之前说过playbook的变量引用,这是传参的一种方式。
playbook还支持很多插件从外部读取数据,比如从文件中读取、从数据库中读取。
lookups的所有操作都是在中控机上进行。目前有58个插件
官网文档:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/plugins/lookup.html#plugin-list
下面介绍几个常用的。
1.lookups file
通过file插件可以读取文件。其内部是使用python打开文件然后把结果返回给变量。
[root@centos3 yaml_test]# cat file_lookup.yaml --- - hosts: all gather_facts: False vars: contents: "{{ lookup('file','/etc/hostname') }}" tasks: - name: debug lookups debug: msg="The contents is {% for i in contents.split("\n") %} {{ i }} {% endfor %}"
执行结果:
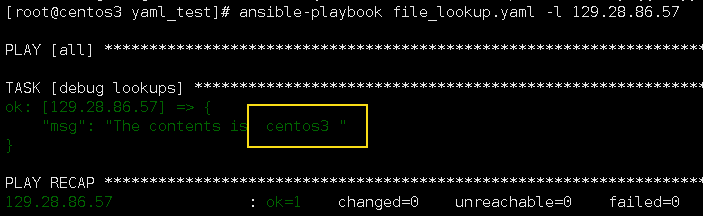
file这个插件读取的是中控机本地的文件,然后拿到数据以供任务使用.
这里使用的是jinjia2的语法.
2.lookups password
passwd这个插件会对传入的内容进行加密处理.
定义:pass_lookup.yaml
--- - hosts: all vars: contents: "{{ lookup('password', 'ansible_book') }}" tasks: - name: debug lookups debug: msg="The contents is {{ contents }}"
执行结果:
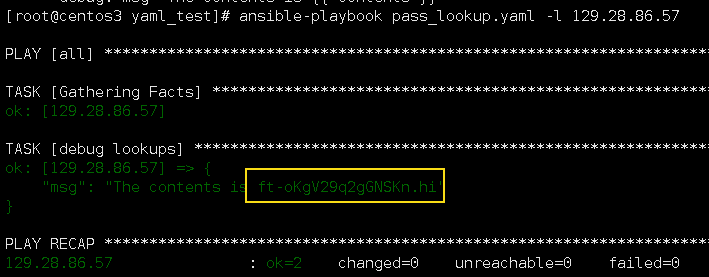
上面的例子就是将ansible_book加密,然后以作他用.
3.lookups pipe
pipe插件运行命令并返回结果。
--- - hosts: all vars: contents: "{{ lookup('pipe', 'date +%Y-%m-%d') }}" tasks: - name: debug lookups debug: msg="The contents is {% for i in contents.split("\n") %} {{ i }} {% endfor %}
执行结果:
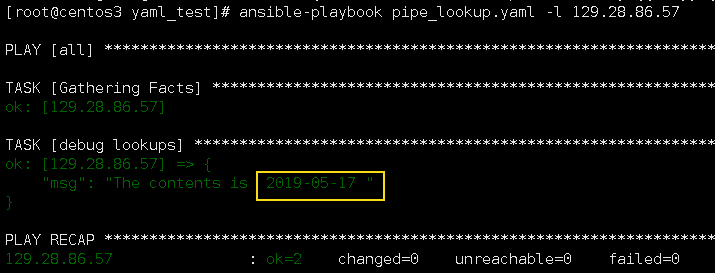
pipe看起和shell一样,也是用来执行命令,但是shell是在管理节点上执行,而pipe是在中控机上执行。
pipe这个插件底层使用的是subprocess这个python库来实现的
subprocess是用来生成新的进程,连接它们的输入输出。Popen类是用来创建和管理进程。
虽然增加一个进程不一定能够解决ansible进程和pipe进程的拥堵问题,但是一般情况还是适用的。
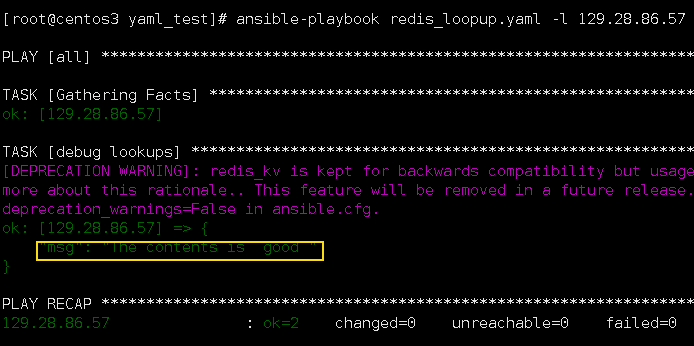
4.lookups redis_kv
redis_kv是用来从本地redis中读取数据。
ansible默认支持的是python2,因此你需要在python2中添加redis这个python包。
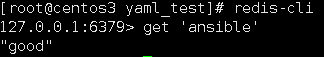
定义: redis_lookup.yaml
--- - hosts: all vars: contents: "{{ lookup('redis_kv', 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379,ansible') }}" tasks: - name: debug lookups debug: msg="The contents is {% for i in contents.split("\n") %} {{ i }} {% endfor %}"
执行结果: