本文首发于公众号:【事件相机】,CVPR2021中的事件相机研究
本文整理了CVPR 2021年中关于事件相机的相关工作(从openaccess上关键词查找得到的,可能有遗漏),并作简要介绍。能力有限,难免理解错误或理解理解不到位,毕竟能发CVPR的大佬肯定比我强。重在分享,如有错误和不同见解,请及时提出。谢谢。
Spatiotemporal Registration for Event-based Visual Odometry [1]
主要贡献:提出了一种新的数据关联方式(Data Association)。所谓Data Association,缩写DA,在事件相机中可以理解为:如果某些事件是由同一个事件源产生的,那么这些事件是关联的。传统的方法,多采用最大对比度的方式进行DA [A1],例如将所有event通过一个warp到某个图像平面然后评估图像的对比度/熵等某些指标,来优化warp参数,最终获得DA与合理的参数。但此文作者指出,原始方法计算量极大,故提出了另一种方法:Spatiotemporal Registration
下面一张图就能解释什么叫“时空回归”。左侧是上面提到的最大化对比度的方法,把每个像素都warp到一起。右面是本文的时空回归,可以看出是把前一半时刻events按照假定参数变化到后一半时刻,来判断重合度。这种批量的方式计算量会小很多。
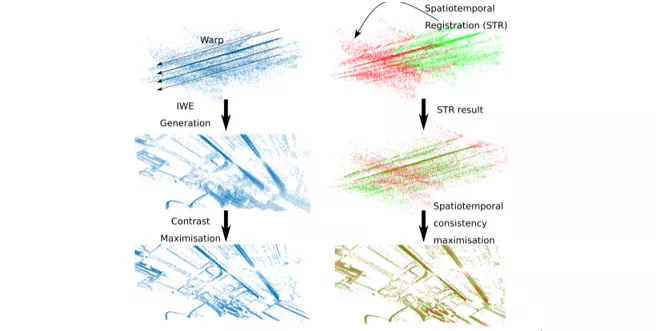 文中详细推导了计算方法和复杂度,表明优于原来的方式。但需要指出,该方法是仅限于纯旋转,不存在平移。那什么情况下是纯旋转问题呢,作者指出在视频消抖、全景重建、形体跟踪是这些纯旋转问题。
文中详细推导了计算方法和复杂度,表明优于原来的方式。但需要指出,该方法是仅限于纯旋转,不存在平移。那什么情况下是纯旋转问题呢,作者指出在视频消抖、全景重建、形体跟踪是这些纯旋转问题。
论文提到了Odometry,利用这种方法可以同时估计相机运动(旋转)参数,就实现了Odom,当然是纯旋转的。那这种我觉得不能算是完整的Odom。
Back to Event Basics: Self-Supervised Learning of Image Reconstruction for Event Cameras via Photometric Constancy [2]
这是一篇关于图像重建的工作,主要亮点为:自监督训练重建网络。我们知道重建系列景点工作E2VID[A2]和 FireNet[A3],都是有监督的训练。那不禁思考,如何“自监督”。自监督不是无监督,是指框架通过自身产生一些参考值来训练所要训练的神经网络。那究竟是用什么自监督的?
