Table of contents
3. Three elements of network communication
Four: Tomcat directory structure
One: web concept
1. Software Architecture
①:C/S
: client
/
server
-‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐> QQ , 360 ....
②:B/S
: Browser
/
Server-side
‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐-‐-‐-‐-‐-‐- and'>
JD, NetEase, Taobao...
2. Resource classification
①: Static resources: After all users visit, the results are the same, called static resources. Static resources
The source can be parsed directly by the browser. * Such as:
html,css,JavaScript
,
jpg
②: Dynamic resources
:
After each user accesses the same resource, the results obtained may be different
,
which is called dynamic resources. After a dynamic resource is accessed, it needs to be converted into a static resource first, and then returned to the browser for parsing by the browser. * Such as
servlet/jsp,php,asp....
3. Three elements of network communication
① IP
: the unique identification of electronic equipment
(
computer
)
in the network.
②Port
: the unique identification of the application in the computer.
0~65536
③Transmission
protocol: specifies the rules for data transmission
- Basic agreement:
- tcp: security protocol, three-way handshake. slightly slower
- udp : Insecure protocol. high speed
Two: Common web servers
1. Concept
- Server: A computer with server software installed
- Server software: receive user requests, process requests, and respond
- Web server software: Receive user requests, process requests, and respond.
In the
web server software,
web projects
can be deployed
to allow users to access these projects through browsers
2. Common web server software
- webLogic : oracle company, a large-scale JavaEE server, supports all JavaEE specifications, and charges.
- webSphere : IBM Corporation, a large-scale JavaEE server, supports all JavaEE specifications, and charges.
- JBOSS : JBOSS company, a large-scale JavaEE server, supports all JavaEE specifications, charges.
- Tomcat : Apache Foundation, a small and medium-sized JavaEE server, only supports a small amount of JavaEE standard servlet/jsp . Open source and free.
Three: Tomcat history
- Tomcat was originally developed by James Duncan Davidson , a software architect at Sun , under the name "JavaWebServer" .
- In 1999, with the help of Davidson , the project merged with the JServ project under the Apache Software Foundation in 1999 , and released the first version (3.x) , which is now Tomcat , which implements Servlet2.2 and the JSP 1.1 specification.
- In 2001 , Tomcat released version 4.0 . As a milestone version, Tomcat completely redesigned its architecture and implemented the Servlet 2.3 and JSP1.2 specifications.
Four: Tomcat installation
1. Download
https://tomcat.apache.org/download-80.cgi
2. Install
Unzip the downloaded
.zip
package to the system directory (it is recommended that there is no Chinese directory without spaces).
Four: Tomcat directory structure
The main directory files of Tomcat are as follows:
|
Table of contents
|
files in directory
|
illustrate
|
|
bin
|
/ | Store Tomcat start, stop and other batch script files |
|
startup.bat ,
startup.sh
|
Startup scripts for
windows
and
linux
|
|
|
shutdown.bat ,
shutdown.sh
|
for
stop scripts under
windows
and
linux
|
|
|
conf
|
/ | Used to store Tomcat related configuration files |
|
Catalina
|
Used to store the Context
configuration for each virtual machine
|
|
|
context.xml
|
Used to define the Context configuration that all
web
applications need to load
Set, if
the web
application specifies its own
context.xml
, the file will be overwritten
|
|
|
catalina.properties
|
Tomcat
environment variable configuration
|
|
|
catalina.policy
|
Security policy configuration for Tomcat running | |
|
logging.properties
|
Tomcat
's log configuration file can be modified through this file
Change
the log level and log path of
Tomcat , etc.
|
|
|
server.xml
|
Core configuration file for Tomcat
server
|
|
|
tomcat-users.xml
|
Define
Tomcat's
default user and role mapping information configuration
|
|
|
web.xml
|
The default deployment description file for all applications in Tomcat , the main
To define the basic
Servlet
and
MIME
mapping.
|
|
|
lib
|
/ |
Dependency packages of Tomcat server
|
|
logs
|
/ |
Tomcat
default log storage directory
|
|
webapps
|
/ |
Tomcat's
default
web
application deployment directory
|
|
work
|
/ |
Temporary directory for web
application
JSP
code generation and compilation
|
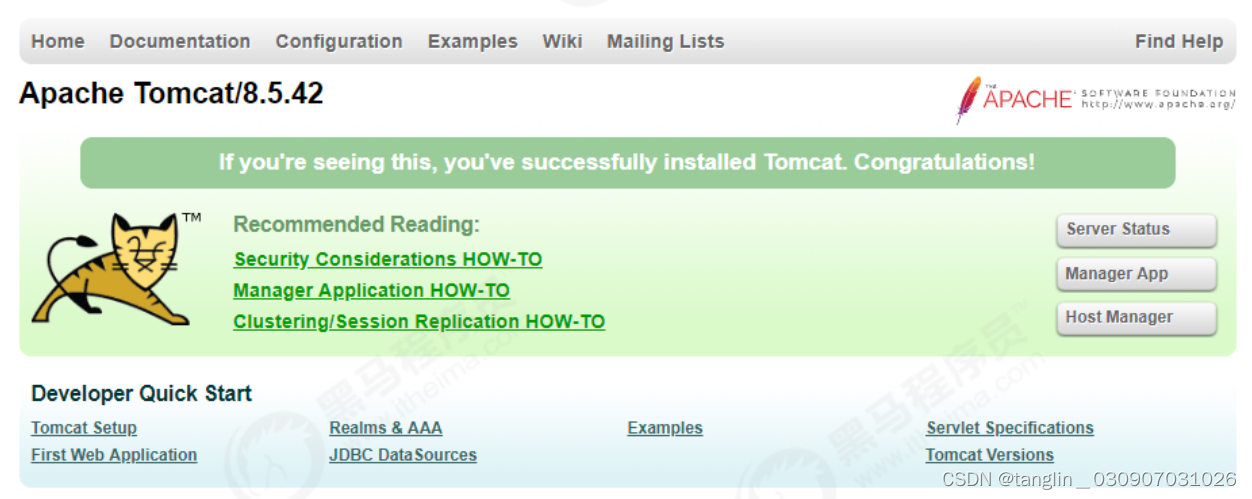
Five: Tomcat starts and stops
start up
Double-click the bin/startup.bat file;
stop
Double-click the bin/shutdown.bat file;
access
http://localhost:8080
Six: Tomcat source code
1. Download
Address:
https://tomcat.apache.org/download-80.cgi

2. run
1) Unzip the zip archive
2
) Enter the decompression directory, create a directory, name it
home
, and move
the conf
and
webapps
directories into
in the home directory
3 ) Create a
pom.xml file
in the current directory
and import the dependency package of tomcat
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF‐8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema‐instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven‐4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>apache‐tomcat‐8.5.42‐src</artifactId>
<name>Tomcat8.5</name>
<version>8.5</version>
<build>
<finalName>Tomcat8.5</finalName>
<sourceDirectory>java</sourceDirectory>
<!‐‐ <testSourceDirectory>test</testSourceDirectory>‐‐>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>java</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
<!‐‐ <testResources>
<testResource>
<directory>test</directory>
</testResource>
</testResources>‐‐>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven‐compiler‐plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF‐8</encoding>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.easymock</groupId>
<artifactId>easymock</artifactId>
<version>3.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ant</groupId>
<artifactId>ant</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>wsdl4j</groupId>
<artifactId>wsdl4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxrpc</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler</groupId>
<artifactId>ecj</artifactId>
<version>4.5.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
4
) In
idea
, import the project
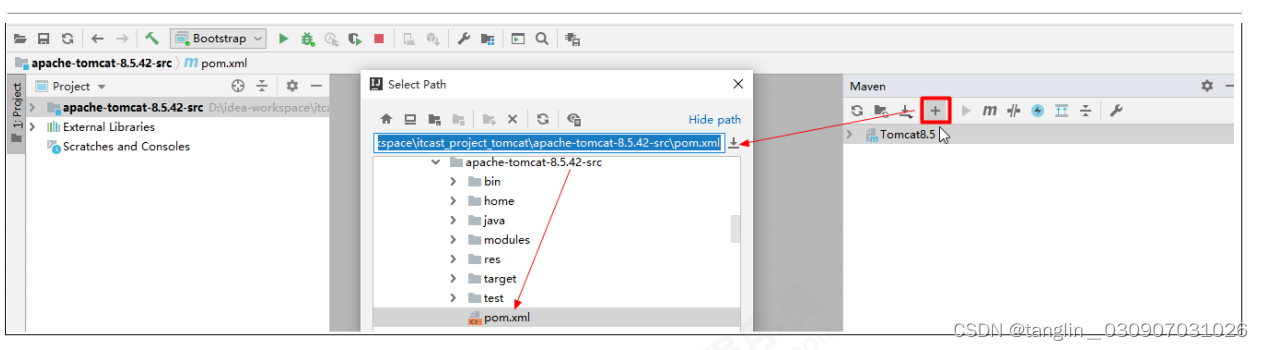
5 ) Configure the startup class of idea , configure MainClass , and configure VM parameters.
