EnumSet
前面我们学习了Enum 和 EnumMap 今天我们学习和枚举相关的最后一个数据类型,那就是EnumSet,EnumSet 是Java 集合框架提供的一个存储元素都是枚举类型的集合,所以建议开始学习之前先学习枚举初识和枚举进阶
EnumSet的说明书
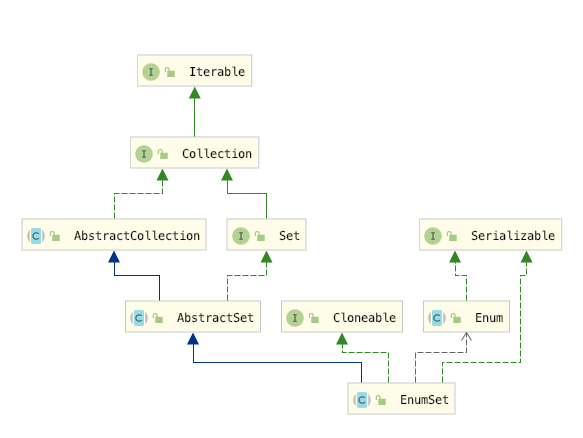
还是按照国际惯例,先看一下EnumSet 的说明书,其实往往很多时候你的困惑都在说明书里写着呢,但是在此之前我们还是先看一下它的继承关系,让我们有一个大概的认识
我们看到EnumSet是属于Java 集合框架下Set 家族的一员,继承了AbstractSet 抽象类和实现Cloneable, Serializable,Enum接口
/**
* A specialized {@link Set} implementation for use with enum types. All of
* the elements in an enum set must come from a single enum type that is
* specified, explicitly or implicitly, when the set is created.
* Set 的一种特殊的实现。不论是显式地还是隐式的,当EnumSets被创建之后,所有的元素都必须是来自同一个枚举变量的,这就是特殊所在
* Enum sets are represented internally as bit vectors. This representation is
* extremely compact and efficient. The space and time performance of this
* class should be good enough to allow its use as a high-quality, typesafe
* alternative to traditional <tt>int</tt>-based "bit flags." Even bulk
* operations (such as <tt>containsAll</tt> and <tt>retainAll</tt>) should
* run very quickly if their argument is also an enum set.
* EnumSet 内部是通过位向量来实现的,这种内部实现是极其紧凑和高效的。它在时间和空间上的高性能使其可以作为使用int来标识bit的高性能、类型安全的替代品
* <p>The iterator returned by the <tt>iterator</tt> method traverses the
* elements in their <i>natural order</i> (the order in which the enum
* constants are declared).
* EnumSet的iterator 方法返回的iterator 中的元素维持了自然顺序(枚举类型常量的声明顺序)
* The returned iterator is <i>weakly consistent</i>: it will never throw {@link ConcurrentModificationException}
* and it may or may not show the effects of any modifications to the set that
* occur while the iteration is in progress.
* 关于这一点就是说它不是快速失败的,如果在遍历的过程中发生了修改也不会抛出异常的(关于这一点上一篇文章中我们也提到了还进行了例子演示,以及原理说明)
* <p>Null elements are not permitted. Attempts to insert a null element
* will throw {@link NullPointerException}. Attempts to test for the
* presence of a null element or to remove one will, however, function
* properly.
*
* <P>Like most collection implementations, <tt>EnumSet</tt> is not
* synchronized. If multiple threads access an enum set concurrently, and at
* least one of the threads modifies the set, it should be synchronized
* externally. This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some
* object that naturally encapsulates the enum set. If no such object exists,
* the set should be "wrapped" using the {@link Collections#synchronizedSet}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access:
* 和大多数集合的实现一样,EnumSet 也不是同步的(线程安全的).
