la caméra obtient une image jpeg
Bibliothèque: libjpeg Méthode d'installation de la bibliothèque: apt-get install libjpeg-dev ou yum install -y libjpeg libjpeg-devel
编译 : gcc camera.c -Wall -g -lrt -ldl -lpthread -ljpeg -march = corei7 -lm -o out
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <asm/types.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <jpeglib.h>
#define deviceName "/dev/video0"
#define WIDTH 640
#define HEIGHT 480
#define OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE 4096
#define CLEAR(x) memset(&(x), 0, sizeof(x))
struct buffer
{
void *start;
size_t length;
};
typedef struct
{
struct jpeg_destination_mgr pub;
JOCTET *buffer;
unsigned char *outbuffer;
int outbuffer_size;
unsigned char *outbuffer_cursor;
int *written;
} mjpg_destination_mgr;
typedef mjpg_destination_mgr *mjpg_dest_ptr;
static char *dev_name = deviceName;
static int fd = -1;
struct buffer *buffers = NULL;
static unsigned int n_buffers = 0;
FILE *file_fd;
static unsigned long file_length;
//static unsigned char *file_name;
METHODDEF(void)
init_destination(j_compress_ptr cinfo)
{
mjpg_dest_ptr dest = (mjpg_dest_ptr)cinfo->dest;
dest->buffer = (JOCTET *)(*cinfo->mem->alloc_small)((j_common_ptr)cinfo, JPOOL_IMAGE, OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE * sizeof(JOCTET));
*(dest->written) = 0;
dest->pub.next_output_byte = dest->buffer;
dest->pub.free_in_buffer = OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE;
}
METHODDEF(boolean)
empty_output_buffer(j_compress_ptr cinfo)
{
mjpg_dest_ptr dest = (mjpg_dest_ptr)cinfo->dest;
memcpy(dest->outbuffer_cursor, dest->buffer, OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE);
dest->outbuffer_cursor += OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE;
*(dest->written) += OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE;
dest->pub.next_output_byte = dest->buffer;
dest->pub.free_in_buffer = OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE;
return TRUE;
}
METHODDEF(void)
term_destination(j_compress_ptr cinfo)
{
mjpg_dest_ptr dest = (mjpg_dest_ptr)cinfo->dest;
size_t datacount = OUTPUT_BUF_SIZE - dest->pub.free_in_buffer;
/* Write any data remaining in the buffer */
memcpy(dest->outbuffer_cursor, dest->buffer, datacount);
dest->outbuffer_cursor += datacount;
*(dest->written) += datacount;
}
void dest_buffer(j_compress_ptr cinfo, unsigned char *buffer, int size, int *written)
{
mjpg_dest_ptr dest;
if (cinfo->dest == NULL)
{
cinfo->dest = (struct jpeg_destination_mgr *)(*cinfo->mem->alloc_small)((j_common_ptr)cinfo, JPOOL_PERMANENT, sizeof(mjpg_destination_mgr));
}
dest = (mjpg_dest_ptr)cinfo->dest;
dest->pub.init_destination = init_destination;
dest->pub.empty_output_buffer = empty_output_buffer;
dest->pub.term_destination = term_destination;
dest->outbuffer = buffer;
dest->outbuffer_size = size;
dest->outbuffer_cursor = buffer;
dest->written = written;
}
//摄像头采集的YUYV格式转换为JPEG格式
int compress_yuyv_to_jpeg(unsigned char *buf, unsigned char *buffer, int size, int quality)
{
struct jpeg_compress_struct cinfo;
struct jpeg_error_mgr jerr;
JSAMPROW row_pointer[1];
unsigned char *line_buffer, *yuyv;
int z;
static int written;
//int count = 0;
//printf("%s\n", buf);
line_buffer = calloc(WIDTH * 3, 1);
yuyv = buf; //将YUYV格式的图片数据赋给YUYV指针
printf("compress start...\n");
cinfo.err = jpeg_std_error(&jerr);
jpeg_create_compress(&cinfo);
/* jpeg_stdio_dest (&cinfo, file); */
dest_buffer(&cinfo, buffer, size, &written);
cinfo.image_width = WIDTH;
cinfo.image_height = HEIGHT;
cinfo.input_components = 3;
cinfo.in_color_space = JCS_RGB;
jpeg_set_defaults(&cinfo);
jpeg_set_quality(&cinfo, quality, TRUE);
jpeg_start_compress(&cinfo, TRUE);
z = 0;
while (cinfo.next_scanline < HEIGHT)
{
int x;
unsigned char *ptr = line_buffer;
for (x = 0; x < WIDTH; x++)
{
int r, g, b;
int y, u, v;
if (!z)
y = yuyv[0] << 8;
else
y = yuyv[2] << 8;
u = yuyv[1] - 128;
v = yuyv[3] - 128;
r = (y + (359 * v)) >> 8;
g = (y - (88 * u) - (183 * v)) >> 8;
b = (y + (454 * u)) >> 8;