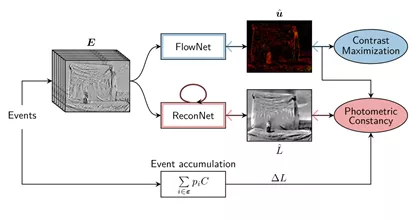
上图是整个训练框架。其中FlowNet是光流预测网络,ReconNet是重建网络,下面的Event Accumulation是带极性的时间积累图。黑色箭头是正向传递过程,得到重建的图后通过,与积累图和光流图比较Photometric Constancy得到误差,反向传播优化重建网络。简单理解为什么这三个可以为什么可以实现自监督:如果重建的图是对的,那么重建图+光流方向,就可以得到理论上产生的事件,那这个应该和时间积累图能够对应。由此实现了自监督。
具体来说,光流预测网络FlowNet可以采用最出名的Ev-FlowNet[A4],也可以用其他的比如本文作者提出的FireFlowNet;而重建网络可以采用E2VID或FireNet等,不做展开。
EvDistill: Asynchronous Events to End-task Learning via Bidirectional Reconstruction-guided Cross-modal Knowledge Distillation [3]
本文关于知识蒸馏,讨论如何用传统图像数据来训练Event数据。我对知识蒸馏、跨模态相关知识不太了解,在这里只能简单摘抄翻译。
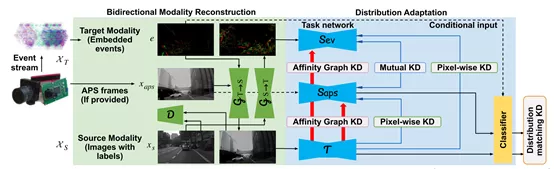
跨模态训练时,一般假设两个模态数据的标签都是已知的,或两个模态的数据是paired的。但这两个对event数据和image数据来说都不现实。作者这里提出了一个“bidirectional modality reconstruction (BMR)”,双向模态模块,从事件重建图像,从图像重建事件,实现了数据的关联。之后呢便通过强大的传统图像的神经网络,teach事件数据这个student网络。本文实现的是一个分割任务。
EventZoom: Learning to Denoise and Super Resolve Neuromorphic Events [4]
提出了降噪超分网络,本文的特点是“EventZoom is trained in anoise-to-noise fashion where the two ends of the network are unfiltered noisyevents, enforcing noise-free event restoration.” 这句话我没有特别理解,认为是训练一个两端都是带噪声的event网络,但实现了降噪。我对降噪和超分辨率也不太了解,所以可能此文理解也有偏差。

比较有新意的一点是,虽然采用了常用的“大屏幕动图”方式,本文录屏时同时录制了不同分辨率的图像。那这样我们同时得到了低分辨率和高分辨率的对应,再在低分辨率事件数据上加一定程度的噪声,在训练时左侧放低分辨率+噪声的数据,右侧放最大分辨率+无人工噪声的数据,训练了这个EventZoom。
Time Lens: Event-based Video Frame Interpolation [5]
视频流插帧的研究。文中指出,之前的插帧方法多采用”synthesis-based”方法,即”predicted frame residuals are directly applied to the key-frames”,但存在鬼影和低纹理区域效果差。本文提出一种”warping-based”方法,并设计了完整的framework如下。
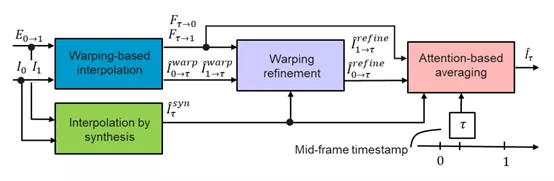
warping-based差值我通俗的理解为,用event估计出光流后,我就可以将key-frame的每个点根据光流情况预测出在某个时刻的图像。这个完整的framework首先经过这个模块得到一个warping预测图并细化,再通过synthesis-based插值法得到一个图,最终两个图经过一个基于注意力机制(简单来说就是权重)的融合得到插值结果。
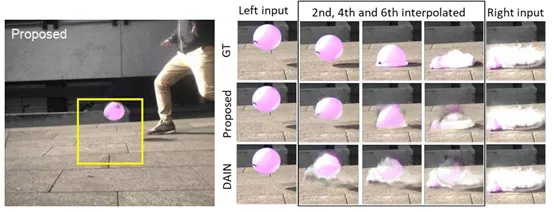
(从实验结果可以看出,能够“脑补”水球落地前到破裂之间的图像)
Event-based Bispectral Photometry using Temporally Modulated Illumination [6]
利用事件相机做光谱分析一类的吧,完全不懂。贴个摘要算了:
Analysis of bispectral difference plays acritical role in various applications that involve rays propagating in a lightabsorbing medium. In general, the bispectral difference is obtained bysubtracting signals at two individual wavelengths captured by ordinary digitalcameras, which tends to inherit the drawbacks of conventional cameras indynamic range, response speed and quantization precision. In this paper, wepropose a novel method to obtain a bispectral difference image using an eventcamera with temporally modulated illumination. Our method is rooted in a keyobservation on the analogy between the bispectral photometry principle of theparticipating medium and the event generating mechanism in an event camera. Bycarefully modulating the bispectral illumination, our method allows to read outthe bispectral difference directly from triggered events. Experiments using aprototype imaging system have verified the feasibility of this novel usage ofevent cameras in photometry based vision tasks, such as 3D shape reconstructionin water.