* 如果有多个线程在同时访问EnumSet并且有不止一个的线程在就该它,那就应该在它的外部加锁(操作之前)
* 一个典型的实现就是就是在一个对象上进行同步,如果不存在这样的对象你可以使用Collections.synchronizedSet方法获取一个该对象的线程安全的封装对象
* 这个操作做好是在它被创建的时候就执行,以防止其他线程对它意想不到的访问
*/
public abstract class EnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* EnumSet 元素的类型
*/
final Class<E> elementType;
/**
* 存储所有的枚举变量
*/
final Enum<?>[] universe;
private static Enum<?>[] ZERO_LENGTH_ENUM_ARRAY = new Enum<?>[0];
EnumSet(Class<E>elementType, Enum<?>[] universe) {
this.elementType = elementType;
this.universe = universe;
}
}
EnumSet 的使用
创建 EnumSet
为了创建一个EnumSet,我们必须先引入java.util.EnumSet ,和其他Set 的实现不一样,EnumSet 没有提供构造方法,这是因为EnumSet的实现是一个抽象类,所以我们必须使用EnumSet提供的静态方法来创建一个EnumSet
创建一个具有指定元素类型的空EnumSet。
EnumSet<E> noneOf(Class<E> elementType)
//创建一个指定元素类型并包含所有枚举值的EnumSet
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> allOf(Class<E> elementType)
// 创建一个包括枚举值中指定范围元素的EnumSet
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> range(E from, E to)
// 初始集合包括指定集合的补集
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> complementOf(EnumSet<E> s)
// 创建一个包括参数中所有元素的EnumSet
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e)
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2)
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3)
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4)
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5)
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E first, E... rest)
//创建一个包含参数容器中的所有元素的EnumSet
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> copyOf(EnumSet<E> s)
<E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> copyOf(Collection<E> c)
1. 使用 allOf(Size)
使用allof()方法创建一个包含指定枚举类型的全部枚举变量的EnumSet,所以和EnumMap 一样的是我们必须先要创建一个枚举类型
enum Size {
SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRALARGE
}
代码
@Test
public void create(){
EnumSet sizes=EnumSet.allOf(Size.class);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + sizes);
}
Output
EnumSet: [SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRALARGE]
Notice the statement,
EnumSet<Size> sizes = EnumSet.allOf(Size.class);
Size.class 代表了我们的参数是我们创建的枚举类型
2. 使用 noneOf(Class)
使用 noneOf()方法创建一个空的枚举集合
@Test
public void create(){
EnumSet sizes2=EnumSet.noneOf(Size.class);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + sizes2);
}
Output
Empty EnumSet : []
上面我们通过创建了一个空的枚举集合
注意: 我们只能插入的Size的枚举变量到该集合,其他类型的变量时不行的,因为我们的Set 的类型就是我们声明的枚举类型——Size
3. 使用 range(e1, e2)
使用 range() 方法创建一个 enum set 包含e1 和 e2 之间的枚举变量(包括e1 和 e2)
@Test
public void create(){
EnumSet sizes3=EnumSet.range(Size.MEDIUM,Size.EXTRALARGE);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + sizes3);
}
Output
EnumSet: [MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRALARGE]
这里我们就只包含了Size.MEDIUM,Size.EXTRALARGE之间的元素。
4. 使用 of(e1…)
使用 of() 方法创建包含指定枚举变量的EnumSet
@Test
public void create(){
EnumSet<Size> sizes4 = EnumSet.of(Size.SMALL, Size.LARGE);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + sizes4);
}
Output
EnumSet2: [SMALL, LARGE]
创建方法总结(noneOf)
noneOf 的实现细节
上面我们只是演示了不同的创建方法的含义,但是并没有说一些细节东西,其实所有的创建方法都是使用调用了noneOf() 方法的,
// allOf
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> allOf(Class<E> elementType) {
EnumSet<E> result = noneOf(elementType);
result.addAll();
return result;
}
// range
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> range(E from, E to) {
if (from.compareTo(to) > 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
EnumSet<E> result = noneOf(from.getDeclaringClass());
result.addRange(from, to);
return result;
}
// of
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e1 ... ) {
EnumSet<E> result = noneOf(e1.getDeclaringClass());
result.add(e1);
result.add(e2);
return result;
}
可以看出所有的方法都调用了noneOf 方法,而且前面我们说EnumSet 是一个抽象类,所以EnumSet没有给我们提供构造方法来创建对象,而是使用静态方法来创建对象,其实到这里我们应该可以猜到EnumSet应该有实现类的,不然它给我们返回什么对象呢?那我们就看一下noneOf里面到底发生了什么
/**
* Creates an empty enum set with the specified element type.
