文章目录
1.概述
Long是long的包装类,最大值为2^63-1 ,最小值为-2^63。对基本数据类型long进行封装,提供了一些处理long数据类型的数据的方法。
2.类图
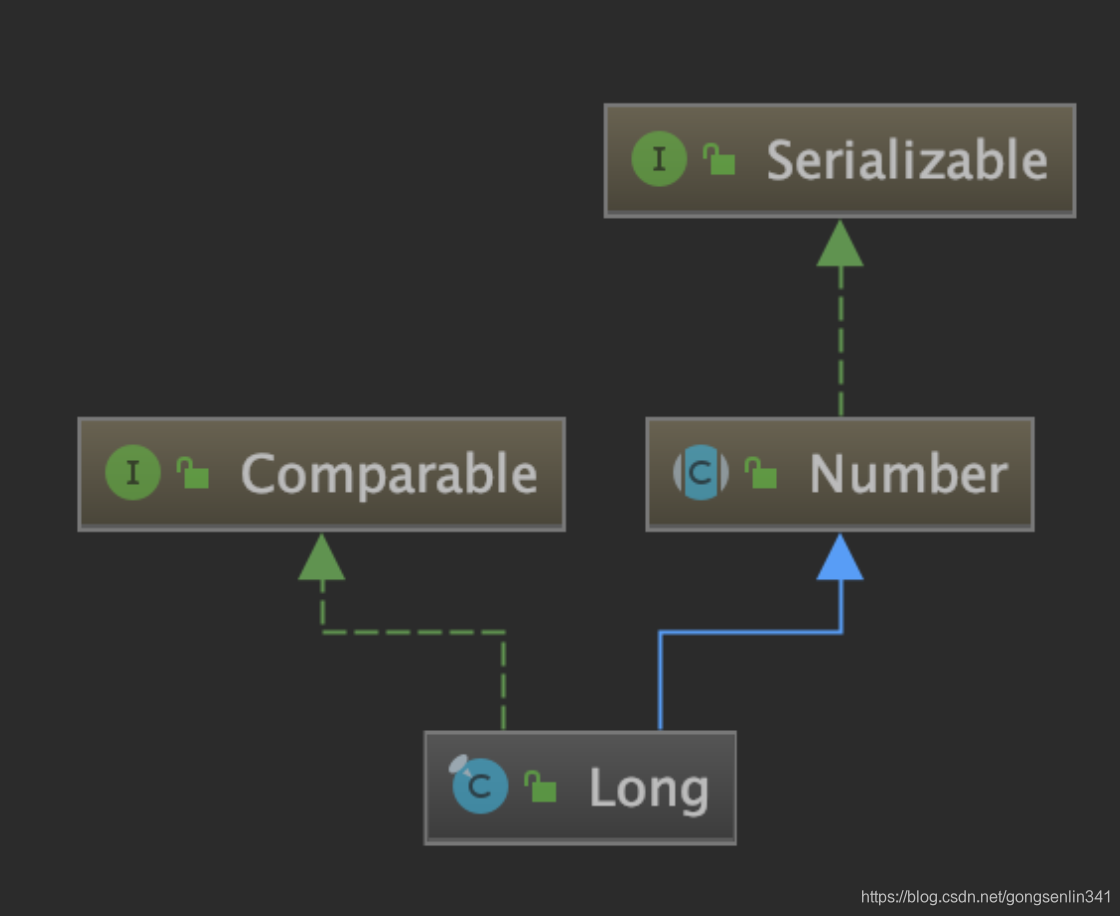
继承了Number,实现了数值类型转换的方法
实现了Comparabel接口对Float对象进行比较
实现了Serializable序列化接口
3.属性
静态常量
@Native public static final long MIN_VALUE = 0x8000000000000000L;//最小值,同样也是补码表示
@Native public static final long MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffffffffffffL;//最大值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static final Class<Long> TYPE = (Class<Long>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("long");//Long.class 对象
@Native public static final int SIZE = 64;//占据64位
public static final int BYTES = SIZE / Byte.SIZE;// 8个字节
@Native private static final long serialVersionUID = 4290774380558885855L;//序列化版本id
私有常量
private final long value;//用于存储long数据
4.构造方法
- Long(long value) 将long赋值给value
public Long(long value) {
this.value = value;
}
- Long(String s) 将字符串解析成10进制的long型数据,赋值给value
public Long(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
this.value = parseLong(s, 10);
}
5.缓存
将-128 ~ 127的long型数据封装成Long对象保存在缓存数组中。
private static class LongCache {
private LongCache(){}
static final Long cache[] = new Long[-(-128) + 127 + 1];
static {
for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++)
cache[i] = new Long(i - 128);
}
}
6.toXXXString
- toString(long i, int radix) 按照进制数 将long型的数据转换成字符串输出
public static String toString(long i, int radix) {
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)
radix = 10;
if (radix == 10)
return toString(i);
char[] buf = new char[65];
int charPos = 64;
boolean negative = (i < 0);
if (!negative) {
i = -i;
}
while (i <= -radix) {
buf[charPos--] = Integer.digits[(int)(-(i % radix))];
i = i / radix;
}
buf[charPos] = Integer.digits[(int)(-i)];
if (negative) {
buf[--charPos] = '-';
}
return new String(buf, charPos, (65 - charPos));
}
- toUnsignedString(long i, int radix) 根据进制数将long型的数据转换成无符号的字符串
public static String toUnsignedString(long i, int radix) {
if (i >= 0)
return toString(i, radix);
else {
switch (radix) {
case 2:
return toBinaryString(i);
case 4:
return toUnsignedString0(i, 2);
case 8:
return toOctalString(i);
case 10:
/*
* We can get the effect of an unsigned division by 10
* on a long value by first shifting right, yielding a
* positive value, and then dividing by 5. This
* allows the last digit and preceding digits to be
* isolated more quickly than by an initial conversion
