosystems .
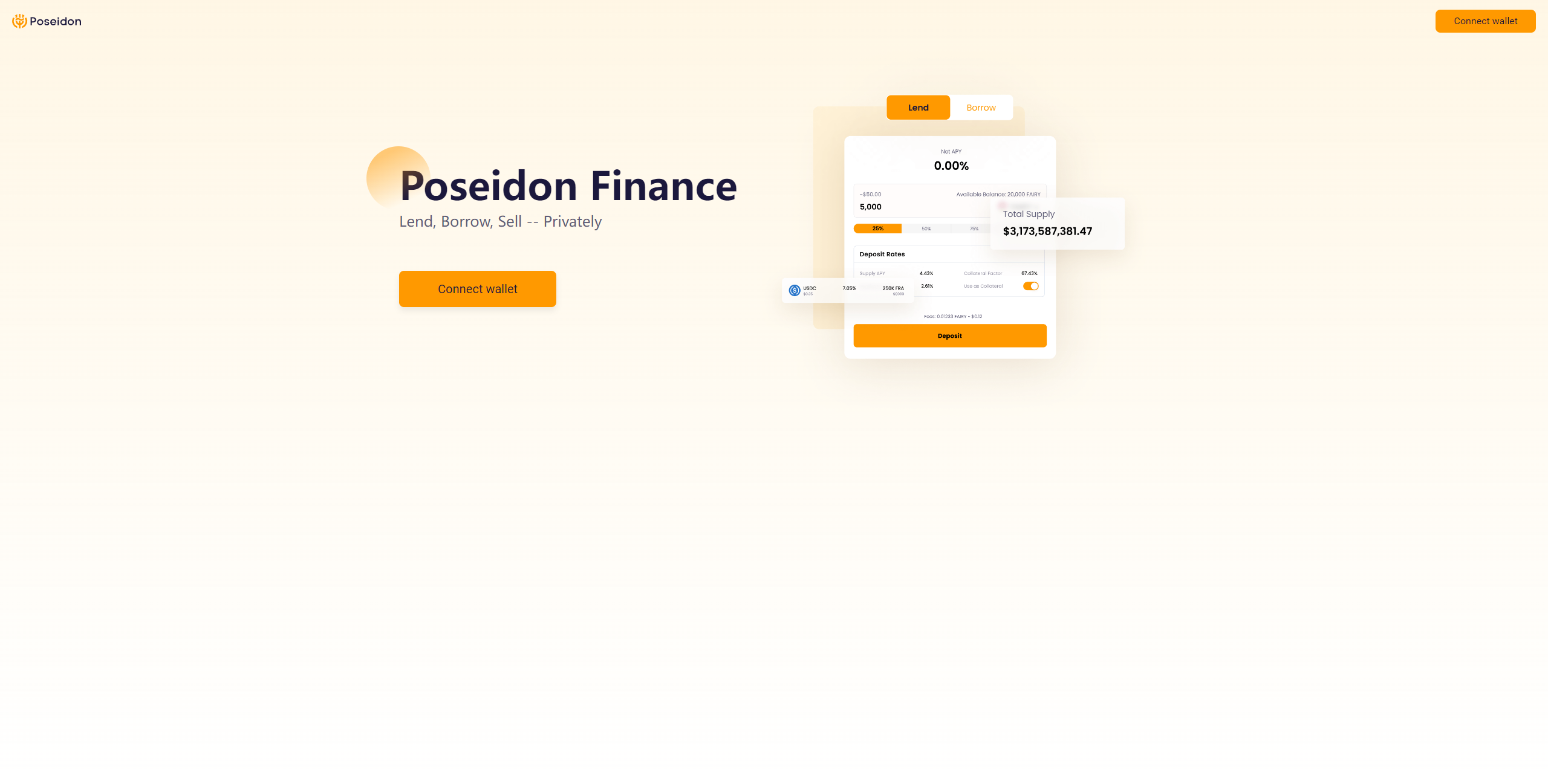
Poseidon aims to prioritize interoperability and privacy, laying the foundation for an open and accessible financial system in the future, based on its pioneering liquidity market (PLM) protocol, allowing users to borrow, lend and earn money through encrypted assets to obtain passive income without revealing identity information on the chain.
4.Hitall
Hitall is an NFT marketplace built on Findora privacy, focusing on GameFi and digital collections, aiming to help more creators around the world launch low-threshold NFTs, and traders can trade without revealing the bidder or bid amount NFT transactions until the end of the transaction.
Hitall is the winner of the ZK Circuit Hackathon event on EthCC.
5.Forland
Forlend is a lightweight, non-custodial, decentralized liquidity protocol designed to provide users with a lightweight, non-custodial decentralized liquidity protocol. It is mainly used to earn interest on deposits and borrowed assets on the Findora chain, providing it with more on-chain liquidity access. Forlend will support FRA, USDT, USDC and other digital assets, deposit them into Forlend and use them as collateral for loans. Currently, the liquidity mining plan of the platform is about to start, and users can earn FLD by depositing, borrowing and pledging on the agreement.
Forlend is also one of the high-quality projects of the ZK Circuit Hackathon on EthCC.

Recent developments in the Findora ecosystem
1. Findora cooperates with Omni X
Findora has partnered with Omni X, a new full-chain NFT protocol, aiming to create the first private and interoperable network for NFTs.

2. Initiation of the ZPrize Competition
Findora and a number of industry-leading institutions jointly launched the ZPrize competition, which aims to promote the application of ZK technology in web3. Zprize will award generous rewards to participants who solve ZK existing problems and promote ZK technology research. Currently, the reward pool of ZPrize Has reached 7 million US dollars.

3. Peter Abilla becomes Chief Commercial Officer of Discreet Labs
In early August, former Harmony core member Peter Abilla joined Findora technology development team Discreet Labs as chief business officer. Peter Abilla served as the vice president of growth marketing and community for Mainframe and ThunderCore, and also worked in community and developer marketing at Oasis Labs, and promoted Harmony to build a healthy DeFi system, bringing growth to the Harmony ecosystem.
Peter Abilla's extensive experience in software development and encryption will help Discreet Labs' project Findora extend Ethereum privacy.
4. Findora France was established
After the end of EthCC5 in Paris last month, Findora established Findora France, which will help Findora further expand its community and ecology in Europe.
5. The Rialto cross-chain bridge Polygon <> Findora Bridge launched by the Findora community has been launched on the testnet
Currently, the Rialto Bridge, a cross-chain bridge launched by the Findora community, is connecting the assets of BNB Chain, Ethereum Chain and Polygon Chain to Findora's privacy protection platform, while supporting tokens and NFT.
At present, the Polygon-to-Findora path cross-chain bridge has been launched on the test network, and at 3:00 pm on August 18th, Pacific Standard Time, an incentivized community test called "Building Up the Bridge" was launched, and the Findora Foundation also sponsored for this event.
When a new path is deployed on mainnet, the Findora Foundation hosts this multi-stage event to get as much community stress testing as possible. Test between the Polygon Mumbai testnet and the Findora Anvil testnet to get a $5 FRA reward and claim an NFT badge from Project Galaxy.