Article directory
awk overview
awk is spliced from the first letters of the last names of its three founders (Alfred Aho, Peter Weinberger and Brian Kernighan).
awk, report generator, formatted text output, awk released by GNU/Linux is currently developed and maintained by the Free Software Foundation (FSF), and is usually also called GNU AWK
You can use "rpm -qi gawk" to view an official description of awk "The gawk package contains the GNU version of AWK text processing utility. AWK is a programming language designed for text processing and typically used as a dataextraction and reporting tool"
The key point is "AWK is a programming language..." Translation: "AWK is a programming language"... NB, it turns out to be a programming language, so it's so awesome. No wonder he is the leader of the Three Musketeers.
[root@rocky8 ~]# rpm -qi gawk
Name : gawk
Version : 4.2.1
Release : 2.el8
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: Sat 12 Nov 2022 05:24:52 PM CST
Group : Unspecified
Size : 2699078
License : GPLv3+ and GPLv2+ and LGPLv2+ and BSD
Signature : RSA/SHA256, Wed 19 May 2021 01:32:23 PM CST, Key ID 15af5dac6d745a60
Source RPM : gawk-4.2.1-2.el8.src.rpm
Build Date : Wed 19 May 2021 10:35:13 AM CST
Build Host : ord1-prod-x86build001.svc.aws.rockylinux.org
Relocations : (not relocatable)
Packager : [email protected]
Vendor : Rocky
URL : https://www.gnu.org/software/gawk/
Summary : The GNU version of the AWK text processing utility
Description :
The gawk package contains the GNU version of AWK text processing utility.
AWK is a programming language designed for text processing and typically used as a dataextraction and reporting tool.
The gawk utility can be used to do quick and easy text pattern matching,extracting or reformatting.
It is considered to be a standard Linux tool for text processing.
Basic use of awk
awk [options] 'program' var= value file....
awk [options] -f programfile var= value file...
program格式: pattern{
action statements;...}
pattern:决定动作语句何时触发事件,比如:BEGIN,END,正则表达式等
action statements:对数据进行处理,放在{
}内指明,常见:print,printf
program通常是放在单引号中,并可以由三种部分组成(EGNIN语句块,模式匹配的通用语句块,END语句块)
常用选项
-F "分隔符"指明输入时用到的字段分隔符,默认的分隔符是若干个连续空白符
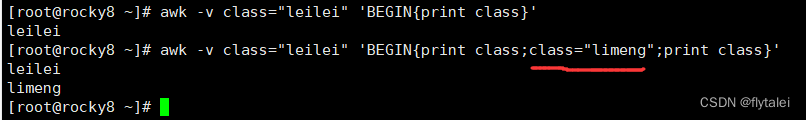
-v var=value 变量赋值
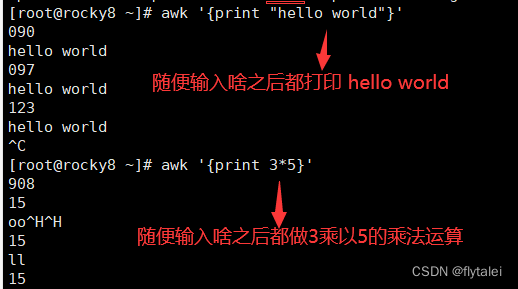
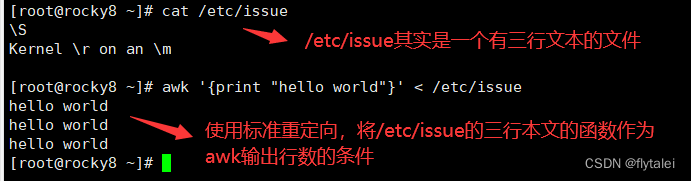
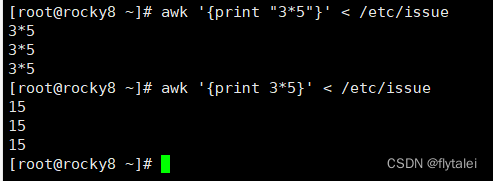
From the above example, we can see that "awk '{print "hello world"}'" is a standard input command, so you can use standard input redirection
awk中打印字符串一定要使用""双引号,
其实java也一样,双引号括起来的都是字符串,否则awk视之为变量。
[root@rocky8 ~]# awk --help
Usage: awk [POSIX or GNU style options] -f progfile [--] file ...
