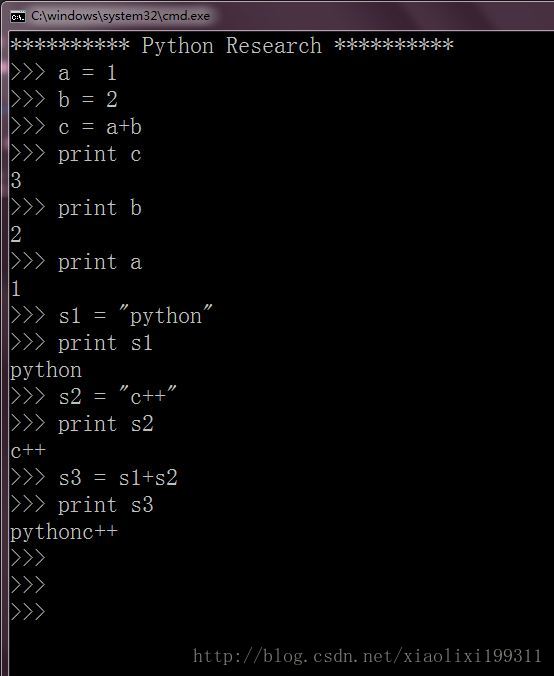
SmallPython
SmallPython介绍
只建立了python的int和string的构造以及相加和打印。虽然很
small,但是还是可以看到C基于对象的编程手法和python的内部对象构造的过程
PyObject、PyTypeObject、PyIntObject、PyStrObject、PyDictObject
PyObject
#ifndef _PYOBJECT_H_
#define _PYOBJECT_H_
#define PyObject_HEAD \
int refCount; \
struct tagPyTypeObject *type
#define PyObject_HEAD_INIT(typePtr)\
0, typePtr
typedef struct tagPyObject
{
PyObject_HEAD;
}PyObject;
#endifPyTypeObject
#ifndef _PYTYPEOBJECT_H_
#define _PYTYPEOBJECT_H_
#include "PyObject.h"
//definition of PyTypeObject
typedef void(*PrintFun)(PyObject* object);
typedef PyObject* (*AddFun)(PyObject* left, PyObject* right);
typedef long(*HashFun)(PyObject* object);
typedef struct tagPyTypeObject
{
PyObject_HEAD;
char* name;
PrintFun print;
AddFun add;
HashFun hash;
}PyTypeObject;
PyTypeObject PyType_Type = { PyObject_HEAD_INIT(0), "type", 0, 0, 0 };
#endifPyIntObject
#ifndef _PYINTOBJECT_H_
#define _PYINTOBJECT_H_
#include "PyObject.h"
#include "PyTypeObject.h"
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct tagPyIntObject
{
PyObject_HEAD;
int value;
}PyIntObject;
PyObject* PyInt_Create(int value);
static void int_print(PyObject* object)
{
PyIntObject* intObject = (PyIntObject*)object;
printf("%d\n", intObject->value);
}
static PyObject* int_add(PyObject* left, PyObject* right)
{
PyIntObject* leftInt = (PyIntObject*)left;
PyIntObject* rightInt = (PyIntObject*)right;
PyIntObject* result = (PyIntObject*)PyInt_Create(0);
if (result == NULL)
{
printf("We have no enough memory!!\n");
}
else
{
result->value = leftInt->value + rightInt->value;
}
return (PyObject*)result;
}
static long int_hash(PyObject* object)
{
return (long)((PyIntObject*)object)->value;
}
PyTypeObject PyInt_Type =
{
PyObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type),
"int",
int_print,
int_add,
int_hash
};
PyObject* PyInt_Create(int value)
{
PyIntObject* object = new PyIntObject;
object->refCount = 1;
object->type = &PyInt_Type;
object->value = value;
return (PyObject*)object;
}
#endifPyStrObject
#ifndef _PYSTROBJECT_H_
#define _PYSTROBJECT_H_
#include "PyObject.h"
#include "PyTypeObject.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct tagPyStrObject
{
PyObject_HEAD;
int length;
long hashValue;
char value[50];
}PyStringObject;
PyObject* PyStr_Create(const char* value);
static void string_print(PyObject* object)
{
PyStringObject* strObject = (PyStringObject*)object;
printf("%s\n", strObject->value);
}
static long string_hash(PyObject* object)
{
PyStringObject* strObject = (PyStringObject*)object;
register int len;
register unsigned char *p;
register long x;
if (strObject->hashValue != -1)
return strObject->hashValue;
len = strObject->length;
p = (unsigned char *)strObject->value;
x = *p << 7;
while (--len >= 0)
x = (1000003 * x) ^ *p++;
x ^= strObject->length;
if (x == -1)
x = -2;
strObject->hashValue = x;
return x;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
static PyObject* string_add(PyObject* left, PyObject* right)
{
PyStringObject* leftStr = (PyStringObject*)left;
PyStringObject* rightStr = (PyStringObject*)right;
PyStringObject* result = (PyStringObject*)PyStr_Create(nullptr);
if (result == NULL)
{
printf("We have no enough memory!!\n");
}
else
{
strcpy_s(result->value, leftStr->value);
strcat_s(result->value, rightStr->value);
}
return (PyObject*)result;
}
PyTypeObject PyString_Type =
{
PyObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type),
"str",
string_print,
string_add,
string_hash
};
PyObject* PyStr_Create(const char* value)
{
PyStringObject* object = new PyStringObject;
object->refCount = 1;
object->type = &PyString_Type;
object->length = (value == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(value);
object->hashValue = -1;
memset(object->value, 0, 50);
if (value != NULL)
{
strcpy_s(object->value, value);
}
return (PyObject*)object;
}
#endifPyDictObject
#ifndef _PYDICTOBJECT_H_
#define _PYDICTOBJECT_H_
#include "PyObject.h"
#include "PyTypeObject.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include <map>
using std::map;
typedef struct tagPyDictObject
{
PyObject_HEAD;
map<long, PyObject*> dict;
}PyDictObject;
