Tinyalsa->Alsa Driver Flow
一、概述
前面分析了 Linux 内核中如何写一个简单的 ALSA 驱动,创建 snd_card,但是没讲解在应用层该如何调用来完成对底层硬件的操作。Linux ALSA 在内核层提供了 alsa-driver,在应用层提供了 alsa-lib,应用程序只需要调用 alsa-lib 提供的 API 即可完成对底层硬件的操作。但由于 ALSA 架构太过于庞大,对于嵌入式设备而言很多功能用不到,且会增加功耗,所以 Android 采用了精简后的 tinyalsa。
二、Tinyalsa
Android 中使用 tinyalsa 控制管理所有模式的音频通路,也可以使用 tinyalsa 提供的工具进行查看、调试。
Tinyalsa 源码位于 android 源码目录下 external/tinyalsa,可以使用 mmm 命令编译,mmm external/tinyalsa
编译 tinyalsa 后会生成四个小工具:
- tinymix
- tinyplay
- inycap
- inypcminfo
2.1 tinypcminfo
tinypcminfo 用于查看 pcm 通道的相关信息,如 PCM 采样率,Channels,采样点数等信息。
tinypcminfo -D <cardx>
其中 -D 后边跟的参数为声卡,可以通过 /proc/asound/cards 查看
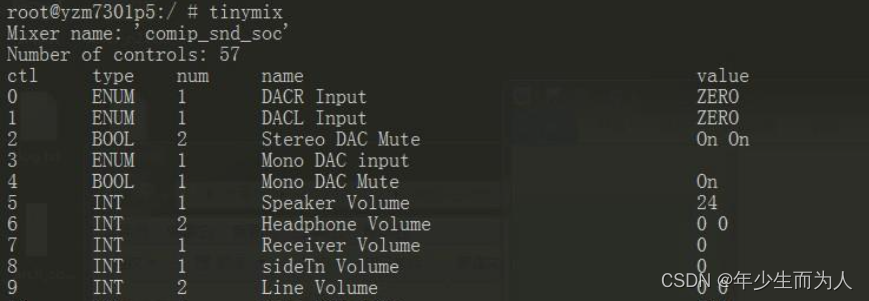
2.2 tinymix
1)tinymix 可以查看系统的音频控件,可直接执行 tinymix 进行查看;
2)tinymix 可以手动设置控件的值,控件可通过 tinymix 查看,或者通过 mixer_paths.xml 查看。
tinymix -help
tinymix [option] [control name/#] [value to set]
options:
--device|-D <cardx>:use the given card # instead of 0.
--all-value|-a:show all possible values/rangs for control.
---tabs-only|-t:separate all columns/values with tabs.
--value-only|-v:show only the value for the selected control.
2.3 tinyplay
tinyplay 是一个简易的音乐播放器,一般用于播放测试。
可以直接进行播放 wav 格式文件,在播放前需要先使用 tinymix 进行相关控件的设置。
tinyplay file.wav [-D card] [-d device] [-p period_size] [-n n_periods]
2.4 tinycap
tinycap 是一个简易的录音软件,一般用于录音测试。
使用之前也需要先设置录音相关的控件,设置好控件后,执行 tinycap xxx.wav 即可将音频录制到 xxx.wav 中。
tinycap file.wav [-D card] [-d device] [-c channels] [-r rate] [-b bits] [-p period_size] [-n n_periods] [-T capture time]
三、Tinyalsa->alsa driver flow 分析
本节主要讲解 tinyalsa 播放音频是如何实现对音频控件控制以及播放的。
3.1 tinymix 配置通路 path
对于使用 tinyalsa 播放的时候,通常需要先通过 tinymix 配置通路,如 mixer,mux,volume control 等,本节以对 dummy.c 中的 "Master Volume" 控制为例讲解即可。
3.1.1 mixer 重要数据结构
在 /tinyalsa/mixer.c 中主要的数据结构是 struct mixer,用来保存该 card 下所有 control info 在 tinyalsa 中的保存,如下:
struct mixer_ctl {
struct mixer *mixer;
struct snd_ctl_elem_info *info;
char **ename;
};
struct mixer {
int fd;
struct snd_ctl_card_info card_info;
/* 为每个 ctl 分配一个 elem_info, 记录该 ctl 的详细信息 */
struct snd_ctl_elem_info *elem_info;
/* 为每个 ctl 分配一个 mixer_ctl, 其中主要成员也是 elem_info, 并且 ctl->info = mixer->elem_info */
struct mixer_ctl *ctl;
unsigned int count;
};