Usage: awk [POSIX or GNU style options] [--] 'program' file ...
POSIX options: GNU long options: (standard)
-f progfile --file=progfile
-F fs --field-separator=fs
-v var=val --assign=var=val
Short options: GNU long options: (extensions)
-b --characters-as-bytes
-c --traditional
-C --copyright
-d[file] --dump-variables[=file]
-D[file] --debug[=file]
-e 'program-text' --source='program-text'
-E file --exec=file
-g --gen-pot
-h --help
-i includefile --include=includefile
-l library --load=library
-L[fatal|invalid] --lint[=fatal|invalid]
-M --bignum
-N --use-lc-numeric
-n --non-decimal-data
-o[file] --pretty-print[=file]
-O --optimize
-p[file] --profile[=file]
-P --posix
-r --re-interval
-s --no-optimize
-S --sandbox
-t --lint-old
-V --version
delimiter in awk default text
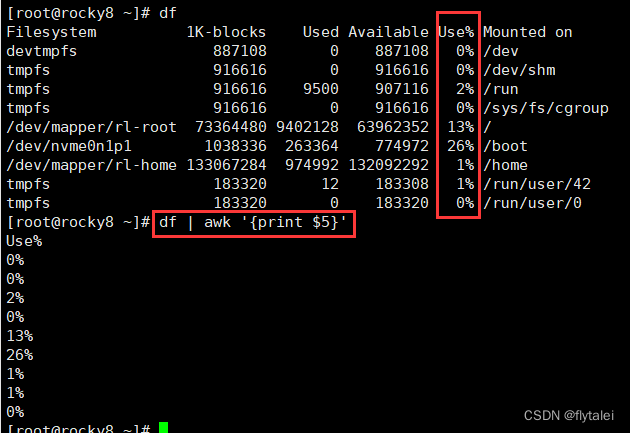
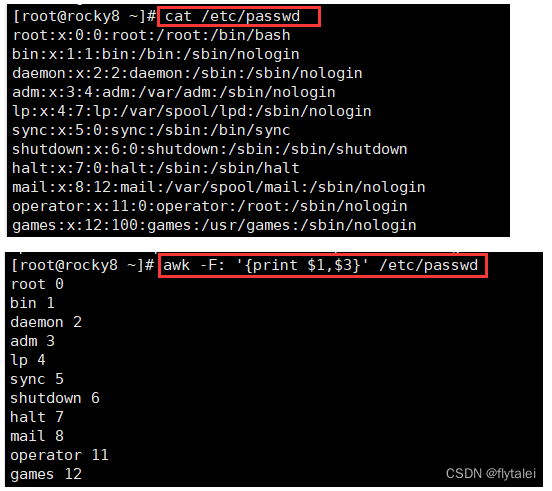
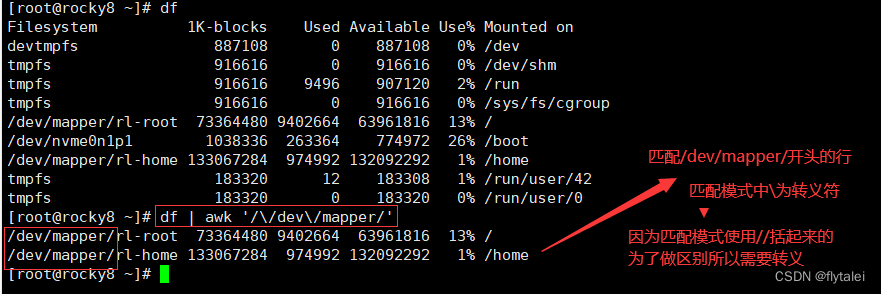
查看磁盘利用率时,df命令格式化输出了6列信息,可以看出这6列信息使用空格隔开。
awk则可以自动识别以空格或tab键分割的列,
awk中使用$1,$2,$3...$5..$n等表示第几列