* 使用指定的枚举类型创建一个空的EnumSet
* @param <E> The class of the elements in the set
* @param elementType the class object of the element type for this enum set
* @return An empty enum set of the specified type.
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>elementType</tt> is null
*/
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> noneOf(Class<E> elementType) {
Enum<?>[] universe = getUniverse(elementType);
if (universe == null)
throw new ClassCastException(elementType + " not an enum");
if (universe.length <= 64)
return new RegularEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
else
return new JumboEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
}
其实EnumSet有两个实现类RegularEnumSet、JumboEnumSet,当枚举类型的枚举变量小于等于64的时候使用RegularEnumSet,否则就使用JumboEnumSet,所以大多时候,我们用的都是RegularEnumSet。
我们注意到上面在noneOf方法中都调用了 getUniverse(elementType),我们看一下这个方法都干了什么,注释信息说这个方法返回了枚举中的全部枚举常量,并且这个返回的结果会被缓存下来,然后被所有调用它的方法共享。
/**
* Returns all of the values comprising E.
* The result is uncloned, cached, and shared by all callers.
*/
private static <E extends Enum<E>> E[] getUniverse(Class<E> elementType) {
return SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess()
.getEnumConstantsShared(elementType);
}
SharedSecrets 是一个比较底层的类了,我们可以不用太关注,只需知道它可以让我我们直接去访问类对象的一些信息即可,这里就是根据枚举类型的Class 信息获取到了全部的枚举常量。
接下来我们再说一下,为什么上面的判断标准是64,而不是其他的数字呢
class RegularEnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> extends EnumSet<E> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3411599620347842686L;
/**
* Bit vector representation of this set. The 2^k bit indicates the
* presence of universe[k] in this set.
*/
private long elements = 0L;
}
class JumboEnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> extends EnumSet<E> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 334349849919042784L;
/**
* Bit vector representation of this set. The ith bit of the jth
* element of this array represents the presence of universe[64*j +i]
* in this set.
*/
private long elements[];
}
RegularEnumSet使用的是一个long属性来存储,而JumboEnumSet是用一个long的数组来存储,这也是为什么和64做比较的原因,因为long只有64位,最多标识64个枚举值,多的只能用数组来存储,
但是我们注意到这两个类我们是没有办法使用的,因为它不是public 类,也就是说只能在同一包下面访问。
其他静态方法是如何通过noneOf返回含有元素的EnumSet
我们还是回到这些静态方法上,我们这里就以of方法为例进行探索
// of
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> of(E e1 ... ) {
// 我们知道noneOf 返回的是一个空的EnumSet
EnumSet<E> result = noneOf(e1.getDeclaringClass());
// 然后发现是将特定的元素添加到了集合中去的,其他方法特使同理的
result.add(e1);
result.add(e2);
return result;
}
EnumSet 添加元素
add()- 添加指定的枚举变量到EnumSetaddAll()添加指定集合中的元素到EnumSet
@Test
public void add() {
// Creating an EnumSet using allOf()
EnumSet<Size> sizes1 = EnumSet.allOf(Size.class);
// Creating an EnumSet using noneOf()
EnumSet<Size> sizes2 = EnumSet.noneOf(Size.class);
// Using add method
sizes2.add(Size.MEDIUM);
System.out.println("EnumSet Using add(): " + sizes2);
// Using addAll() method
sizes2.addAll(sizes1);
System.out.println("EnumSet Using addAll(): " + sizes2);