Event-based Synthetic Aperture Imaging with a Hybrid Network [7]
这篇文章场景比较有趣啦,虽然也是重建,但相机前面有一些遮挡,属于合成孔径成像(Syntheticaperture imaging)相关内容。先看图:
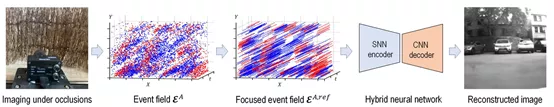
图片就说清楚实在干什么了,核心是网络中的编解码器,有趣的是编码器采用了SNN,现在SNN用的还不是很多。感兴趣的细看论文吧。
Turning Frequency to Resolution: Video Super-resolution via Event Cameras [8]
文章发现图像超分辨率的质量和帧率有关,所以用Event去提高帧率然后超分。个人没有太看懂文章,和上面的几篇相比没有眼前一亮的感觉,就不多做介绍了。
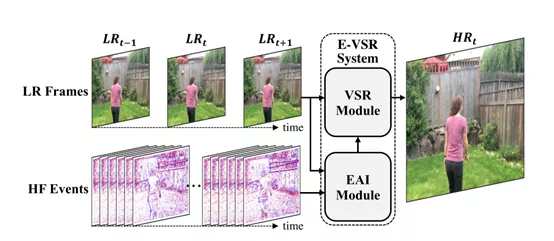
Learning to Reconstruct High Speed and High Dynamic Range Videos from Events [9]
看名字就知道是在干什么了。我Deep Learning不熟,所以文章内容并不是very impressive。
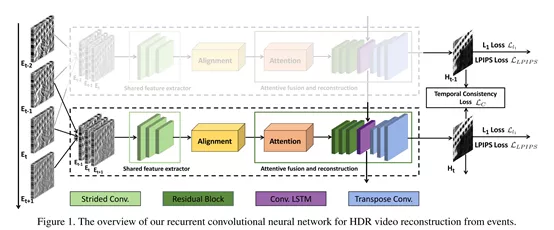
Indoor Lighting Estimation using an Event Camera [10]
这工作比较有趣,通过事件相机来估计室内环境中光源的位置。
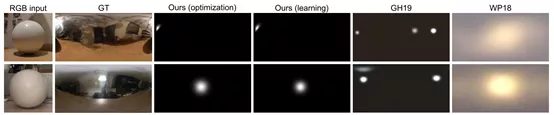
利用事件相机对准一个球体,根据球体表面产生的event,估计房间中的光源位置。涉及到了光学模型和神经网络,方法不做展开。
作者指出,目前有一些局限性,即必须要求室内从黑暗环境中开灯,由事件相机记录下开灯的整个过程,而且只能有一个光源。虽然有这么多局限性,但我感觉挺有意思的,查了下估计室内光源有什么用,好像对于VR/AR场景比较有帮助。
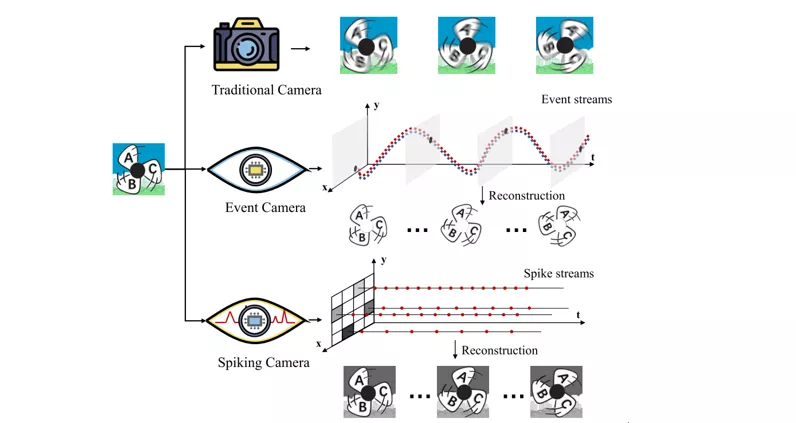
High-speed Image Reconstruction through Short-term Plasticity for Spiking Cameras [11]
这篇文章讲的其实并不是Event Camera,而是Spiking Camera。有点儿像但不一样,我可能有机会深入研究以后再介绍吧。
总结
CVPR2021中对Event Camera的研究,主要集中视频领域,包括重建[2][7][9]、插值[5]、降噪超分[4],其他的有数据处理[1]、光照估计[10]、知识蒸馏[3]、光谱分析[6]。其中除了[1][6]外,都是Learning-based的方法,不禁感慨DL真的是到处扩张。
参考文献:
[1] Daqi Liu; Alvaro Parra; Tat-Jun Chin:Spatiotemporal Registration for Event-Based Visual Odometry.