‐Dcatalina.home=D:/idea‐workspace/itcast_project_tomcat/apache‐tomcat‐
8.5.42‐src/home
‐Dcatalina.base=D:/idea‐workspace/itcast_project_tomcat/apache‐tomcat‐
8.5.42‐src/home
‐Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager
‐Djava.util.logging.config.file=D:/idea‐
workspace/itcast_project_tomcat/apache‐tomcat‐8.5.42‐
src/home/conf/logging.properties
6 ) Start the main method, run Tomcat , and access Tomcat .

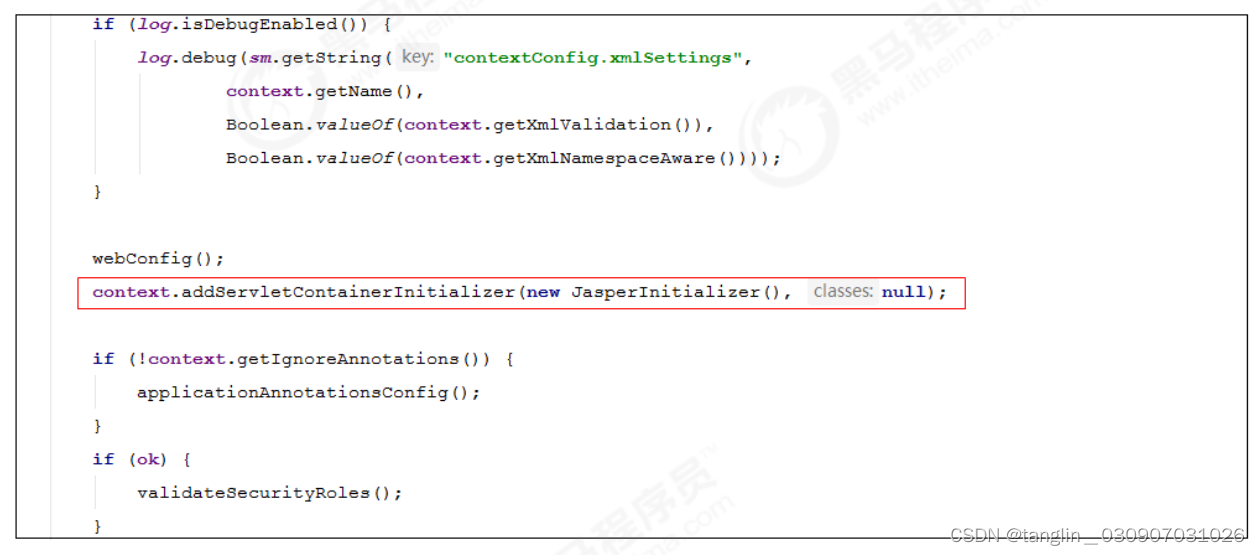
The reason for the above exception is that we
did not start
org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap directly
There is JasperInitializer
loaded
, making it impossible to compile
the JSP
. The solution is in
tomcat
's source code
ContextConfig
Manually initialize the JSP parser in the
configureStart function
in :
context.addServletContainerInitializer(new JasperInitializer(), null);
7 ) Restart tomcat and you can access normally.