牛客国庆集训派对Day6 A-Birthday (最小费用最大流)
题目大意:
宇扬在蛋糕上插了 n (1<=n<=50)支蜡烛,并把蛋糕分为 m (2<=m<=50)个区域。
因为某种原因,他必须把第i根蜡烛插在第ai个区域或第bi个区域。区域之间是不相交的。
宇扬在一个区域内同时摆放x支蜡烛就要花费x^{2}的时间。
布置蛋糕所用的总时间是他在每个区域花的时间的和,求布置蛋糕最少时间。
解题思路:
这是一个最小费用最大流的问题,难点在于如何建图,建完图跑一下模板问题就解决了。
下面说一下思路:
首先建立一个源点( 0 ),一个汇点( n+m+1 ),
然后源点与每个蜡烛 i 建立一条 (1,0)流量为1费用为0的边,
然后蜡烛 i 与两个区域ai,bi 分别建立一条 (1,0)流量为1费用为0的边,
最后每个区域与汇点建立对应的流量费用边即可。
难点就在于最后的的流量费用边如何建立,因为耗费的时间和区域内蜡烛的数量成正比,x支蜡烛对应x^{2}的时间,很显然只有1支蜡烛的话,建一条(1,1)流量为1费用为1的边即可,而区域内有多根蜡烛要怎么办呢。
解决这个问题就用到了等差数列的求和公式
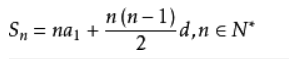
推导一下可得 k^{2}= 1+3+5+……+(2*k-1); 即建立n条流量为1费用为(x * x - (x-1) * (x-1))的边即可。
下面上图(手太残了,图画的有点丑 ):

Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1111, MAXM = 11111, inf = 1e9;
struct Edge{
int to, next, cap, flow, cost;
}e[MAXM];
int head[MAXN] ,tol,N;
int pre[MAXN], dis[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
void init(int n){
N = n;
tol = 0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int cap,int cost){
e[tol].to = v;
e[tol].cap = cap;
e[tol].cost = cost;
e[tol].flow = 0;
e[tol].next = head[u];
head[u] = tol++;
e[tol].to = u;
e[tol].cap = 0;
e[tol].cost = -cost;
e[tol].flow = 0;
e[tol].next = head[v];
head[v] = tol++;
}
bool spfa(int s,int t){
queue<int> q;
memset(pre,-1,sizeof pre);
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
for(int i = s; i <= t; ++i){
dis[i] = inf;
}
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = 1;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = 0;
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if(e[i].cap > e[i].flow && dis[v] > dis[u] + e[i].cost){
dis[v] = dis[u] + e[i].cost;
pre[v] = i;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v] = 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
if(pre[t] == -1) return 0;
else return 1;
}
int minCostMaxFlow(int s,int t,int &cost){
int flow = 0;
cost = 0;
while(spfa(s,t)){
int Min = inf;
for(int i = pre[t]; i != -1; i = pre[e[i^1].to]){
if(Min > e[i].cap - e[i].flow)
Min = e[i].cap - e[i].flow;
}
for(int i = pre[t]; i != -1; i = pre[e[i^1].to]){
e[i].flow += Min;
e[i ^ 1].flow -= Min;
cost += e[i].cost * Min;
}
flow += Min;
}
return flow;
}
int main()
{
//#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
// freopen("input.in","r",stdin);
//#endif
int n,m,x,y,cost;
cin>>n>>m;
init(n+m+1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin>>x>>y;
addedge(0,i,1,0);
addedge(i,x+n,1,0);
addedge(i,y+n,1,0);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
for(int j=1;j<=50;j++)
addedge(i+n,m+n+1,1,j*j-(j-1)*(j-1)); //x的平方-(x-1)的平方
}
}
minCostMaxFlow(0,n+m+1,cost);
cout<<cost<<endl;
return 0;
}