ZB is playing a card game where the goal is to make straights. Each card in the deck has a number between 1 and M(including 1 and M). A straight is a sequence of cards with consecutive values. Values do not wrap around, so 1 does not come after M. In addition to regular cards, the deck also contains jokers. Each joker can be used as any valid number (between 1 and M, including 1 and M).
You will be given N integers card[1] .. card[n] referring to the cards in your hand. Jokers are represented by zeros, and other cards are represented by their values. ZB wants to know the number of cards in the longest straight that can be formed using one or more cards from his hand.
Input
The first line contains an integer T, meaning the number of the cases.
For each test case:
The first line there are two integers N and M in the first line (1 <= N, M <= 100000), and the second line contains N integers card[i] (0 <= card[i] <= M).
Output
For each test case, output a single integer in a line – the longest straight ZB can get.
Sample Input
2
7 11
0 6 5 3 0 10 11
8 1000
100 100 100 101 100 99 97 103
Sample Output
5
3
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 10;
int a[MAXN], b[MAXN], sum[MAXN];
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
int n, m;
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
memset(b, 0, sizeof(b));
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
int cnt = 0, ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
b[a[i]] = 1;
if(a[i] == 0) cnt++;
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
if(b[i]) ans++;
sum[i] = ans;
}
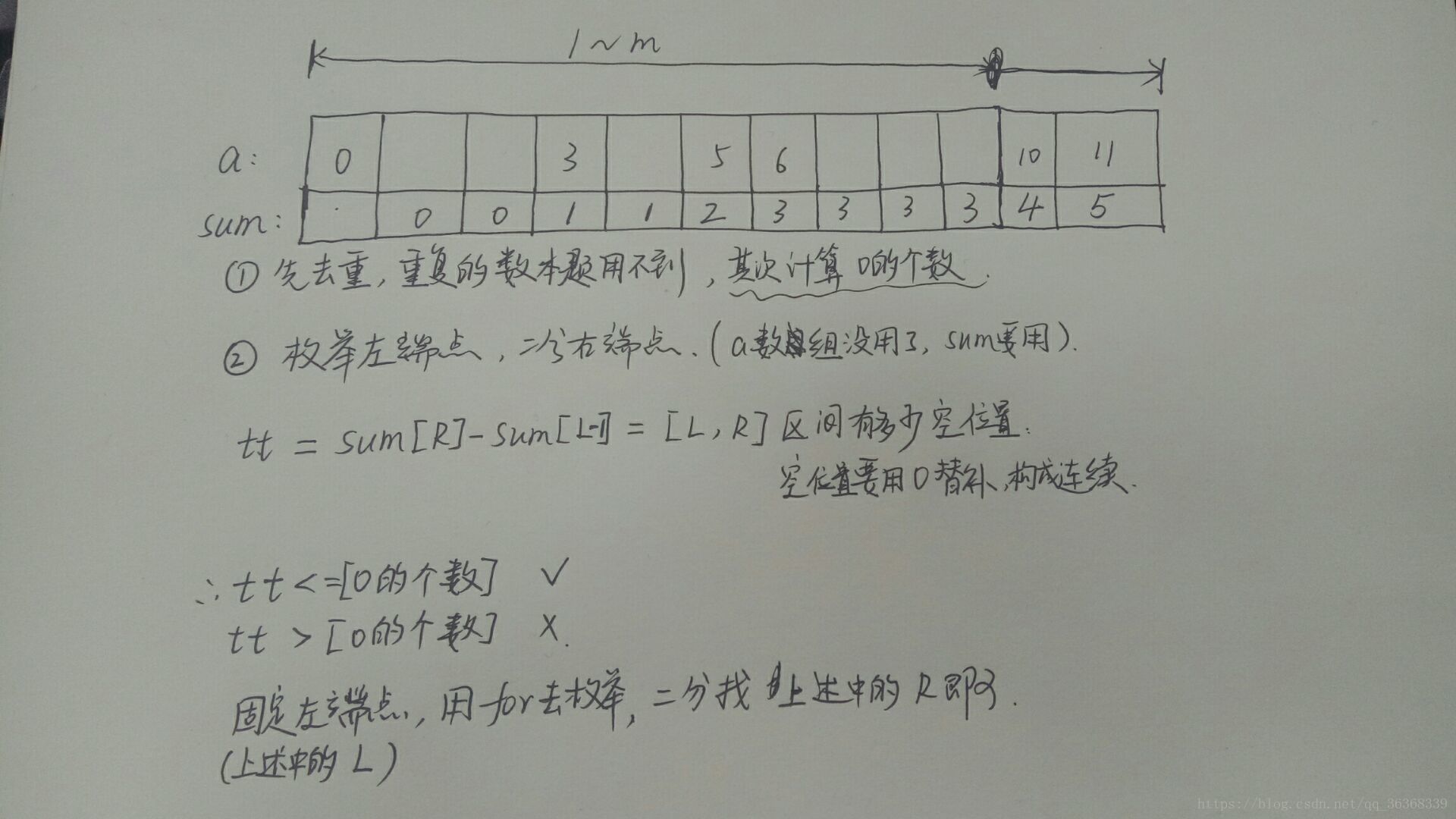
int maxn = 1;//注意这个点
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int L = i, R = m + 1;
while(R - L > 1) {
int mid = (L + R) >> 1;
int tt = (mid - i + 1 - sum[mid] + sum[i - 1]);
if(tt <= cnt) {
maxn = max(maxn, mid - i + 1);
L = mid;
}
else R = mid;
}
}
printf("%d\n", maxn);
}
return 0;
}下面我用树状数组写的,第一发超时,第二发优化掉常数,625ms险过,有意思了。。。
对这种静态查值,没必要用数据结构优化,动态的更新比较好用。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 10;
int a[MAXN], b[MAXN], s[MAXN];
int n, m;
inline int lowbit(int x) {
return x & (-x);
}
inline int update(int i, int x) {
while(i <= m) {
s[i] += x;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
inline int query(int x) {
int sum = 0;
while(x > 0) {
sum += s[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return sum;
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
memset(b, 0, sizeof(b));
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
int cnt = 0, ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(a[i] == 0) cnt++;
if(b[a[i]] || !a[i]) continue;
b[a[i]] = 1;
update(a[i], 1);
}
int maxn = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int L = i, R = m + 1;
int ans = query(i - 1);
while(R - L > 1) {
int mid = (L + R) >> 1;
//int tt = (mid - i + 1 - (query(mid) - query(i - 1))); //这样写会超时,优化常数600ms过了;
int tt = (mid - i + 1 - (query(mid) - ans));
if(tt <= cnt) {
maxn = max(maxn, mid - i + 1);
L = mid;
}
else R = mid;
}
}
printf("%d\n", maxn);
}
return 0;
}