[2] Federico Paredes-Valles; Guido C. H. E.de Croon: Back to Event Basics: Self-Supervised Learning of ImageReconstruction for Event Cameras via Photometric Constancy.
[3] Lin Wang; Yujeong Chae; Sung-Hoon Yoon;Tae-Kyun Kim; Kuk-Jin Yoon: EvDistill: Asynchronous Events To End-Task Learningvia Bidirectional Reconstruction-Guided Cross-Modal Knowledge Distillation.
[4] Peiqi Duan; Zihao W. Wang; Xinyu Zhou;Yi Ma; Boxin Shi: EventZoom: Learning To Denoise and Super Resolve NeuromorphicEvents.
[5] Stepan Tulyakov; Daniel Gehrig;Stamatios Georgoulis; Julius Erbach; Mathias Gehrig; Yuanyou Li; DavideScaramuzza: Time Lens: Event-Based Video Frame Interpolation.
[6] Tsuyoshi Takatani; Yuzuha Ito; AyakaEbisu; Yinqiang Zheng; Takahito Aoto: Event-Based Bispectral Photometry UsingTemporally Modulated Illumination.
[7] Xiang Zhang; Wei Liao; Lei Yu; WenYang; Gui-Song Xia: Event-Based Synthetic Aperture Imaging With a HybridNetwork.
[8] Yongcheng Jing; Yiding Yang; XinchaoWang; Mingli Song; Dacheng Tao: Turning Frequency to Resolution: VideoSuper-Resolution via Event Cameras.
[9] Yunhao Zou; Yinqiang Zheng; TsuyoshiTakatani; Ying Fu: Learning To Reconstruct High Speed and High Dynamic RangeVideos From Events.
[10] Zehao Chen; Qian Zheng; Peisong Niu;Huajin Tang; Gang Pan: Indoor Lighting Estimation Using an Event Camera.
[11] Yajing Zheng; Lingxiao Zheng; ZhaofeiYu; Boxin Shi; Yonghong Tian; Tiejun Huang: High-Speed Image ReconstructionThrough Short-Term Plasticity for Spiking Cameras.
[A1] Guillermo Gallego, Mathias Gehrig, andDavide Scaramuzza. Focus is all you need: Loss functions for event-basedvision. In Proceedings ofthe IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and PatternRecognition, pages 12280–12289, 2019.
[A2] H. Rebecq, R. Ranftl, V. Koltun, andD. Scaramuzza, “High speed and high dynamic range video with an event camera,”IEEE Trans. on Pattern Anal. and Mach. Intell., 2019.
[A3] C. Scheerlinck, H. Rebecq, D. Gehrig,N. Barnes, R. Mahony, and D. Scaramuzza, “Fast image reconstruction with anevent camera,” in IEEE Winter Conf. Appl. Comput. Vis. (WACV), 2020, pp.156–163.
[A4] A. Z. Zhu and L. Yuan, “EV-FlowNet:Self-supervised optical flow estimation for event-based cameras,” in Robot.:Science and Systems (RSS), 2018.
欢迎关注微信公众号【事件相机】,分享和交流事件相机的相关研究与应用。
公众号后台回复:CVPR2021,下载本文介绍的论文。