从上述结构体可以看出每个 ctl 都有一个对应的 elem_info 用来描述该 ctl 详细信息,如下:
struct snd_ctl_elem_info {
struct snd_ctl_elem_id id; /* W: element ID */
snd_ctl_elem_type_t type; /* R: value type - SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_TYPE_* */
unsigned int access; /* R: value access (bitmask) - SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ACCESS_* */
unsigned int count; /* count of values */
__kernel_pid_t owner; /* owner's PID of this control */
union {
struct {
long min; /* R: minimum value */
long max; /* R: maximum value */
long step; /* R: step (0 variable) */
} integer;
struct {
long long min; /* R: minimum value */
long long max; /* R: maximum value */
long long step; /* R: step (0 variable) */
} integer64;
struct {
unsigned int items; /* R: number of items */
unsigned int item; /* W: item number */
char name[64]; /* R: value name */
__u64 names_ptr; /* W: names list (ELEM_ADD only) */
unsigned int names_length;
} enumerated;
unsigned char reserved[128];
} value;
union {
unsigned short d[4]; /* dimensions */
unsigned short *d_ptr; /* indirect - obsoleted */
} dimen;
unsigned char reserved[64-4*sizeof(unsigned short)];
};
elem_id主要是用来区分 Control 的,定义如下:
struct snd_ctl_elem_id {
unsigned int numid; /* numeric identifier, zero = invalid */
snd_ctl_elem_iface_t iface; /* interface identifier */
unsigned int device; /* device/client number */
unsigned int subdevice; /* subdevice (substream) number */
unsigned char name[SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ID_NAME_MAXLEN]; /* ASCII name of item */
unsigned int index; /* index of item */
};
其中 numid 在 snd_ctl_add() 时会递增,用于表示 ctl 编号;name 即该 ctl name,即分别对应 tinymix 下的 ctl & name;
type表示该 control value 的类型,即对应 tinymix 下的 type;- access 表示该 control 的访问能力,如 write & read 等;
- count 表示该 control 控制的 value 数量,例如对于 stereo volume reg 不一样时则 count 为 2,
即对应 tinymix 下的 num; - value 根据上述 type 的不同选择对应的 union,其保存着当前 ctl 当前的状态,
即对应 tinymix 下的 value;
上述的字段中在 tinymix 中都会显示,如下:
3.1.2 打开 mixer 设备
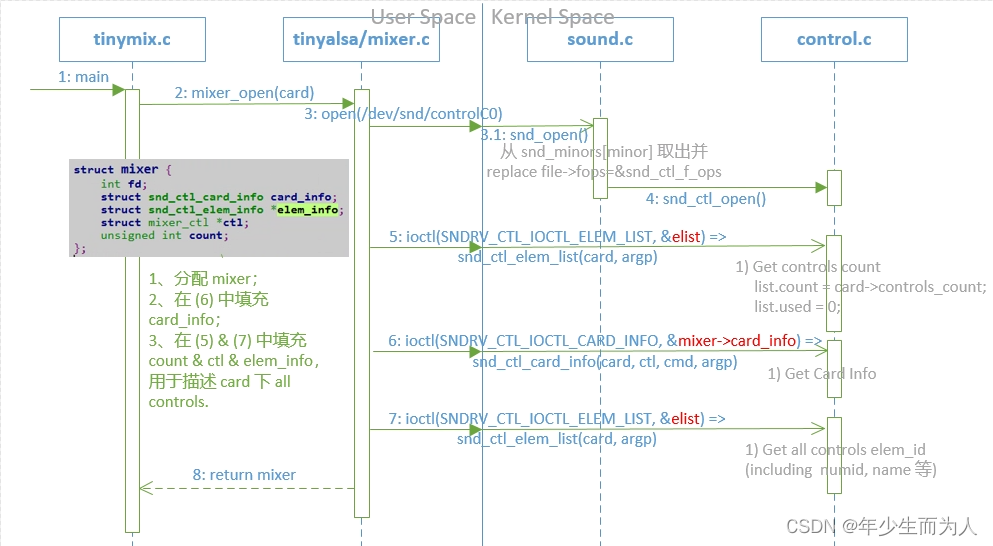
tinymix 首先调用 mixer_open()【/tinyalsa/mixer.c】 打开 mixer 设备,其中该函数主要实现的内容是 open /dev/snd/controlC%u 设备,并且通过 ioctl 函数获取该 card 下所有 kcontrol info,并且填充在 mixer 中,如下:
struct mixer *mixer_open(unsigned int card)
{
struct snd_ctl_elem_list elist;
struct snd_ctl_elem_id *eid = NULL;
struct mixer *mixer = NULL;
unsigned int n;
int fd;
char fn[256];
//1、打开 /dev/snd/ControlC%u 设备;
snprintf(fn, sizeof(fn), "/dev/snd/controlC%u", card);
fd = open(fn, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
return 0;
//2、通过 IOCTL_ELEM_LIST 获取 card->controls_count;
memset(&elist, 0, sizeof(elist));
if (ioctl(fd, SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_LIST, &elist) < 0)
goto fail;
//3、分配 mixer, 以及为 all controls 分配对应的 ctl & elem_info 等;
mixer = calloc(1, sizeof(*mixer));
if (!mixer)
goto fail;
mixer->ctl = calloc(elist.count, sizeof(struct mixer_ctl));
mixer->elem_info = calloc(elist.count, sizeof(struct snd_ctl_elem_info));
if (!mixer->ctl || !mixer->elem_info)
goto fail;
if (ioctl(fd, SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_CARD_INFO, &mixer->card_info) < 0)
goto fail;
eid = calloc(elist.count, sizeof(struct snd_ctl_elem_id));
if (!eid)
goto fail;
mixer->count = elist.count;
mixer->fd = fd;
elist.space = mixer->count;
elist.pids = eid;
//4、通过 IOCTL_ELEM_LIST 获取 elem_id (including numid, name 等), 并且最终将 elist info 填充到 mixer->ctl 中.
if (ioctl(fd, SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_LIST, &elist) < 0)
goto fail;
for (n = 0; n < mixer->count; n++) {
struct mixer_ctl *ctl = mixer->ctl + n;
ctl->mixer = mixer;
ctl->info = mixer->elem_info + n;
ctl->info->id.numid = eid[n].numid;
strncpy((char *)ctl->info->id.name, (char *)eid[n].name,
SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ID_NAME_MAXLEN);
ctl->info->id.name[SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_ID_NAME_MAXLEN - 1] = 0;
}
free(eid);
return mixer;
fail:
/* TODO: verify frees in failure case */
if (eid)
free(eid);
if (mixer)
mixer_close(mixer);
else if (fd >= 0)
close(fd);
return 0;
}
针对上述 mixer.c 中 call 到 alsa driver 的内容没有给出详细介绍,这里提供自己画的 flow 时序图,如下:
3.1.3 通过写 mixer 设备=>设置 control 的值
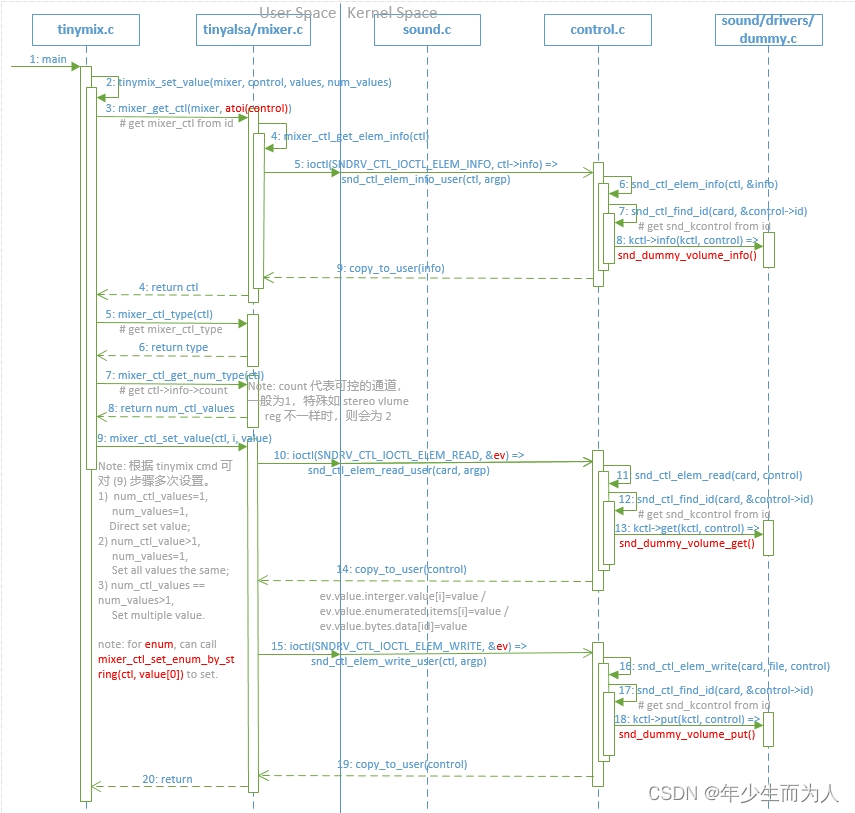
在前面一节中已经通过 mixer_open() 打开并获得了 mixer,包含了 card 下所有 control info,接下来则可以通过 ctl id/name 找到要控制的 ctl,并设置 control 值到 alsa driver,实现对音频控件的控制,详细实现如下:
static void tinymix_set_value(struct mixer *mixer, const char *control,
char **values, unsigned int num_values)
{
struct mixer_ctl *ctl;
enum mixer_ctl_type type;
unsigned int num_ctl_values;
unsigned int i;
//1、通过 id / name 找到对应的 ctl
if (isdigit(control[0]))
ctl = mixer_get_ctl(mixer, atoi(control));
else
ctl = mixer_get_ctl_by_name(mixer, control);
if (!ctl) {
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid mixer control\n");
return;
}
type = mixer_ctl_get_type(ctl);
num_ctl_values = mixer_ctl_get_num_values(ctl);
if (type == MIXER_CTL_TYPE_BYTE) {
tinymix_set_byte_ctl(ctl, values, num_values);
return;
}
if (isdigit(values[0][0])) {
if (num_values == 1) {
/* Set all values the same */
int value = atoi(values[0]);
for (i = 0; i < num_ctl_values; i++) {
//2、对相应的 ctl 设置 value
if (mixer_ctl_set_value(ctl, i, value)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: invalid value\n");
return;
}
}
} else {
/* Set multiple values */
if (num_values > num_ctl_values) {
fprintf(stderr,
"Error: %d values given, but control only takes %d\n",
num_values, num_ctl_values);
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < num_values; i++) {
if (mixer_ctl_set_value(ctl, i, atoi(values[i]))) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: invalid value for index %d\n", i);
return;
}
}
}
} else {
if (type == MIXER_CTL_TYPE_ENUM) {
if (num_values != 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Enclose strings in quotes and try again\n");
return;
}
if (mixer_ctl_set_enum_by_string(ctl, values[0]))
fprintf(stderr, "Error: invalid enum value\n");
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: only enum types can be set with strings\n");
}
}
}
最终通过 mixer.c 中的 mixer_ctl_set_value() 函数通过 ioctl 将 value 设置给音频控件,如下:
int mixer_ctl_set_value(struct mixer_ctl *ctl, unsigned int id, int value)
{
struct snd_ctl_elem_value ev;
int ret;
if (!ctl || (id >= ctl->info->count))
return -EINVAL;
memset(&ev, 0, sizeof(ev));
ev.id.numid = ctl->info->id.numid;
ret = ioctl(ctl->mixer->fd, SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_READ, &ev);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
switch (ctl->info->type) {
case SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
ev.value.integer.value[id] = !!value;
break;
case SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_TYPE_INTEGER:
ev.value.integer.value[id] = value;
break;
case SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_TYPE_ENUMERATED:
ev.value.enumerated.item[id] = value;
break;
case SNDRV_CTL_ELEM_TYPE_BYTES:
ev.value.bytes.data[id] = value;
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
return ioctl(ctl->mixer->fd, SNDRV_CTL_IOCTL_ELEM_WRITE, &ev);
}
针对上述 mixer.c 中 call 到 alsa driver 的内容没有给出详细介绍,这里提供自己画的 flow 时序图,如下:
3.2 tinyplay 播放 pcm
在使用 tinymix 配置好音频通路时,就可以使用 tinyplay 播放 wav pcm 文件,本节以对 dummy.c 为例进行播放简单穿插讲解即可。
3.2.1 tinyalsa pcm 重要数据结构
在 tinyalsa/pcm.c 中重要的数据结构是 struct pcm,用来保存播放 pcm stream 对应的所有 info,定义如下:
struct pcm {
int fd; //使用的 pcm dev
unsigned int flags; //代表 pcm direction
int running:1;
int prepared:1;
int underruns;
unsigned int buffer_size;
unsigned int boundary;
char error[PCM_ERROR_MAX];
struct pcm_config config;
struct snd_pcm_mmap_status *mmap_status;
struct snd_pcm_mmap_control *mmap_control;
struct snd_pcm_sync_ptr *sync_ptr;
void *mmap_buffer;
unsigned int noirq_frames_per_msec;
int wait_for_avail_min;
};
flags代表该 pcm stream 方向,定义有 PCM_OUT、PCM_IN、PCM_MMAP 等;buffer_size等于 period_size * period_count,在 pcm driver 中会 apply runtime->status->hw_ptr,runtime->control->appl_ptr 在 [0, buffer_size-1];config播放的 pcm stream 的配置,具体描述看如下定义:
/* Configuration for a stream */
struct pcm_config {
unsigned int channels;
unsigned int rate;
unsigned int period_size;
unsigned int period_count;
enum pcm_format format;
/* Values to use for the ALSA start, stop and silence thresholds, and
* silence size. Setting any one of these values to 0 will cause the
* default tinyalsa values to be used instead.
* Tinyalsa defaults are as follows.
*
* start_threshold : period_count * period_size
* stop_threshold : period_count * period_size
* silence_threshold : 0
* silence_size : 0
*/
unsigned int start_threshold;
unsigned int stop_threshold;
unsigned int silence_threshold;
unsigned int silence_size;
/* Minimum number of frames available before pcm_mmap_write() will actually
* write into the kernel buffer. Only used if the stream is opened in mmap mode