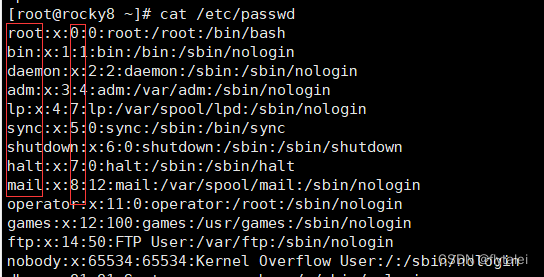
Take out the username and uid in /etc/passwd

Count the top IPs that appear most frequently
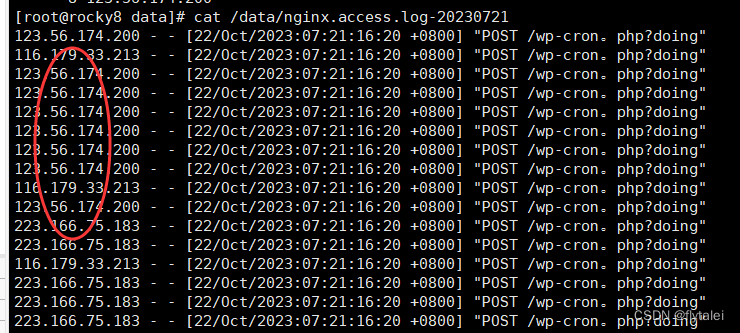
Use awk to filter
awk '{print $1}' /data/nginx.access.log-20230721 |sort |uniq -c|sort -nr|head -3
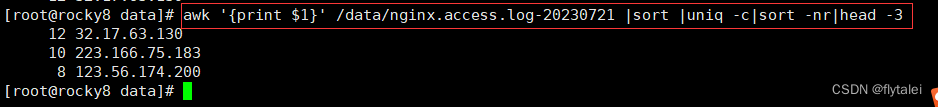
Filter using cut
cut -d" " -f1 /data/nginx.access.log-20230721 |sort |uniq -c|sort -nr|head -3
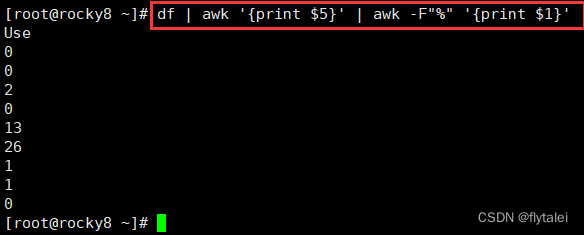
Get the number of partition utilization
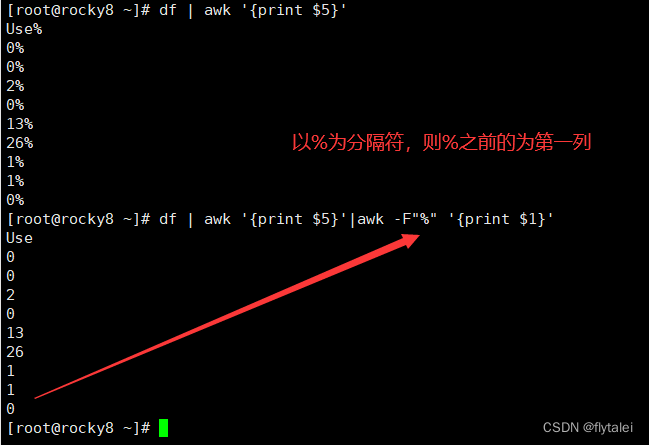
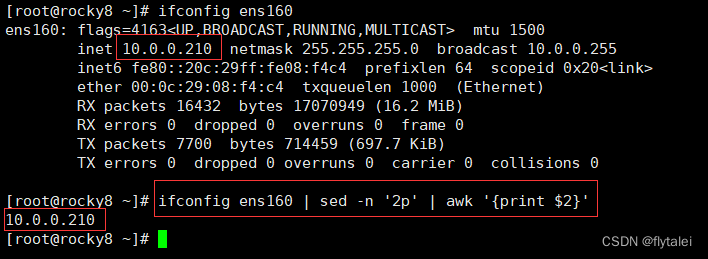
Extract the ip address in the network card configuration file
ifconfig ens160 | sed -n '2p' | awk '{print $2}'
awk common built-in variables
Variables in awk are divided into: built-in and custom variables
awk内置变量可以使用man帮助查看使用说明
摁“/”开始搜索关键字,
摁“n(小写)”查看下一个匹配,
摁“N(大写)”查看上一个匹配)
[root@rocky8 ~]# man awk

FS
The input field separator, a space by default. See Fields, above.
FS The input field separator, a space by default. See Fields, above.