*(ptr++) = (r > 255) ? 255 : ((r < 0) ? 0 : r);
*(ptr++) = (g > 255) ? 255 : ((g < 0) ? 0 : g);
*(ptr++) = (b > 255) ? 255 : ((b < 0) ? 0 : b);
if (z++)
{
z = 0;
yuyv += 4;
}
}
row_pointer[0] = line_buffer;
jpeg_write_scanlines(&cinfo, row_pointer, 1);
}
jpeg_finish_compress(&cinfo);
jpeg_destroy_compress(&cinfo);
free(line_buffer);
return (written);
}
//读取一帧的内容
static int read_frame(void)
{
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
int ret;
//unsigned int i;
CLEAR(buf);
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
int ff = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buf); //出列采集的帧缓冲
if (ff < 0)
printf("failture\n");
unsigned char src[buf.length + 1];
unsigned char dest[buf.length + 1];
assert(buf.index < n_buffers);
printf("buf.index dq is %d,\n", buf.index);
memcpy(src, buffers[buf.index].start, buf.length);
ret = compress_yuyv_to_jpeg(src, dest, (WIDTH * HEIGHT), 80); //数据转换
fwrite(dest, ret, 1, file_fd); //转换后的数据写入
ff = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf); //重新入列
if (ff < 0)
printf("failture VIDIOC_QBUF\n");
return 1;
}
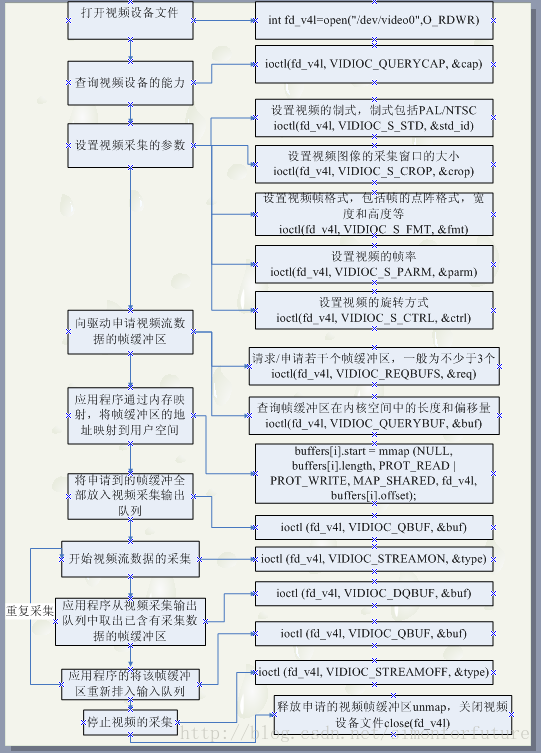
int get_picture()
{
struct v4l2_capability cap;
struct v4l2_format fmt;
unsigned int i;
enum v4l2_buf_type type;
file_fd = fopen("test-mmap.jpg", "w");
fd = open(dev_name, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK, 0);
int ff = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap); //获取摄像头参数
if (ff < 0)
{
printf("failture VIDIOC_QUERYCAP\n");
}
printf("driver:%s\n",cap.driver);
printf("card:%s\n",cap.card);
printf("bus_info:%s\n",cap.bus_info);
printf("version:%d\n",cap.version);
printf("capabilities:%x\n",cap.capabilities);
if ((cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE) == V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE)
{
printf("Device %s: supports capture.\n",deviceName);
}
if ((cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING) == V4L2_CAP_STREAMING)
{
printf("Device %s: supports streaming.\n",deviceName);
}
struct v4l2_fmtdesc fmt1;
int ret;
memset(&fmt1, 0, sizeof(fmt1));
fmt1.index = 0;
fmt1.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
while ((ret = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT, &fmt1)) == 0) //查看摄像头所支持的格式
{
fmt1.index++;
printf("{ pixelformat = '%c%c%c%c', description = '%s' }\n",
fmt1.pixelformat & 0xFF, (fmt1.pixelformat >> 8) & 0xFF,
(fmt1.pixelformat >> 16) & 0xFF, (fmt1.pixelformat >> 24) & 0xFF,
fmt1.description);
}
CLEAR(fmt);
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = WIDTH;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = HEIGHT;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV;
fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED;
ff = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt); //设置图像格式
if (ff < 0)
printf("failture VIDIOC_S_FMT\n");
if(-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_FMT, &fmt)){//得到图片格式
perror("get format failed!");
return -1;
}
printf("fmt.type:\t\t%d\n",fmt.type);
printf("pix.pixelformat:\t%c%c%c%c\n", \
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat & 0xFF,\
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 8) & 0xFF, \
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 16) & 0xFF,\
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 24) & 0xFF);
printf("pix.width:\t\t%d\n",fmt.fmt.pix.width);
printf("pix.height:\t\t%d\n",fmt.fmt.pix.height);
printf("pix.field:\t\t%d\n",fmt.fmt.pix.field);
file_length = fmt.fmt.pix.bytesperline * fmt.fmt.pix.height; //计算图片大小
struct v4l2_requestbuffers req;
CLEAR(req);
req.count = 1;
req.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
req.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &req); //申请缓冲,count是申请的数量
if (ff < 0)
printf("failture VIDIOC_REQBUFS\n");
if (req.count < 1)
printf("Insufficient buffer memory\n");
buffers = calloc(req.count, sizeof(*buffers)); //内存中建立对应空间
for (n_buffers = 0; n_buffers < req.count; ++n_buffers)
{
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
CLEAR(buf);
