Here I will share with you some of the knowledge I have summarized on the Internet, I hope it will be helpful to everyone
The reason for this article is that after the package was released in the code warehouse, my colleague asked me "Why is the version in package. To pay attention to the version number of this warehouse, just synchronize it when publishing and tagging, so there is a practice in this article.
In the node.js part, we have to have a script that changes the warehouse code and leave it to ci to execute
./script/..We first need to add a update-version.jsscript to the directory in the project directory
//update-version.js
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
const newVersion = process.argv[2].replace(/^v/, '');; // 获取命令行参数中的新版本号,并过滤v字头
if (!newVersion) {
console.log('请传入新版本号,版本号遵循semver规范 .eg: 1.0.0, 1.0.1, 1.1.0');
process.exit(1);
}
// 获取当前命令行上下文路径
const currentDirectory = process.cwd();
// 获取 package.json 文件中的版本号
const packageJsonPath = path.join(currentDirectory, 'package.json');
const packageJsonContent = fs.readFileSync(packageJsonPath, 'utf8');
const packageJson = JSON.parse(packageJsonContent);
const currentVersion = packageJson.version;
// 更新 package.json 文件中的版本号
packageJson.version = newVersion;
fs.writeFileSync(packageJsonPath, JSON.stringify(packageJson, null, 2));
console.log(`版本号已从 ${currentVersion} 更新为 ${newVersion}`);
Next, after the package.json script is configured, it can be directly used to npm run version <version> trigger the script to change the version number. Of course, this premise is to keep this script for developers to use on the command line.
{
"name": "version workflow",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "version update demo",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
//...
"version": "node ./scripts/update-version.js"
},
//...
}
CI: How to make the behavior of the release package directly synchronize with the version number in the code repository?
Next is the highlight, how to make the behavior of the release package directly synchronize with the version number in the code warehouse? Here we use the github action provided by github . For specific operations and syntax, you can check the official documents, so this article will not expand too much.
We need to add a file with the following path in the root directory of the warehouse.github/workflows/update-action.yml
name: Update Package Version
on:
release:
types: [released]
jobs:
update:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Update package.json
run: |
node ./scripts/update-version.js ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Commit changes
run: |
git config user.name "Your github name"
git config user.email "your github email"
git add .
git commit -m "Update version to ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }} for release ${
{ github.ref }}"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
We added an update job to the state releasein the hook . releasedIt will do the following things (in the script step)
- 【Checkout code】 Cut out a new code branch;
- [Update package.json] Execute update-version.js in the new branch to pass in and
tag_nameupdate our project version number; - [Commit changes] Create a new commit with your customized git config user information;
- 【Push changes】Push changes back to the trunk;
ps:正确来说应该在发布执行动作前prereleased执行我们的 job 但是没用这个的原因如下:
Note: The
prereleasedtype will not trigger for pre-releases published from draft releases, but thepublishedtype will trigger. If you want a workflow to run when stable and pre-releases publish, subscribe topublishedinstead ofreleasedandprereleased.
当这个脚本推送后,执行发布后自动更新版本,不用在关注这个版本修改问题。 你会得到下面的效果。
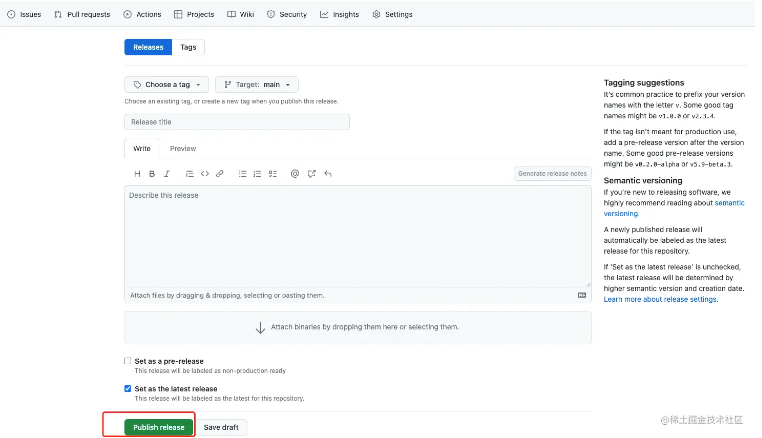
在你的仓库发布界面填写正确tag后发布
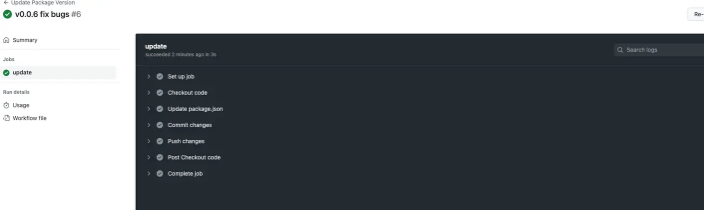
触发update job 更改完成
你可能遇到最多的坑
- action 执行失败
Process completed with exit code 129." Node.js 12 actions are deprecated. Please update the following actions to use Node.js 16: actions/checkout@v2. For more information, see https://github.blog/changelog/2022-09-22-github-actions-all-actions-will-begin-running-on-node16-instead-of-node12/.