* to BigInteger.
*/
long quot = (i >>> 1) / 5;
long rem = i - quot * 10;
return toString(quot) + rem;
case 16:
return toHexString(i);
case 32:
return toUnsignedString0(i, 5);
default:
return toUnsignedBigInteger(i).toString(radix);
}
}
}
- toHexString(long i)转16进制字符串
public static String toHexString(long i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 4);
}
static String toUnsignedString0(long val, int shift) {
// assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
int mag = Long.SIZE - Long.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
char[] buf = new char[chars];
formatUnsignedLong(val, shift, buf, 0, chars);
return new String(buf, true);
}
- toBinaryString(long i) 将long型转换成2进制字符串。
public static String toBinaryString(long i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 1);
}
static String toUnsignedString0(long val, int shift) {
// assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
int mag = Long.SIZE - Long.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
char[] buf = new char[chars];
formatUnsignedLong(val, shift, buf, 0, chars);
return new String(buf, true);
}
- toString(long i) 将long型数据转换成字符串
public static String toString(long i) {
if (i == Long.MIN_VALUE)
return "-9223372036854775808";
int size = (i < 0) ? stringSize(-i) + 1 : stringSize(i);
char[] buf = new char[size];
getChars(i, size, buf);
return new String(buf, true);
}
static void getChars(long i, int index, char[] buf) {
long q;
int r;
int charPos = index;
char sign = 0;
if (i < 0) {
sign = '-';
i = -i;
}
// Get 2 digits/iteration using longs until quotient fits into an int
while (i > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
q = i / 100;
// really: r = i - (q * 100);
r = (int)(i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2)));
i = q;
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitOnes[r];
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitTens[r];
}
// Get 2 digits/iteration using ints
int q2;
int i2 = (int)i;
while (i2 >= 65536) {
q2 = i2 / 100;
// really: r = i2 - (q * 100);
r = i2 - ((q2 << 6) + (q2 << 5) + (q2 << 2));
i2 = q2;
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitOnes[r];
buf[--charPos] = Integer.DigitTens[r];
}
// Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
// assert(i2 <= 65536, i2);
for (;;) {
q2 = (i2 * 52429) >>> (16+3);
r = i2 - ((q2 << 3) + (q2 << 1)); // r = i2-(q2*10) ...