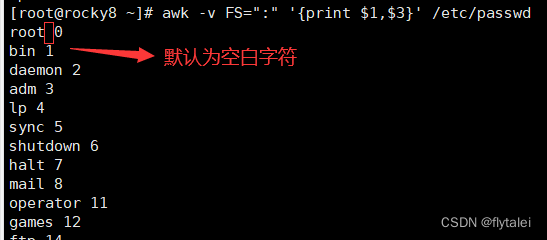
FS:输入字段分隔符,默认为空白字符,功能相当于-F
-F fs --field-separator=fs
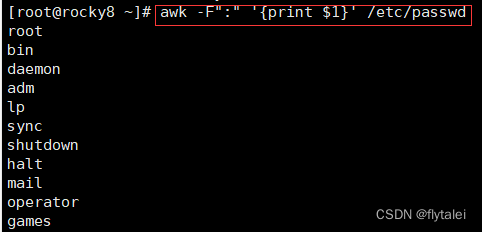
Select the first word in the /etc/passwd file
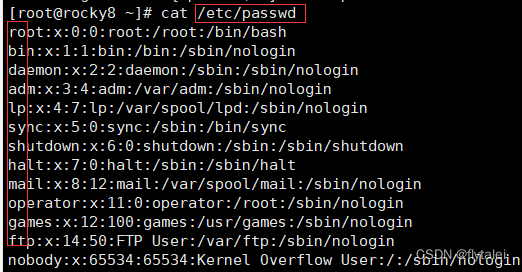
awk -v FS=":" '{print $1}' /etc/passwd
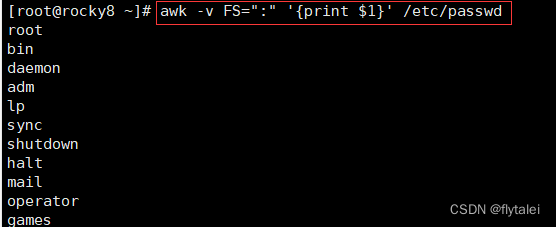
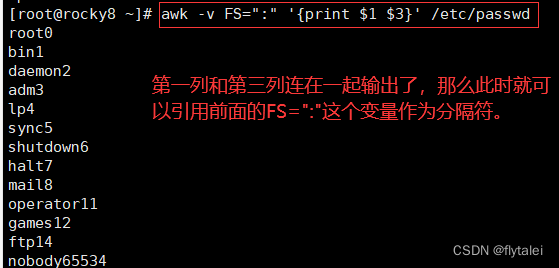
虽然"-F"也能达到"FS"一样的的效果,但是要知道这两者有着本质上的区别,
"FS"是变量,是变量就可以在不同的地方引用,而"-f"就不行。
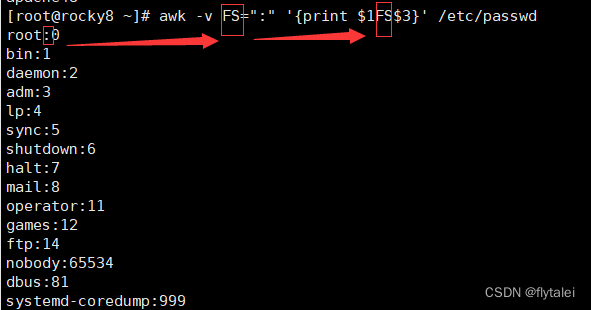
/etc/passwd文件的内容中,使用“:”做分隔的较多,那么我在输出打印时,我可以继续引用"FS=":""这个变量作为我输出内容的格式分隔符。
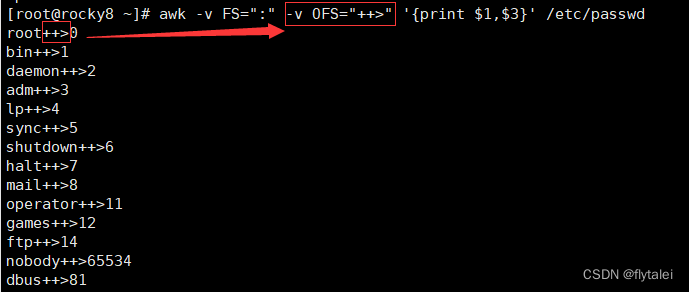
OFS
OFS The output field separator, a space by default.
OFS:输出字段分隔符,默认空白字符。
RS
RS The input record separator, by default a newline.
