Table des matières
2. Exporter le package de framework MVC personnalisé
3. Utilisez un package de framework MVC personnalisé
4. Optimiser l'ajout, la suppression, la modification, la couche de requête et le servlet
1. Optimiser la couche d'ajout, de suppression, de modification et de requête
2. Optimiser l'ajout, la suppression, la modification et la requête du code Servlet
1. Configurez l'étiquette personnalisée PageTag
2. construction de l'environnement de la page jsp
Introduction
Dans l'article précédent, nous avons optimisé les trois problèmes majeurs que sont l'initialisation du sous-contrôleur, la redondance du code des pages sautantes et l'encapsulation d'entité des paramètres de requête. À l'heure actuelle, notre MVC personnalisé peut répondre à la plupart des besoins. Permettez-moi de vous présenter utilisez notre package de framework MVC personnalisé et l'optimisation des opérations CRUD.
(Je téléchargerai tous les codes suivants sur CSDN, bienvenue pour télécharger ou lire les deux premiers blogs)
2. Exporter le package de framework MVC personnalisé
Tout d'abord, avant de l'utiliser, nous devons d'abord exporter le MVC personnalisé que nous avons écrit dans le fichier jar.
Étape 1 : Trouver le package sur le MVC personnalisé
Nos packs framework et model
Étape 2 : Cliquez avec le bouton droit sur Exporter pour exporter
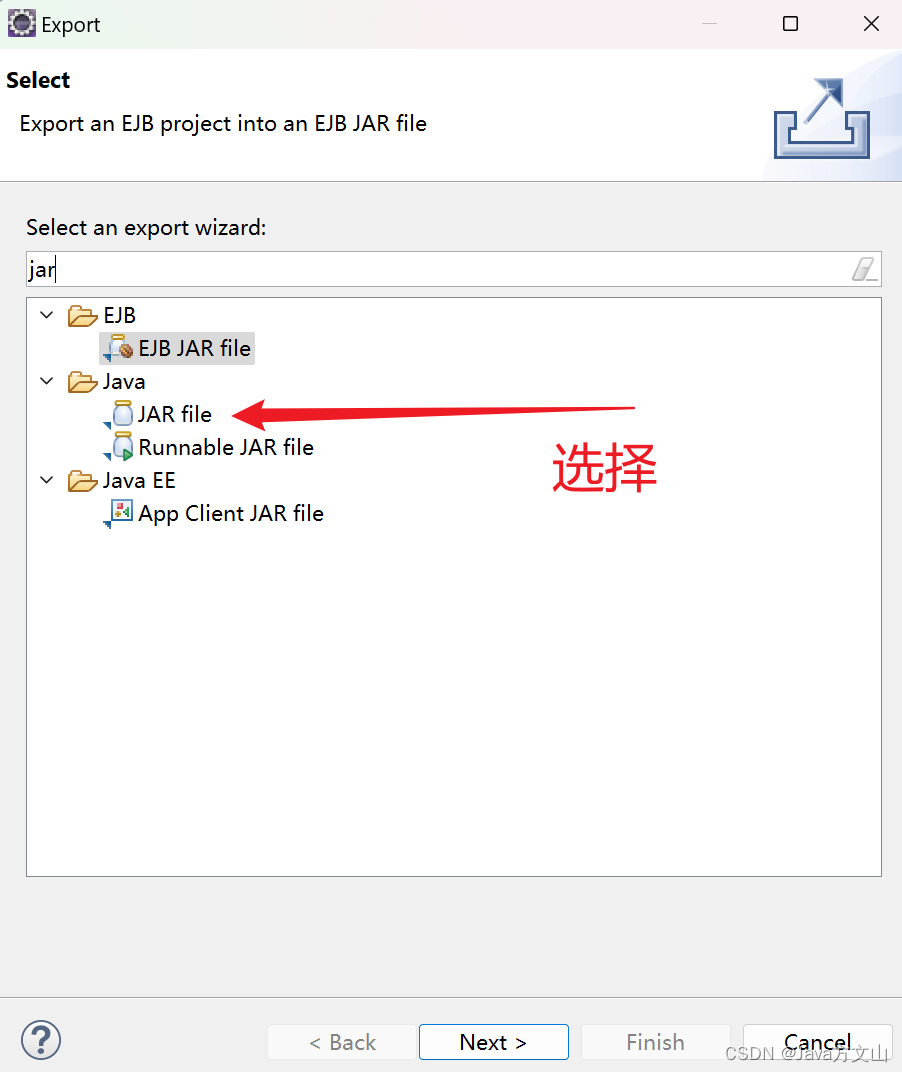
Étape 3 : Sélectionnez le fichier JAR
Étape 4 : Choisissez l'emplacement dont vous avez besoin pour stocker et enregistrez-le, cliquez simplement sur Terminer
De cette façon, le package de framework MVC personnalisé que nous avons écrit est prêt ! !
3. Utilisez un package de framework MVC personnalisé
①Créez un projet Web et importez les packages de rack requis (en particulier les packages de rack écrits par nous-mêmes)
②Créer une boîte à outils (utils) et importer les fichiers requis
Remarque : Ici, il est préférable de tester notre classe d'assistance de base de données (DBAccess), si la connexion à la base de données est réussie
③Importer notre fichier de configuration de sous-contrôle mvc.xml
Il est préférable de créer un nouveau package de ressources de dossier source pour enregistrer
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <config> <action path="/book" type="com.zking.web.BookAction"> <forward name="list" path="/bookList.jsp" redirect="false" /> <forward name="toList" path="/book.action?methodName=list" redirect="true" /> <forward name="toEdit" path="/bookEdit.jsp" redirect="false" /> </action> </config>Le fichier de configuration xml ici est différent de celui de l'architecture MVC personnalisée [中], car il existe trois cas pour ajouter, supprimer, modifier et vérifier des opérations, la première interface de requête, la seconde modifiant l'interface de données d'initialisation et la troisième ajoutant , suppression et modification des opérations après exécution Appelez la méthode list pour synchroniser d'abord les données, puis echo.
④Le fichier web.xml configure manuellement le contrôleur central (DispatchServlet)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"> <display-name>xmymvc_crud</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.zking.framework.DispatchServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>configurationLocation</param-name> <param-value>/mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>Bons conseils :
Parce que nous avions l'habitude d'annoter le contrôleur central (DispatchServlet) pour intercepter la demande de servlet et terminer la configuration initiale, mais maintenant le contrôleur central (DispatchServlet) est quelque chose dans le package rack, nous devons donc configurer manuellement le fichier xml qui doit être analysé (/mvc.xml).
4. Optimiser l'ajout, la suppression, la modification, la couche de requête et le servlet
1. Optimiser la couche d'ajout, de suppression, de modification et de requête
Créer des entités de base de données et des packages dao
Classe d'entité
package com.zking.entity; public class Book { private int bid; private String bname; private float price; public int getBid() { return bid; } public void setBid(int bid) { this.bid = bid; } public String getBname() { return bname; } public void setBname(String bname) { this.bname = bname; } public float getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(float price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book [bid=" + bid + ", bname=" + bname + ", price=" + price + "]"; } }Ici, nous pouvons optimiser notre code de couche Dao et intégrer des ajouts, des suppressions et des modifications dans un seul code.