buf[--charPos] = Integer.digits[r];
i2 = q2;
if (i2 == 0) break;
}
if (sign != 0) {
buf[--charPos] = sign;
}
}
- toOctalString(long i)转8进制字符串
public static String toOctalString(long i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 3);
}
7.stringSize 求long数据的长度
static int stringSize(long x) {
long p = 10;
for (int i=1; i<19; i++) {
if (x < p)
return i;
p = 10*p;
}
return 19;
}
8. parseXXX
- parseLong(String s, int radix) 按照进制数 将字符串解析成long数据
public static long parseLong(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
long result = 0;
boolean negative = false;
int i = 0, len = s.length();
long limit = -Long.MAX_VALUE;
long multmin;
int digit;
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Long.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+')
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
i++;
}
multmin = limit / radix;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
if (digit < 0) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result -= digit;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
return negative ? result : -result;
}
- parseLong(String s) 内部调用上面的方法 默认10进制数
public static long parseLong(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseLong(s, 10);
}
- parseUnsignedLong(String s, int radix) 根据进制数 将字符串解析成无符号的long型数据 若字符串第一位是负号则报错
public static long parseUnsignedLong(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException {
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
int len = s.length();
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
if (firstChar == '-') {
throw new
NumberFormatException(String.format("Illegal leading minus sign " +
"on unsigned string %s.", s));
} else {
if (len <= 12 || // Long.MAX_VALUE in Character.MAX_RADIX is 13 digits
(radix == 10 && len <= 18) ) { // Long.MAX_VALUE in base 10 is 19 digits
return parseLong(s, radix);
}
// No need for range checks on len due to testing above.
long first = parseLong(s.substring(0, len - 1), radix);
int second = Character.digit(s.charAt(len - 1), radix);
if (second < 0) {
throw new NumberFormatException("Bad digit at end of " + s);
}
long result = first * radix + second;
if (compareUnsigned(result, first) < 0) {
/*
* The maximum unsigned value, (2^64)-1, takes at
* most one more digit to represent than the
* maximum signed value, (2^63)-1. Therefore,
* parsing (len - 1) digits will be appropriately
* in-range of the signed parsing. In other
* words, if parsing (len -1) digits overflows
* signed parsing, parsing len digits will
* certainly overflow unsigned parsing.
*
* The compareUnsigned check above catches
* situations where an unsigned overflow occurs
* incorporating the contribution of the final
* digit.
*/
throw new NumberFormatException(String.format("String value %s exceeds " +
"range of unsigned long.", s));
}
return result;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
}
- parseUnsignedLong(String s) 默认10进制解析字符串为long数据
public static long parseUnsignedLong(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseUnsignedLong(s, 10);
}
9.valueOf
- valueOf(String s, int radix) 将字符串解析成long再调用valueOf(long l)将其封装成Long
public static Long valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException {
return Long.valueOf(parseLong(s, radix));
}
- valueOf(String s) 将字符串解析long再调用valueOf(long l)将其封装成Long
public static Long valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException
{
return Long.valueOf(parseLong(s, 10));
}
- valueOf(long l)将long封装成Long
public static Long valueOf(long l) {
final int offset = 128;
if (l >= -128 && l <= 127) { // will cache
return LongCache.cache[(int)l + offset];
}
return new Long(l);
}
10.XXXValue 转换成其他类型的数值返回
public byte byteValue() {
return (byte)value;
}
public short shortValue() {
return (short)value;
}
public int intValue() {
return (int)value;
}
public long longValue() {
return value;
}
public float floatValue() {
return (float)value;
}
public double doubleValue() {
return (double)value;
}
11.hashCode
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Long.hashCode(value);
}
public static int hashCode(long value) {
return (int)(value ^ (value >>> 32));
}
12.其他方法
- remainderUnsigned(long dividend, long divisor) 求余数
public static long remainderUnsigned(long dividend, long divisor) {
if (dividend > 0 && divisor > 0) { // signed comparisons
return dividend % divisor;
} else {
if (compareUnsigned(dividend, divisor) < 0) // Avoid explicit check for 0 divisor
return dividend;
else
return toUnsignedBigInteger(dividend).
remainder(toUnsignedBigInteger(divisor)).longValue();
}
}
- divideUnsigned(long dividend, long divisor) 除法运算
public static long divideUnsigned(long dividend, long divisor) {
if (divisor < 0L) { // signed comparison
// Answer must be 0 or 1 depending on relative magnitude
// of dividend and divisor.
return (compareUnsigned(dividend, divisor)) < 0 ? 0L :1L;
}
if (dividend > 0) // Both inputs non-negative
return dividend/divisor;
else {
/*
* For simple code, leveraging BigInteger. Longer and faster
* code written directly in terms of operations on longs is
* possible; see "Hacker's Delight" for divide and remainder
* algorithms.