PyObject* PyDict_GetItem(PyObject* target, PyObject* key)
{
long keyHashValue = (key->type)->hash(key);
map<long, PyObject*>& dict = ((PyDictObject*)target)->dict;
map<long, PyObject*>::iterator it = dict.find(keyHashValue);
map<long, PyObject*>::iterator end = dict.end();
if (it == end)
{
return nullptr;
}
return it->second;
}
int PyDict_SetItem(PyObject* target, PyObject* key, PyObject* value)
{
long keyHashValue = (key->type)->hash(key);
PyDictObject* dictObject = (PyDictObject*)target;
(dictObject->dict)[keyHashValue] = value;
return 0;
}
//function for PyDict_Type
static void dict_print(PyObject* object)
{
PyDictObject* dictObject = (PyDictObject*)object;
printf("{\n");
map<long, PyObject*>::iterator it = (dictObject->dict).begin();
map<long, PyObject*>::iterator end = (dictObject->dict).end();
for (; it != end; ++it)
{
//print key
printf("%d : ", it->first);
//print value
PyObject* value = it->second;
(value->type)->print(value);
printf(",\n");
}
printf("}\n");
}
PyTypeObject PyDict_Type =
{
PyObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type),
"dict",
dict_print,
0,
0
};
PyObject* PyDict_Create()
{
//create object
PyDictObject* object = new PyDictObject;
object->refCount = 1;
object->type = &PyDict_Type;
return (PyObject*)object;
}
#endifEXC
#ifndef _EXC_H_
#define _EXC_H_
#include "PyObject.h"
#include "PyIntObject.h"
#include "PyDictObject.h"
#include "PyStrObject.h"
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
PyDictObject LocalEnvironment = { 1, &PyDict_Type, map<long, PyObject*>() };
PyDictObject* m_LocalEnvironment = &LocalEnvironment;
void ExcutePrint(string symbol);
PyObject* GetObjectBySymbol(string& symbol);
void ExcuteAdd(string& target, string& source);
void ExcuteCommand(string& command)
{
string::size_type pos = 0;
if ((pos = command.find("print ")) != string::npos)
{
ExcutePrint(command.substr(6));
}
else if ((pos = command.find(" = ")) != string::npos)
{
string target = command.substr(0, pos);
string source = command.substr(pos + 3);
ExcuteAdd(target, source);
}
}
int IsSourceAllDigit(string& str){
int len = str.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
if (!isdigit(str[i])){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
void ExcuteAdd(string& target, string& source)
{
string::size_type pos;
if (IsSourceAllDigit(source))
{
PyObject* intValue = PyInt_Create(atoi(source.c_str()));
PyObject* key = PyStr_Create(target.c_str());
PyDict_SetItem((PyObject*)m_LocalEnvironment, key, intValue);
}
else if (source.find("\"") != string::npos)
{
PyObject* strValue = PyStr_Create(source.substr(1, source.size() - 2).c_str());
PyObject* key = PyStr_Create(target.c_str());
PyDict_SetItem((PyObject*)m_LocalEnvironment, key, strValue);
}
else if ((pos = source.find("+")) != string::npos)
{
PyObject* leftObject = GetObjectBySymbol(source.substr(0, pos));
PyObject* rightObject = GetObjectBySymbol(source.substr(pos + 1));
if (leftObject != NULL && rightObject != NULL && leftObject->type == rightObject->type)
{
PyObject* resultValue = (leftObject->type)->add(leftObject, rightObject);
PyObject* key = PyStr_Create(target.c_str());
PyDict_SetItem((PyObject*)m_LocalEnvironment, key, resultValue);
}
(m_LocalEnvironment->type)->print((PyObject*)m_LocalEnvironment);
}
}
PyObject* GetObjectBySymbol(string& symbol)
{
PyObject* key = PyStr_Create(symbol.c_str());
PyObject* value = PyDict_GetItem((PyObject*)m_LocalEnvironment, key);
//是不是应该加上delete
delete key;
if (value == NULL)
{
cout << "[Error] : " << symbol << " is not defined!!" << endl;
return nullptr;
}
return value;
}
void ExcutePrint(string symbol)
{
PyObject* object = GetObjectBySymbol(symbol);
if (object != NULL)
{
PyTypeObject* type = object->type;
type->print(object);
}
}
#endif
main
#include "exc.h"
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char* info = "********** Python Research **********\n";
char* prompt = ">>> ";
string m_Command;
int main()
{
cout << info;
cout << prompt;
while (getline(cin, m_Command)){
if (m_Command.size() == 0){
cout << prompt;
continue;
}
else if (m_Command == "exit"){
return 0;
}
else{
ExcuteCommand(m_Command);
}
cout << prompt;
}
//资源是不是应该回收
return 0;
}