这是由于默认action job 执行环境的nodejs 版本与actions 包中执行脚本不匹配导致,所以一定要使用 checkout@v3 版本 actions/checkout@v3
- 各种不熟悉 action 语法取值导致的问题
可以优化的地方
我们前面提交的这个流程发布还是有个问题,你永远有个更超前的 commit hash 在你发布的 tag 之后

所以这个action 还有需要继续优化的地方,那就是同步更新tag hash
name: Update Package Version
on:
release:
types: [released]
jobs:
update:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Update package.json
run: |
node ./scripts/update-version.js ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Commit changes
run: |
git config user.name "Your github name"
git config user.email "your github email"
git add .
git commit -m "Update version to ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }} for release ${
{ github.ref }}"
git_hash=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD)
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Tag Push changes
run: |
git tag -f ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }} $git_hash
git push --force origin ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
这里相比之前的版本增加了 Tag Push changes 这个步骤,在最后获取这个版本更新产生的 $git_hash强制更新到发布的 tag 上。
我们看看效果

最后我们看版本发布管理中的 tag hash
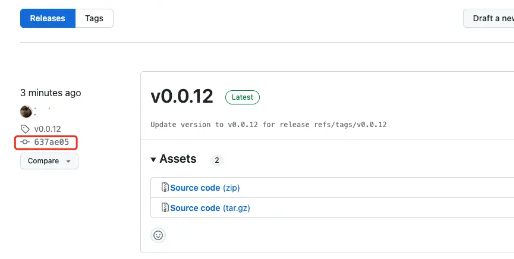
搞定!
可以再优化的地方
现在我们还有个问题,就是在执行 Commit changes 这个步骤时每次 git config user.name "Your github name" git config user.email "your github email" 这里是写死的,我们可以根据 GitHub Actions 中有一些预设的环境变量可以读取到当前用户的账号和邮箱信息。通过 ${
{ env.GITHUB_ACTOR }} 获取到当前执行的 Actions 的用户账号,通过 ${
{ env.GITHUB_ACTOR }}@users.noreply.github.com 获取到当前执行的 Actions 的用户邮箱(该邮箱为 noreply 邮箱,用于 GitHub 的通知,无法发送邮件)。注意,该邮箱不一定是用户本身的真实邮箱,可能是 GitHub 默认的邮箱。
如果需要获取当前 GitHub 账号的真实邮箱地址,可以通过 GitHub REST API 进行查询,具体可以参考官方文档:
这样我们就需要在Commit Changes之前再加一个Set Git user步骤
- name: Set Git user
env:
GITHUB_ACTOR: ${
{ github.actor }}
GITHUB_EMAIL: ${
{ github.actor }}@users.noreply.github.com
run: |
git config --global user.name "${
{ env.GITHUB_ACTOR }}"
git config --global user.email "${
{ env.GITHUB_EMAIL }}"
name: Update Package Version
on:
release:
types: [released]
jobs:
update:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Update package.json
run: |
node ./scripts/update-version.js ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Set Git user
env:
GITHUB_ACTOR: ${
{ github.actor }}
GITHUB_EMAIL: ${
{ github.actor }}@users.noreply.github.com
run: |
git config --global user.name "${
{ env.GITHUB_ACTOR }}"
git config --global user.email "${
{ env.GITHUB_EMAIL }}"
- name: Commit changes
run: |
git add .
git commit -m "Update version to ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }} for release ${
{ github.ref }}"
git_hash=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD)
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Tag Push changes
run: |
git tag -f ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }} $git_hash
git push --force origin ${
{ github.event.release.tag_name }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${
{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