}
Output
EnumSet using add(): [MEDIUM]
EnumSet using addAll(): [SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRALARGE]
这里我们就以add 方法为例说一下它是如何通过位向量实现添加操作的,其他方法同理
/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the set changed as a result of the call
*
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>e</tt> is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
typeCheck(e);
long oldElements = elements;
elements |= (1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal());
return elements != oldElements;
}
add操作实际是用位运算,将这个long值对应你传入的枚举值的下标的那个bit位改成1,比如我传入的是Size.MEDIUM, 对应的ordinal是1,则是将elements的bit位中的第2位改成1,
EnumSet 获取元素
为了获取EnumSet中的元素我们可以使用iterator() 方法
@Test
public void access() {
// Creating an EnumSet using allOf()
EnumSet<Size> sizes = EnumSet.allOf(Size.class);
Iterator<Size> iterate = sizes.iterator();
System.out.print("EnumSet: ");
while(iterate.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterate.next());
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
Output
EnumSet: SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRALARGE,
EnumSet 删除元素
remove()- 删除指定元素removeAll()- 删除全部元素
@Test
public void remove() {
// Creating EnumSet using allOf()
EnumSet<Size> sizes = EnumSet.allOf(Size.class);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + sizes);
// Using remove()
boolean value1 = sizes.remove(Size.MEDIUM);
System.out.println("Is MEDIUM removed? " + value1);
System.out.println(sizes);
// Using removeAll()
boolean value2 = sizes.removeAll(sizes);
System.out.println("Are all elements removed? " + value2);
System.out.println(sizes);
}
Output
EnumSet: [SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRALARGE]
Is MEDIUM removed? true
[SMALL, LARGE, EXTRALARGE]
Are all elements removed? true
[]
EnumSet 的其他方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
copyOf() |
Creates a copy of the EnumSet |
contains() |
Searches the EnumSet for the specified element and returns a boolean result |
isEmpty() |
Checks if the EnumSet is empty |
size() |
Returns the size of the EnumSet |
clear() |
Removes all the elements from the EnumSet |
EnumSet的使用场景
EnumSet 相比 HashSet, TreeSet 提供了一个更加高效的方式来存储枚举变量。
一个EnumSet 对象只存储一个枚举类型的变量,因此JVM已经提前知道所有可能的元素,这也就是为什么EnumSet 内部使用的是一系列的Bits 来实现的,Bits标识了特定位置上的枚举变量是否存在
EnumSet最有价值的是其内部实现原理,采用的是Bit 来实现的,它体现出来的是一种高效的数据处理方式,而且这种思想在很多地方都用的到,例如计算UV 或者在一些表示有没有或者是不是的场景中,比较有名的就是布隆过滤器
备注 很多人也将其称为位向量,既然是向量那就可以计算。
总结
- EnumSet 是一个用来存储枚举常量的集合,其底层是通过位向量实现的,所以有比较好的一个性能。
- 其实EnumSet有两个实现类RegularEnumSet、JumboEnumSet,当枚举类型的枚举常量的数目等于64的时候使用RegularEnumSet,否则就使用JumboEnumSet,但是我们注意到这两个类我们是没有办法使用的,因为它是protected修饰的(省略了),也就是说只能在同一包下面访问。这两个子类只是对于EnumSet的接口的实现方式不同,不同的地方就是根据调用方的Enum的值得个数来决定的,对于调用方来说是不需要关心这些细节的,所以这两个子类只需要是protected就可以,并且通过静态工厂类返回给调用方,以后如果有更牛逼的算法出现时,只需要再扩展出一个子类就可以了,而调用方是无感知的,比较符合开闭原则。
- 所有的创建创建方法其实都是调用了noneOf 创建方法,先创建一个空的EnumSet(RegularEnumSet或者JumboEnumSet),然后通过添加元素的方式将数据添加进去。