Routines courantes pour ajouter, supprimer, modifier et vérifier
1. Établir des liens
2. Objets prédéfinis PreparedStatement
3. Définir des espaces réservés ? Valeur de
4.pst.executeUpdate();Ainsi, nous pouvons optimiser le code répété et la réflexion
BaseDao (CRUD général)
package com.zking.util; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import com.zking.entity.Book; import com.zking.util.DBAccess; import com.zking.util.PageBean; import com.zking.util.StringUtils; /** * 所有Dao层的父类 * BookDao * UserDao * OrderDao * ... * @author Administrator * * @param <T> */ public class BaseDao<T> { /** * 通用的增删改方法 * @param book * @throws Exception */ public void executeUpdate(String sql, T t, String[] attrs) throws Exception { Connection con = DBAccess.getConnection(); PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql); /* * 思路: * 1.从传进来的t中读取属性值 * 2.往预定义对象中设置了值 */ for (int i = 0; i < attrs.length; i++) { Field f = t.getClass().getDeclaredField(attrs[i]); f.setAccessible(true); pst.setObject(i+1, f.get(t)); } pst.executeUpdate(); } /** * 通用分页查询 * @param sql * @param clz * @return * @throws Exception */ public List<T> executeQuery(String sql,Class<T> clz,PageBean pageBean) throws Exception{ List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); Connection con = DBAccess.getConnection();; PreparedStatement pst = null; ResultSet rs = null; if(pageBean != null && pageBean.isPagination()) { String countSQL = getCountSQL(sql); pst = con.prepareStatement(countSQL); rs = pst.executeQuery(); if(rs.next()) { pageBean.setTotal(String.valueOf(rs.getObject(1))); } String pageSQL = getPageSQL(sql,pageBean); pst = con.prepareStatement(pageSQL); rs = pst.executeQuery(); }else { pst = con.prepareStatement(sql); rs = pst.executeQuery(); } while (rs.next()) { T t = clz.newInstance(); Field[] fields = clz.