2, 第二步骤,我们来看下我们的界面
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
// 计数器功能,来改下redux-thunk 操作
class ReduxSagaHa extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
const { count, add } = this.props;
return (
<div>
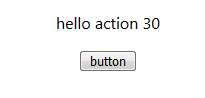
<p>hello action {count}</p>
<button onClick={() => { this.go() }}>button</button>
</div>
)
}
//我们自身的逻辑
go() {
//加入在这里执行异步操作
this.props.add();
}
}
export default connect(state => ({ count: state.count }),
{
// add: () => (dispatch) => {
// setTimeout(() => {
// dispatch({ type: 'add' });
// }, 1000);
// }
add: () => ({ type: 'add' })
}
)(ReduxSagaHa);
以上没啥,就是用connect 函数连接一下redux
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import { combineReducers } from "redux"
import mySaga from './sagas'
//引入中间键盘
import logger from "redux-logger"
// import thunk from "redux-thunk"
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware()
// 用户状态的纯函数
function UseReducer(state = { isLogin: false }, action) {
const type = action.type;
switch (type) {
case "login":
// 登陆的方法
let newState = {
...state,
isLogin: true
}
return newState;
// 退出的方法
case "logout":
let newS = {
...state,
isLogin: false
}
return newS;
default:
return state;
}
}
// 两个reducer 我开始测试 combineReducer
function nameReducer(state = { "name": "action" }, action) {
const type = action.type;
switch (type) {
case "init":
let newState = {
...state,
name: "tiantian"
}
return newState;
default:
return state;
}
}
// 计数器
function CountReducer(state = 10, action) {
const type = action.type;
switch (type) {
case "add":
// state++;
// console.log("更改的操作。。。" + state);
return state;
case "minus":
state--;
return state;
case "asyncAdd":
// 我打印这个就是想看下,它咋接收参数的!
console.log(action);
state++;
return state;
case "setValue":
state += action.value;
return state;
default:
return state;
}
}
// applyMiddleware 使用中间键
const store = createStore(combineReducers({
count: CountReducer,
name: nameReducer,
user: UseReducer
}), applyMiddleware(logger, sagaMiddleware));
sagaMiddleware.run(mySaga)
export default store;sagas.js
import { call, put, takeEvery } from 'redux-saga/effects'
// 这是地道的异步操作的逻辑
function asyncAdd(arg) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(arg + 10);
}, 1000);
});
}
// 函数生成器
function* addCount(action) {
try {
// 调用异步操作的方法, 在这里会返回 20 正确结果的Promise , value
const value = yield call(asyncAdd, 0);
console.log("value=" + value);
// 将count 值,更新为20
yield put({ type: "setValue", value });
} catch (e) {
// 出错的逻辑,我这里暂时不处理!
yield put({ type: "USER_FETCH_FAILED", message: e.message });
}
}
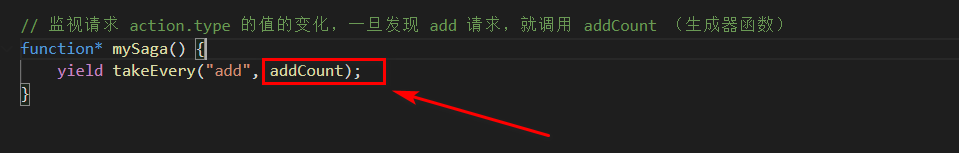
function* mySaga() {
yield takeEvery("add", addCount);
}
export default mySaga;saga的原理非常简单,就是监听action 请求,一旦发现,就去执行我们的生成器函数
saga 配置

逻辑我给顺一下,毕竟是线性的

这个时候已经发送 请求了 dispatch({type:'add'})


总之异步的操作都被抽取出来了,很是舒服,爱咋写咋写
行,初步就这些,我们回头继续, dva umi 都要搞定!