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = n_buffers;
if (-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &buf)) //映射用户空间
printf("VIDIOC_QUERYBUF error\n");
buffers[n_buffers].length = buf.length;
buffers[n_buffers].start = mmap(NULL, buf.length, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, buf.m.offset); //通过mmap建立映射关系
if (MAP_FAILED == buffers[n_buffers].start)
printf("mmap failed\n");
}
for (i = 0; i < n_buffers; ++i)
{
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
CLEAR(buf);
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = i;
if (-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf)) //申请到的缓冲进入列队
printf("VIDIOC_QBUF failed\n");
}
type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &type)) //开始捕捉图像数据
printf("VIDIOC_STREAMON failed\n");
for (;;) //这一段涉及到异步IO
{
fd_set fds;
struct timeval tv;
int r;
FD_ZERO(&fds); //将指定的文件描述符集清空
FD_SET(fd, &fds); //在文件描述符集合中增加一个新的文件描述符
/* Timeout. */
tv.tv_sec = 2;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
r = select(fd + 1, &fds, NULL, NULL, &tv); //判断是否可读(即摄像头是否准备好),tv是定时
if (-1 == r)
{
if (EINTR == errno)
continue;
printf("select err\n");
}
if (0 == r)
{
fprintf(stderr, "select timeout\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (read_frame()) //如果可读,执行read_frame函数
break;
}
//unmap:
for (i = 0; i < n_buffers; ++i)
if (-1 == munmap(buffers[i].start, buffers[i].length))
printf("munmap error");
type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &type))
printf("VIDIOC_STREAMOFF");
close(fd);
fclose(file_fd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
get_picture();
return 0;
}Simple: obtenez une image au format YUYV. Il doit être ouvert avec un outil spécial, tel que RawView. Ou vous convertissez en jpeg
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#define FMT V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV
//#define FMT V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG
#define COUNT 3 //缓冲数量
#define deviceName "/dev/video0"
int main(void)
{
int fd, i;
unsigned char *datas[COUNT];
//经典操作v4l2的方法:打开设备->查看设备功能->设置图片格式->申请帧缓冲->内存映射->帧缓冲入列->开始采集->读数据(包括处理数据)->帧缓冲重新入列->关闭设备。
fd = open(deviceName, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open camera");
return 1;
}
//确定操作的设备文件是摄像头相关的
struct v4l2_capability cap;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap) < 0)
{
perror("query cap");
return 2;
}
if (!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE))
{
printf("invalid camera");
return 3;
}
printf("driver:%s\n",cap.driver);
printf("card:%s\n",cap.card);
printf("bus_info:%s\n",cap.bus_info);
printf("version:%d\n",cap.version);
printf("capabilities:%x\n",cap.capabilities);
if ((cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE) == V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE)
{
printf("Device %s: supports capture.\n",deviceName);
}
if ((cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING) == V4L2_CAP_STREAMING)
{
printf("Device %s: supports streaming.\n",deviceName);
}
//设置图像数据格及分辨率
struct v4l2_format fmt;
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = 640;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = 480;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = FMT;
//fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt)){//设置图片格式
perror("set format failed!");
return -1;
}
if(-1 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_FMT, &fmt)){//得到图片格式
perror("get format failed!");
return -1;
}
printf("fmt.type:\t\t%d\n",fmt.type);
printf("pix.pixelformat:\t%c%c%c%c\n", \
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat & 0xFF,\
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 8) & 0xFF, \
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 16) & 0xFF,\
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 24) & 0xFF);
printf("pix.width:\t\t%d\n",fmt.fmt.pix.width);
printf("pix.height:\t\t%d\n",fmt.fmt.pix.height);
printf("pix.field:\t\t%d\n",fmt.fmt.pix.field);
//让摄像头驱动申请出3个图像数据缓冲区。 当驱动在一个缓冲区采集数据时, 应用程序可以访问另一个已采集好的缓冲区.