RS:输入记录record分隔符,指定输入时的换行符。
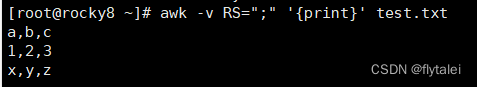
Use ";" semicolon as the delimiter to wrap the output content in new lines.

awk -v RS=";" '{print}' test.txt
ORS
ORS The output record separator, by default a newline.
ORS:输出记录分隔符,输出时用指定符号代替换行符
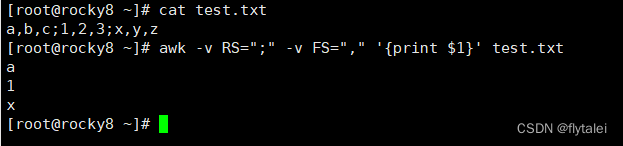
awk -v RS=";" -v FS="," -v ORS="->" '{print $1}' test.txt

NF
NF The number of fields in the current input record.
NF:当前输入记录中的字段数。
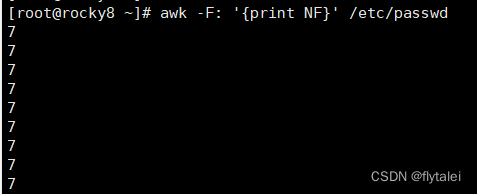
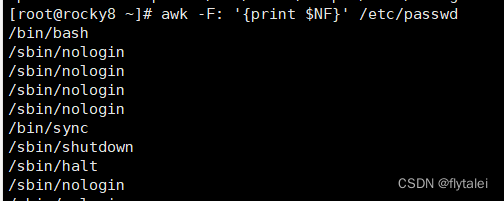
There are 7 fields separated by ":", and "$NF" is the value of the last field.

awk -F: '{print $NF}' /etc/passwd
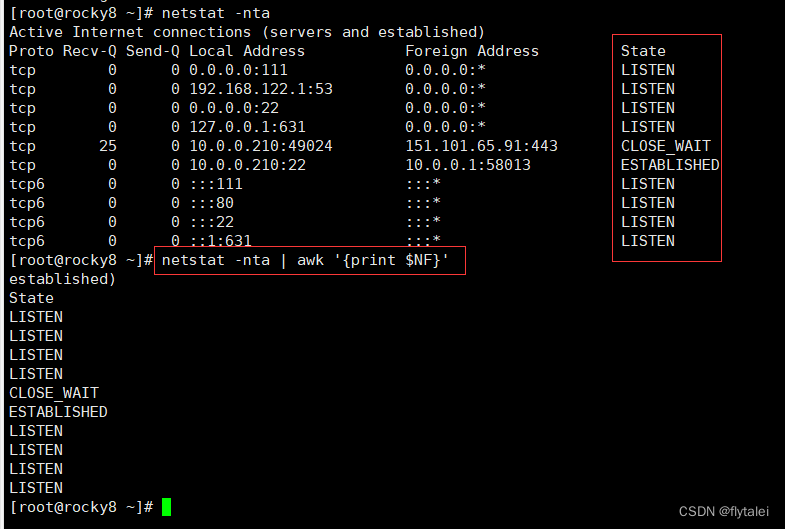
Get connection status information
netstat -nta | awk '{print $NF}'
Get the penultimate field of the /etc/passwd file
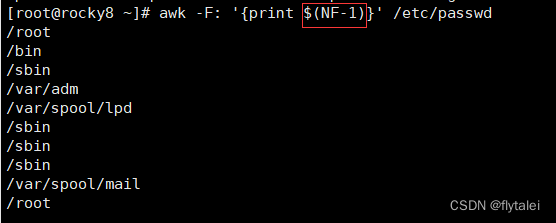
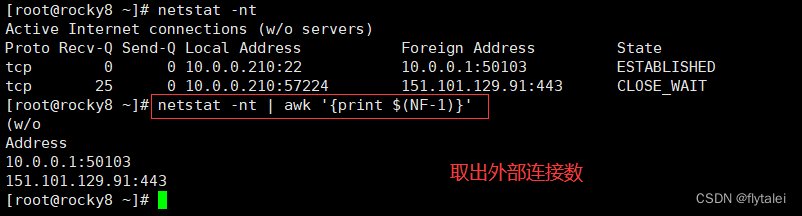
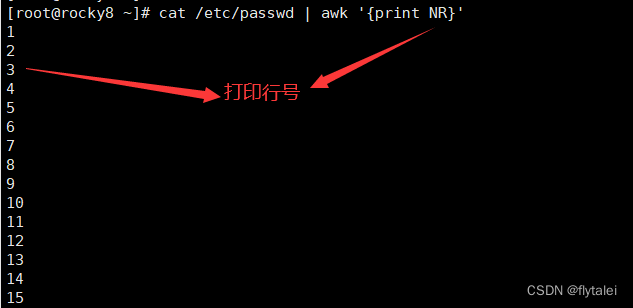
NR
NR The total number of input records seen so far.