*/
return toUnsignedBigInteger(dividend).
divide(toUnsignedBigInteger(divisor)).longValue();
}
}
- highestOneBit(long i) 最高位为1的位次
public static long highestOneBit(long i) {
// HD, Figure 3-1
i |= (i >> 1);
i |= (i >> 2);
i |= (i >> 4);
i |= (i >> 8);
i |= (i >> 16);
i |= (i >> 32);
return i - (i >>> 1);
}
- lowestOneBit(long i) 最低位为1的位次
public static long lowestOneBit(long i) {
// HD, Section 2-1
return i & -i;
}
- numberOfLeadingZeros(long i) 最高位1之前的0的个数
public static int numberOfLeadingZeros(long i) {
// HD, Figure 5-6
if (i == 0)
return 64;
int n = 1;
int x = (int)(i >>> 32);
if (x == 0) { n += 32; x = (int)i; }
if (x >>> 16 == 0) { n += 16; x <<= 16; }
if (x >>> 24 == 0) { n += 8; x <<= 8; }
if (x >>> 28 == 0) { n += 4; x <<= 4; }
if (x >>> 30 == 0) { n += 2; x <<= 2; }
n -= x >>> 31;
return n;
}
- 最低位1之后0的个数
public static int numberOfTrailingZeros(long i) {
// HD, Figure 5-14
int x, y;
if (i == 0) return 64;
int n = 63;
y = (int)i; if (y != 0) { n = n -32; x = y; } else x = (int)(i>>>32);
y = x <<16; if (y != 0) { n = n -16; x = y; }
y = x << 8; if (y != 0) { n = n - 8; x = y; }
y = x << 4; if (y != 0) { n = n - 4; x = y; }
y = x << 2; if (y != 0) { n = n - 2; x = y; }
return n - ((x << 1) >>> 31);
}
- bitCount(long i) 二进制数中为1的个数
public static int bitCount(long i) {
// HD, Figure 5-14
i = i - ((i >>> 1) & 0x5555555555555555L);
i = (i & 0x3333333333333333L) + ((i >>> 2) & 0x3333333333333333L);
i = (i + (i >>> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0fL;
i = i + (i >>> 8);
i = i + (i >>> 16);
i = i + (i >>> 32);
return (int)i & 0x7f;
}
- 循环左移
public static long rotateLeft(long i, int distance) {
return (i << distance) | (i >>> -distance);
}
- 循环右移
public static long rotateRight(long i, int distance) {
return (i >>> distance) | (i << -distance);
}
- 翻转
public static long reverse(long i) {
// HD, Figure 7-1
i = (i & 0x5555555555555555L) << 1 | (i >>> 1) & 0x5555555555555555L;
i = (i & 0x3333333333333333L) << 2 | (i >>> 2) & 0x3333333333333333L;
i = (i & 0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0fL) << 4 | (i >>> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0fL;
i = (i & 0x00ff00ff00ff00ffL) << 8 | (i >>> 8) & 0x00ff00ff00ff00ffL;
i = (i << 48) | ((i & 0xffff0000L) << 16) |
((i >>> 16) & 0xffff0000L) | (i >>> 48);
return i;
}
public static long reverseBytes(long i) {
i = (i & 0x00ff00ff00ff00ffL) << 8 | (i >>> 8) & 0x00ff00ff00ff00ffL;
return (i << 48) | ((i & 0xffff0000L) << 16) |
((i >>> 16) & 0xffff0000L) | (i >>> 48);
}
- 求符号位
public static int signum(long i) {
// HD, Section 2-7
return (int) ((i >> 63) | (-i >>> 63));
}
- 运算
public static long sum(long a, long b) {
return a + b;
}
public static long max(long a, long b) {
return Math.max(a, b);
}
public static long min(long a, long b) {
return Math.min(a, b);
}