struct v4l2_requestbuffers req;
req.count = COUNT;//申请缓冲数量
req.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
req.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &req);//申请缓冲
printf("requestbuffers count= %d\n",req.count);
if (req.count < 2)
{
perror("buffer memory is Insufficient! \n");
return -1;
}
//实际上不管申请多少个缓冲区,都是一块连续一片区域。所以还需要查询出每个缓冲区在这个区域上的开始地址及缓冲区大小
struct v4l2_buffer buffer;
for (i = 0; i < COUNT; i++)
{
buffer.index = i; //第几个缓冲区(第几个映射地址)
buffer.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buffer.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &buffer) < 0)// 查询帧缓冲区在内核空间的长度和偏移量
{
perror("query buffer");
return 2;
}
printf("length = %d , offset = %d\n", buffer.length, buffer.m.offset);
//把驱动里每个缓冲区映射到当前进程来
datas[i] = mmap(NULL, buffer.length, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, buffer.m.offset);
if (MAP_FAILED == datas[i])
{
perror("mmap");
return 3;
}
/*经过检查之后,可以将缓冲区加入到采集队列——自己理解加入采集队列的意义*/
//把每个缓冲区加入图像的采集队列。 驱动只会把摄像头的图像数据填入到采集队列的缓冲区.
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buffer) < 0)//将申请到的帧缓冲区全部放入视频采集输出队列
{
perror("qbuf");
return 4;
}
}
//循环采集开始,启动摄像头的数据采集.
int on = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &on) < 0) //开始视频流数据的采集
{
perror("stream on");
return 5;
}
//从驱动里取出图像数据。先让采集好数据的一个缓冲区退出采集队列.
struct v4l2_buffer buff;
buff.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buff.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buff) < 0)//应用程序从视频采集输出队列中取出已含有采集数据的帧缓冲区
{
perror("dqbuf");
return 6;
}
printf("index = %d, bytesused = %d\n", buff.index, buff.bytesused);
// datas[buff.index] 可访问到退出队列的缓冲区的地址
FILE *fl = fopen("./test.YUYV", "w");
fwrite(datas[buff.index], 1, buff.bytesused, fl); //数据写入到本地文件
fclose(fl);
// //在循环使用时,用完的数据缓冲区应重新加入采集队列.
// if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buff) < 0)//将申请到的帧缓冲区全部放入视频采集输出队列
// {
// perror("qbuf");
// return 4;
// }
//退出步骤:
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &on); //应用程序将该帧缓冲区重新挂入输入队列
for (i = 0; i < COUNT; i++)
munmap(datas[i], buffer.length); //释放申请的视频帧缓冲区
close(fd);//关闭视频流
return 0;
}
RawViewer1.0 est un lecteur pour visualiser et lire des fichiers yuv. Il prend en charge la visualisation et la lecture et les transformations géométriques, la mise en miroir horizontale, la mise en miroir verticale, la transposition d'image, la mise à l'échelle et la rotation d'image, etc.

Référence: https://blog.csdn.net/clc4210408/article/details/6953664
Référence: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41248872/article/details/83031000