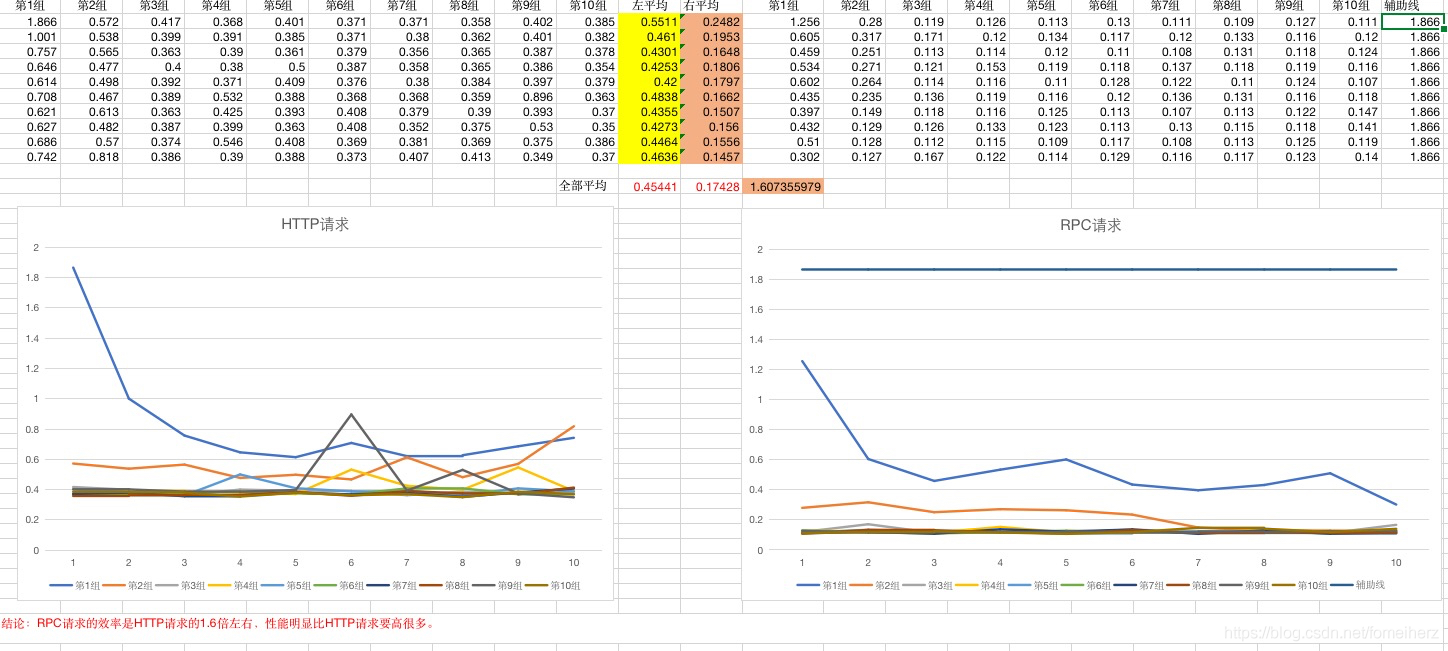
결론부터 시작하겠습니다. RPC 요청의 효율성은 HTTP 요청의 약 1.6 배이고 성능은 HTTP 요청보다 훨씬 높습니다.
이유 분석 : RESTful은 상호 작용을위한 HTTP 프로토콜을 기반으로하며 HTTP 프로토콜에는 많은 양의 요청 헤더 및 응답 헤더 정보가 포함됩니다. Dubbo는 전송을위한 dubbo의 커스텀 바이너리 프로토콜을 기반으로하며 메시지 본문은 비교적 단순하고 전송 데이터는 훨씬 작습니다.
HTTP 요청 코드 :
// 服务端基于spring boot搭建
// 服务端代码
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@RequestMapping("/helloworld")
public String helloworld() {
return "hello world";
}
}
// 客户端代码
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
public class HelloworldTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println("------------------");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
restTemplate.getForObject("http://127.0.0.1/helloworld", String.class);
if (i % 1000 == 0) {
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println(stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
}
}
}
}
}
RPC 코드 :
// dubbo-demo工程的代码,详情请看:https://github.com/apache/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-demo
// 服务端
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name + ", response from provider: " + RpcContext.getContext().getLocalAddress();
}
}
// 客户端
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Prevent to get IPV6 address,this way only work in debug mode
//But you can pass use -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true,then it work well whether in debug mode or not
System.setProperty("java.net.preferIPv4Stack", "true");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{
"META-INF/spring/dubbo-demo-consumer.xml"});
context.start();
DemoService demoService = (DemoService) context.getBean("demoService"); // get remote service proxy
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println("-----------");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
demoService.sayHello("world"); // call remote method
if (i % 1000 == 0) {
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println(stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
}
}
}
}
}