NR:输出记录的行号。
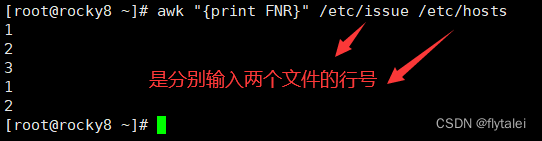
FNR
FNR The input record number in the current input file.
FNR:各文件分别计数,记录的行号。
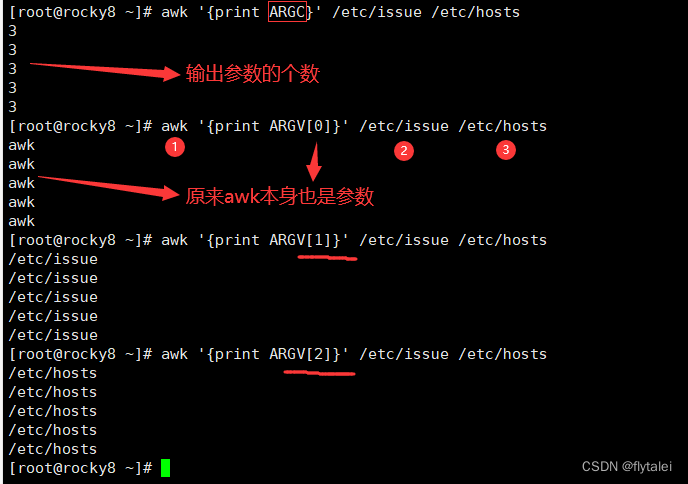
ARGC and ARGV
The number of output parameters and specific parameters

pattern pattern
PATTERN:根据pattern条件,过滤匹配到的行,在做处理
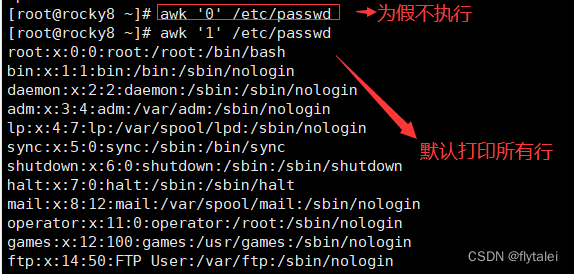
1. If not specified: empty pattern, matches every line
1.如果未指定:空模式,匹配每一行
例如:awk -F: '{print $1,$3}' /etc/passwd
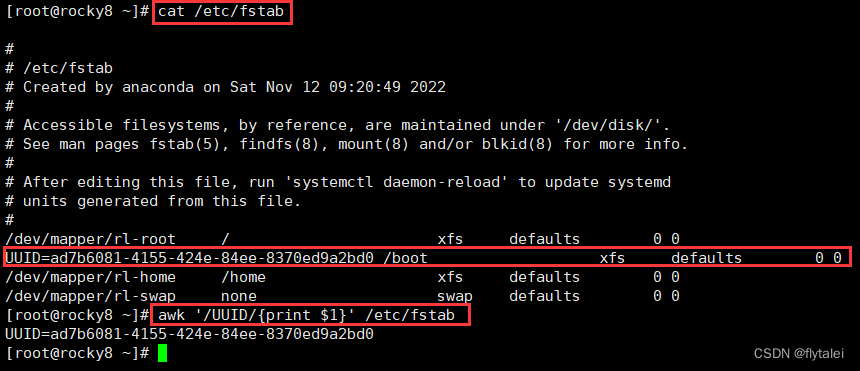
2./regular expression/: Only processes lines that can match the pattern and needs to be enclosed in //
2./regular expression/:仅处理能够模式匹配到的行,需要用//括起来
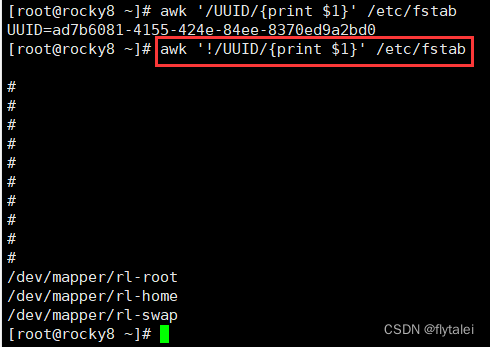
例如:awk '/UUID/{print $1}' /etc/fstab
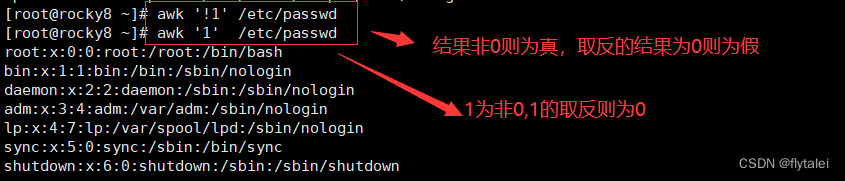
awk '!/UUID/{print $1}' /etc/fstab "!为取反"
3.relational expression: Relational expression will be processed only if the result is "true"
真:结果为非0值,非空字符串
假:结果为0值或空字符串

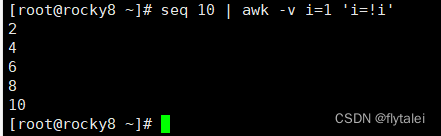
4.line ranges: line ranges
不支持直接用行号,但可以使用变量NR间接指定行号
/part1/,/part2/ 不支持直接给出数字格式
