前言
学习总结一下Hive的分桶表。
- 分桶规则:对分桶字段值进行哈希,哈希值除以桶的个数求余,余数决定了该条记录在哪个桶中,也就是余数相同的在一个桶中。
- 优点:1、提高join查询效率 2、提高抽样效率
1、建表
通过 clustered by(字段名) into bucket_num buckets 分桶,意思是根据字段名分成bucket_num个桶
create table test_bucket (
id int comment 'ID',
name string comment '名字'
)
comment '测试分桶'
clustered by(id) into 4 buckets
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' ;
2、插入数据
2.1 数据
buckt_data.txt
1,name1
2,name2
3,name3
4,name4
5,name5
6,name6
7,name7
8,name8
9,name9
2.2 load data
直接load data不会有分桶的效果,这样和不分桶一样,在HDFS上只有一个文件。
load data local inpath '/root/dkl/data/buckt_data.txt' into table test_bucket;
需要借助中间表
create table test (
id int comment 'ID',
name string comment '名字'
)
comment '测试分桶中间表'
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' ;
先将数据load到中间表
load data local inpath '/root/dkl/data/buckt_data.txt' into table test;
然后通过下面的语句,将中间表的数据插入到分桶表中,这样会产生四个文件。
insert into test_bucket select * from test;
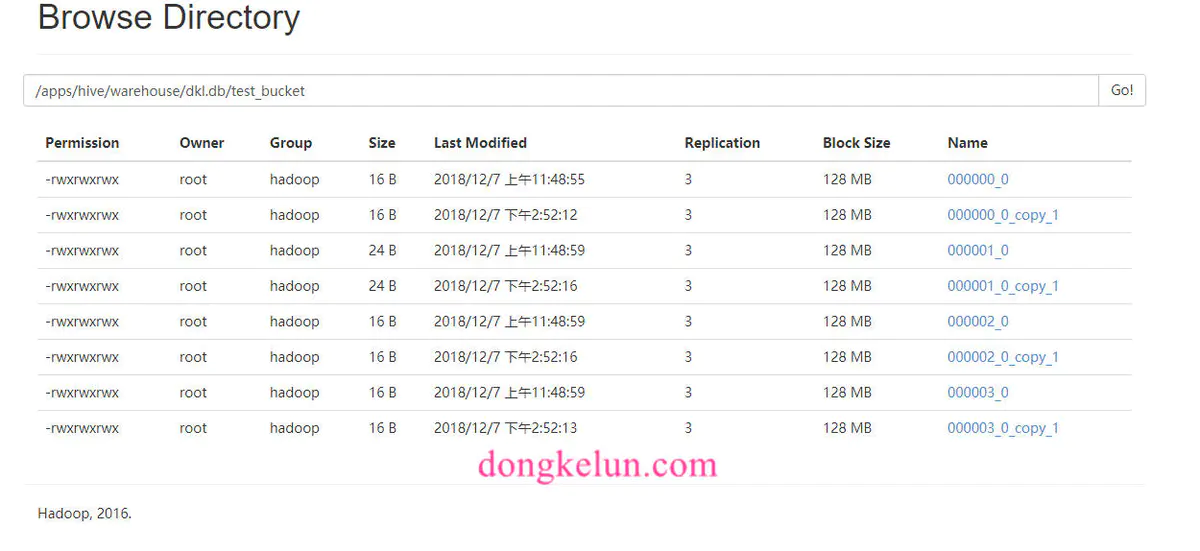
2.3 结果
HDFS:桶是以文件的形式存在的,而不是像分区那样以文件夹的形式存在。

看一下每个文件下存放的都是什么数据
可以看到除以4余数相同的确实在一个文件里,也就是在一个桶中。

我们用sql语句查出来的顺序和文件存放的顺序是一致的。
2.4 再次插入数据
这样会再产生新的四个文件
3、分桶排序
上面建的表每个桶内的数据是没有排序的,可以将上面的数据打乱,先看一下
buckt_data.txt
5,name5
2,name2
7,name7
3,name3
8,name8
4,name4
6,name6
1,name1
9,name9
删除表数据
truncate table test_bucket;
truncate table test;
重新按上面讲的,导入打乱的数据。
load data local inpath '/root/dkl/data/buckt_data.txt' into table test;
insert into test_bucket select * from test;
确实没有排序(默认按文件里的顺序)
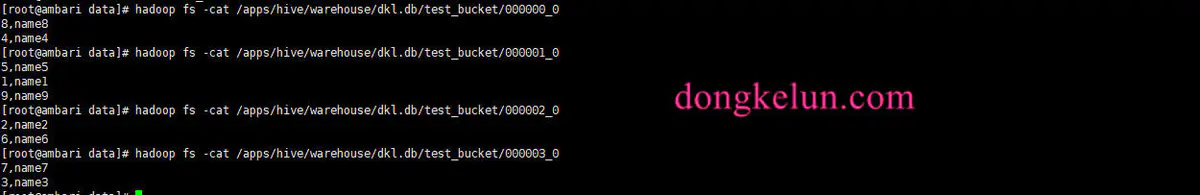
下面按id升序排序
3.1 建表
create table test_bucket_sorted (
id int comment 'ID',
name string comment '名字'
)
comment '测试分桶'
clustered by(id) sorted by (id) into 4 buckets
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' ;
3.2 插入数据
insert into test_bucket_sorted select * from test;
3.3 查看结果
用sql看和用hadoop命令看每个文件,结果每个桶内都是按id升序排序的,也就是和最开始的截图是一样的。
3.4 好处
因为每个桶内的数据是排序的,这样每个桶进行连接时就变成了高效的归并排序
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zhihaoma/article/details/52539986
4、提高join查询效率
假设表A和表B进行join,join的字段为id
条件:
- 1、两个表为大表
- 2、两个表都为分桶表
- 3、A表的桶数是B表桶数的倍数或因子
这样join查询时候,表A的每个桶就可以和表B对应的桶直接join,而不用全表join,提高查询效率
比如A表桶数为4,B表桶数为8,那么桶数对应关系为
| 表A | 表B |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 0 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 7 |
5、提高抽样效率
5.1 sql示例:
hive> select * from test_bucket tablesample (bucket 1 out of 2);
OK
8 name8
4 name4
2 name2
6 name6
hive> select * from test tablesample (bucket 1 out of 2 on id);
OK
2 name2
8 name8
4 name4
6 name6
5.2 区别:
- 分桶表后面可以不带on 字段名,不带时默认的是按分桶字段,也可以带,而没有分桶的表则必须带
- 按分桶字段取样时,因为分桶表是直接去对应的桶中拿数据,在表比较大时会提高取样效率
5.3 语法:
tablesample (bucket x out of y on id);
x表示从哪个桶(x-1)开始,y代表分几个桶,也可以理解分x为分子,y为分母,及将表分为y份(桶),取第x份(桶)
所以这时对于分桶表是有要求的,y为桶数的倍数或因子,
- x=1,y=2,取2(4/y)个bucket的数据,分别桶0(x-1)和桶2(0+y)
- x=1,y=4, 取1(4/y)个bucket的数据,即桶0
- x=2,y=8, 取1/2(4/y)个bucket的数据,即桶0的一半
x的范围:[1,y]