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field f : fields) { f.setAccessible(true); f.set(t, rs.getObject(f.getName())); } list.add(t); } return list; } /** * 将原生SQL转换成符合条件的总记录数countSQL * @param sql * @return */ private String getCountSQL(String sql) { return "select count(1) from ("+sql+") t"; } /** * 将原生SQL转换成pageSQL * @param sql * @param pageBean * @return */ private String getPageSQL(String sql,PageBean pageBean) { return sql + " limit "+ pageBean.getStartIndex() +","+pageBean.getRows(); } }BookDao hérite de BaseDao
package com.zking.dao; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; import com.zking.entity.Book; import com.zking.util.BaseDao; import com.zking.util.DBAccess; import com.zking.util.PageBean; import com.zking.util.StringUtils; public class BookDao extends BaseDao<Book>{ public void add(Book book) throws Exception { String sql = "insert into t_mvc_book values(?,?,?)"; super.executeUpdate(sql, book, new String[] {"bid","bname","price"}); } public void edit(Book book) throws Exception { String sql = "update t_mvc_book set bname = ?, price = ? where bid = ?"; super.executeUpdate(sql, book, new String[] {"bname","price","bid"}); } public void delete(Book book) throws Exception { String sql = "delete from t_mvc_book where bid = ?"; super.executeUpdate(sql, book, new String[] {"bid"}); } public List<Book> list(Book book,PageBean pageBean) throws Exception { String sql = "select * from t_mvc_book where 1=1 "; String bname = book.getBname(); if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(bname)) { sql += " and bname like '%"+bname+"%'"; } return super.executeQuery(sql, Book.class, pageBean); } }2. Optimiser l'ajout, la suppression, la modification et la requête du code Servlet
Créez un servlet qui hérite d'ActionSupport et implémente ModelDriver<entité qui doit être exploitée>
package com.zking.web; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.zking.dao.BookDao; import com.zking.entity.Book; import com.zking.framework.ActionSupport; import com.zking.framework.ModelDriver; import com.zking.util.PageBean; /** * @author Java方文山 * */ public class BookAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriver<Book>{ private Book book = new Book(); private BookDao bookDao = new BookDao(); @Override public Book getModel() { return book; } public String add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { try { bookDao.add(book); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "toList"; } public String list(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { try { PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(); pageBean.setPagination(true); pageBean.setRequest(req); List<Book> list = bookDao.list(book,pageBean); req.setAttribute("books", list); req.setAttribute("pageBean", pageBean); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "list"; } public String delete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { try { bookDao.delete(book); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "toList"; } public String edit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { try { bookDao.edit(book); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "toList"; } /** * 跳转到新增修改页面 * @param req * @param resp * @return */ public String toEdit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { try { /* * 如果是跳转修改页面,那么需要做bid条件的精准查询 */ if(book.getBid() != 0) { List<Book> list = bookDao.list(book, null); req.setAttribute("b", list.get(0)); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "toEdit"; } }Comme mentionné précédemment, nous avons trois situations de saut, nous avons donc également trois valeurs de retour (notez que le fichier xml est configuré)
5. Pratique de cas
1. Configurez l'étiquette personnalisée PageTag
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd" version="2.0"> <description>zking 1.1 core library</description> <display-name>zking core</display-name> <tlib-version>1.1</tlib-version> <short-name>zking</short-name> <uri>http://jsp.veryedu.cn</uri> <tag> <name>page</name> <tag-class>com.zking.tag.PageTag</tag-class> <body-content>JSP</body-content> <attribute> <name>pageBean</name> <required>true</required> <rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue> </attribute> </tag> </taglib>Mettez-le dans le répertoire web-inf
2. construction de l'environnement de la page jsp
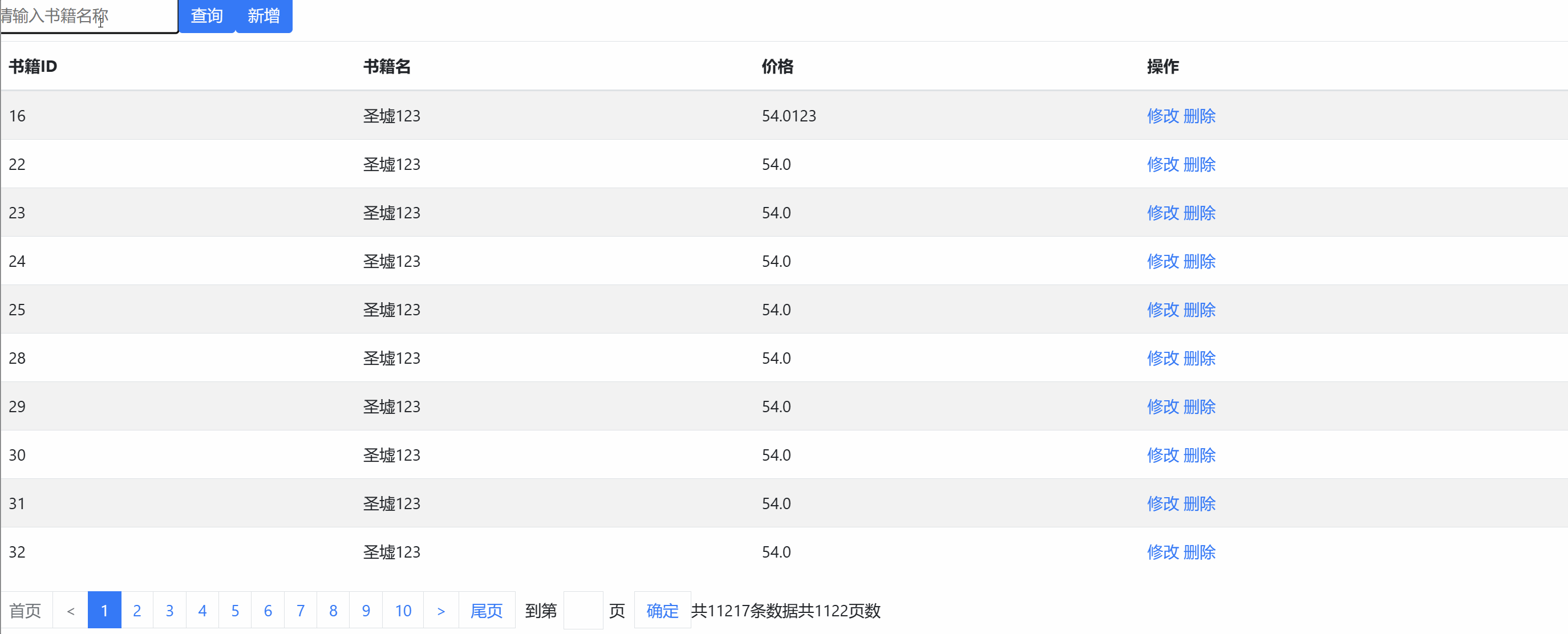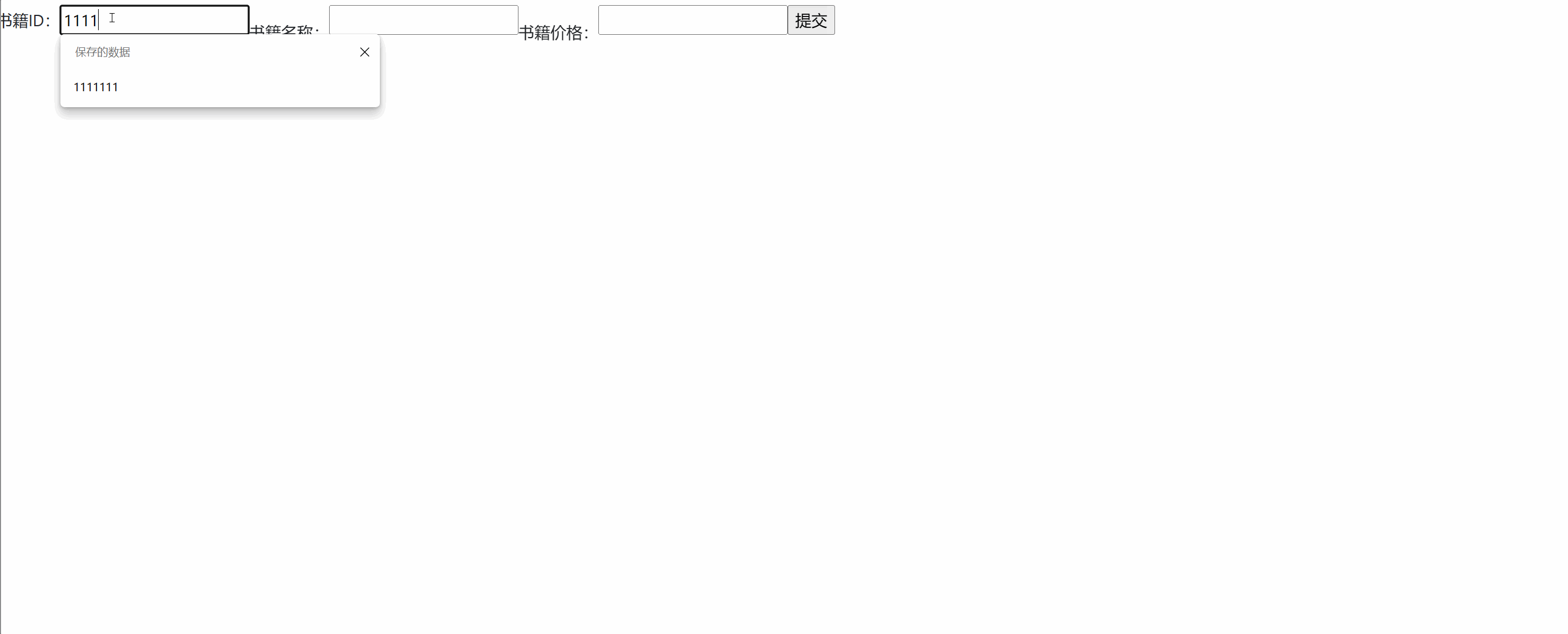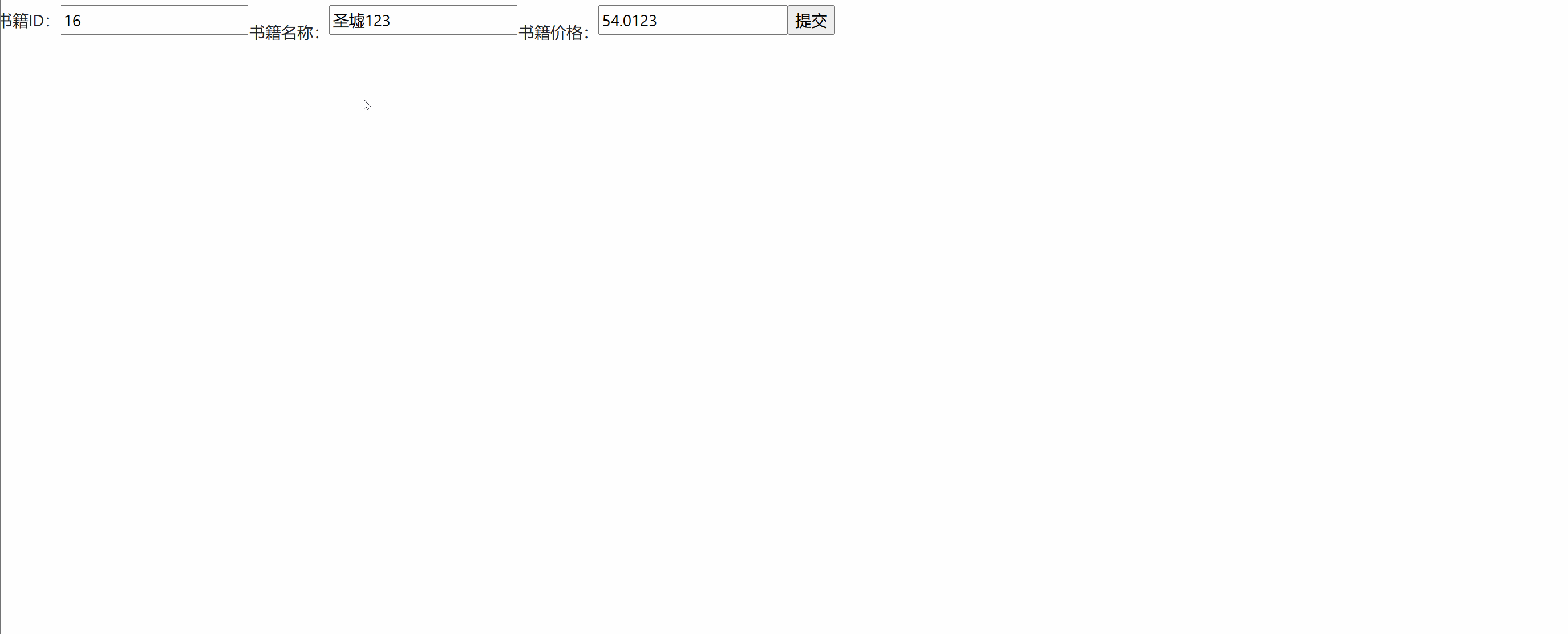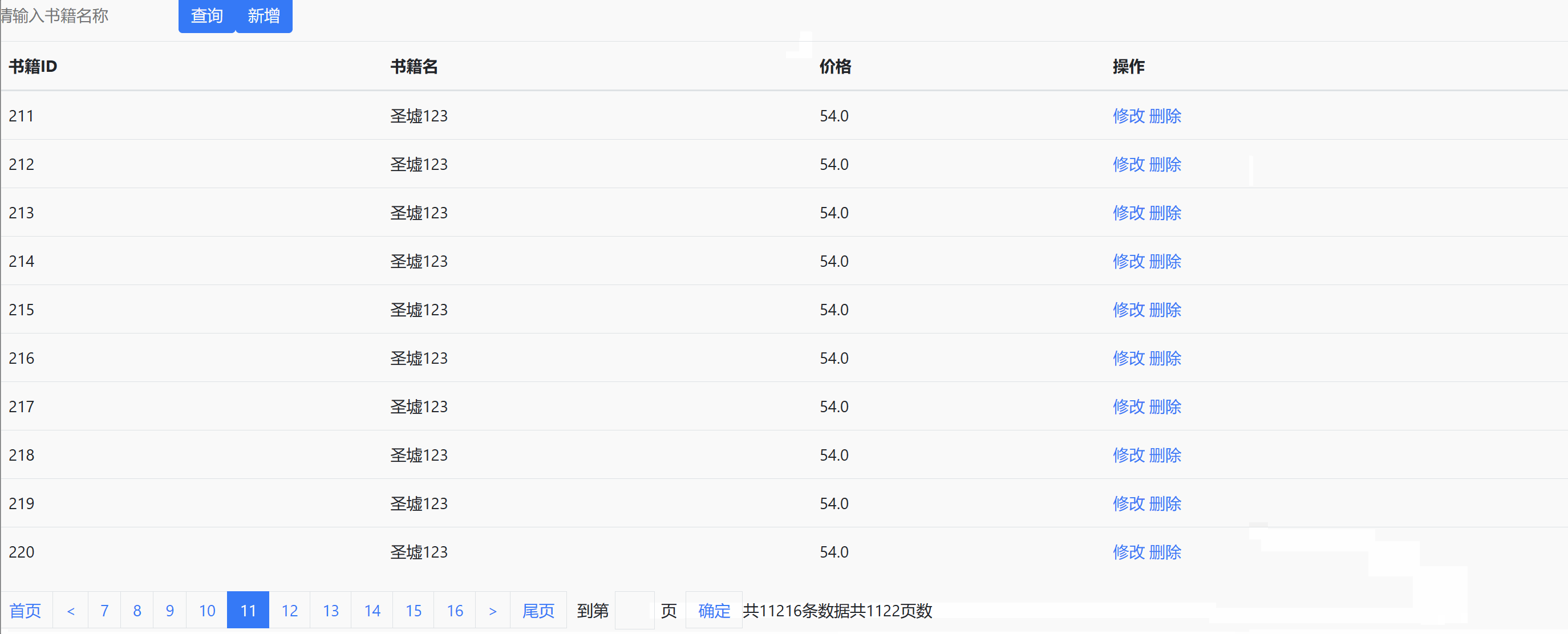
Page d'accueilbookList.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://jsp.veryedu.cn" prefix="z"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <link href="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/4.5.0/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet"> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/4.5.0/js/bootstrap.js"></script> <title>书籍列表</title> <style type="text/css"> .page-item input { padding: 0; width: 40px; height: 100%; text-align: center; margin: 0 6px; } .page-item input, .page-item b { line-height: 38px; float: left; font-weight: 400; } .page-item.go-input { margin: 0 10px; } </style> </head> <body> <c:if test="${empty pageBean}"> <jsp:forward page="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=list"></jsp:forward> </c:if> <form class="form-inline" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=list" method="post"> <div class="form-group mb-2"> <input type="text" class="form-control-plaintext" name="bname" placeholder="请输入书籍名称"> <!