Print the lines starting with b and ending with h in the /etc/passwd file

Conditional judgment if-else
[root@rocky8 ~]# awk 'BEGIN{score=88;if(score>=80){print "good"}else if(score>=60){print "pass"}else{print "no pass"}}'
good
[root@rocky8 ~]# awk 'BEGIN{score=78;if(score>=80){print "good"}else if(score>=60){print "pass"}else{print "no pass"}}'
pass
[root@rocky8 ~]# awk 'BEGIN{score=58;if(score>=80){print "good"}else if(score>=60){print "pass"}else{print "no pass"}}'
no pass
[root@rocky8 ~]#
[root@rocky8 ~]# cat score.txt
name score
zhangsan 100
lisi 90
zhaoliu 70
wangwu 55
[root@rocky8 ~]# awk 'NR!=1{score=$2;if(score>=80){print $1,"good"}else if(score>=60){print $1, "pass"}else{print $1, "no pass"}}' score.txt
zhangsan good
lisi good
zhaoliu pass
wangwu no pass
[root@rocky8 ~]#
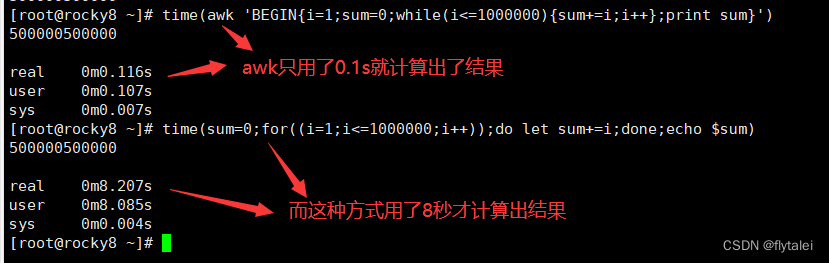
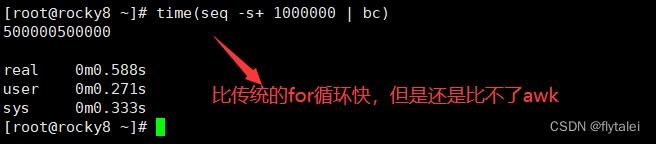
while loop
[root@rocky8 ~]# awk 'BEGIN{i=1;sum=0;while(i<=100){sum+=i;i++};print sum}'
5050
[root@rocky8 ~]# sum=0;for((i=1;i<=100;i++));do let sum+=i;done;echo $sum
5050
[root@rocky8 ~]#