-- <input name="rows" value="20" type="hidden"> --> <!-- 不想分页 --> <input name="pagination" value="true" type="hidden"> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary mb-2">查询</button> <a class="btn btn-primary mb-2" href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=toEdit">新增</a> </form> <table class="table table-striped "> <thead> <tr> <th scope="col">书籍ID</th> <th scope="col">书籍名</th> <th scope="col">价格</th> <th scope="col">操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <c:forEach var="b" items="${books }"> <tr> <td>${b.bid }</td> <td>${b.bname }</td> <td>${b.price }</td> <td><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=toEdit&bid=${b.bid}">修改</a> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=delete&bid=${b.bid}">删除</a> </td> </tr> </c:forEach> </tbody> </table> <z:page pageBean="${pageBean }"></z:page> </body> </html>Modifier/ajouter une page bookEdit.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://jsp.veryedu.cn" prefix="z"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <link href="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/4.5.0/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet"> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/4.5.0/js/bootstrap.js"></script> <title>书籍新增/修改</title> </head> <body> <form class="form-inline" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=${empty b ? 'add' : 'edit'}" method="post"> 书籍ID:<input type="text" name="bid" value="${b.bid }"><br> 书籍名称:<input type="text" name="bname" value="${b.bname }"><br> 书籍价格:<input type="text" name="price" value="${b.price }"><br> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>3. Présentation du cas
En voyant cela, je pense que vous devez avoir votre propre compréhension du MVC personnalisé ! !
Jusqu'à présent, la trilogie MVC personnalisée est terminée ! !