* (pcm_open() called with PCM_MMAP flag set). Use 0 for default.
*/
int avail_min;
};
3.2.2 打开 pcm 设备
tinyplay 播放 pcm wav 音频时,首先会 parser wav 出 audio pcm data,最后通过 tinyplay.c 下 play_sample() 函数调用 tinyalsa pcm.c 函数,最终通过控制 pcm device 实现将 audio data 送到硬体中。本节省略对 wav parser 等的分析,主要分析 play_sample() 函数。
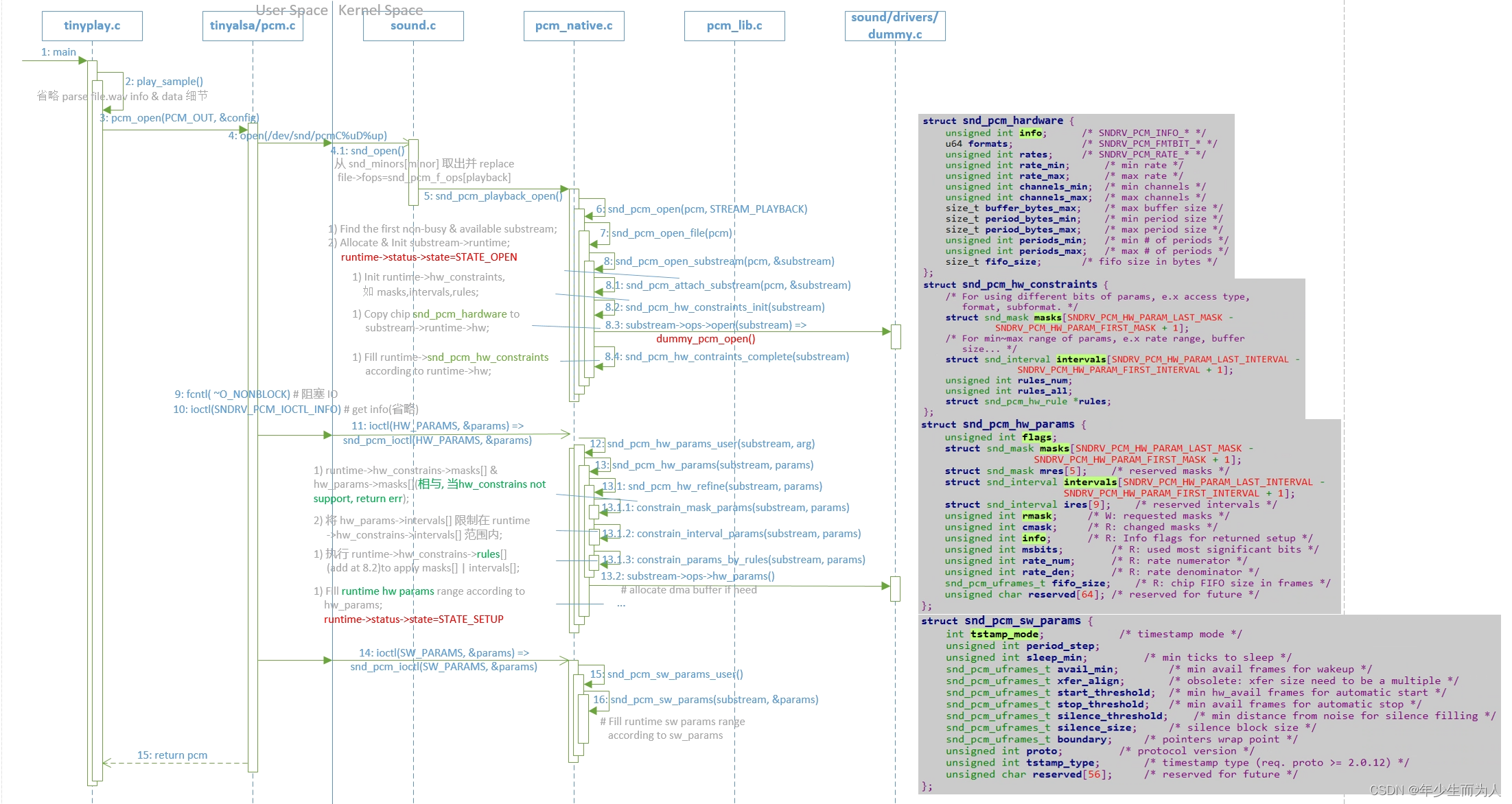
首先调用 pcm_open() 函数打开并配置 pcm 设备,其中该函数主要实现是根据参数 open(/dev/snd/pcmC%uD%u%c),并且根据 pcm_config 等参数通过 ioctl 设置 hw_params & sw_params,最终返回 pcm 实例,其定义实现如下:
struct pcm *pcm_open(unsigned int card, unsigned int device,
unsigned int flags, struct pcm_config *config)
{
struct pcm *pcm;
struct snd_pcm_info info;
struct snd_pcm_hw_params params;
struct snd_pcm_sw_params sparams;
char fn[256];
int rc;
//1、分配 pcm 实例, 并将相关 input params 填充到 pcm 实例中;
pcm = calloc(1, sizeof(struct pcm));
if (!pcm || !config)
return &bad_pcm; /* TODO: could support default config here */
pcm->config = *config;
snprintf(fn, sizeof(fn), "/dev/snd/pcmC%uD%u%c", card, device,
flags & PCM_IN ? 'c' : 'p');
pcm->flags = flags;
//2、open /dev/snd/pcmC%uD%u%c 设备, 通过 fcntl 设置为阻塞IO
pcm->fd = open(fn, O_RDWR|O_NONBLOCK);
if (pcm->fd < 0) {
oops(pcm, errno, "cannot open device '%s'", fn);
return pcm;
}
if (fcntl(pcm->fd, F_SETFL, fcntl(pcm->fd, F_GETFL) &
~O_NONBLOCK) < 0) {
oops(pcm, errno, "failed to reset blocking mode '%s'", fn);
goto fail_close;
}
if (ioctl(pcm->fd, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_INFO, &info)) {
oops(pcm, errno, "cannot get info");
goto fail_close;
}
//3、根据 input params:config 初始化 hw params 并通过 ioctl 设置 hw params 给 pcm device;
param_init(¶ms);
param_set_mask(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FORMAT,
pcm_format_to_alsa(config->format));
param_set_mask(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_SUBFORMAT,
SNDRV_PCM_SUBFORMAT_STD);
param_set_min(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIOD_SIZE, config->period_size);
param_set_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_SAMPLE_BITS,
pcm_format_to_bits(config->format));
param_set_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FRAME_BITS,
pcm_format_to_bits(config->format) * config->channels);
param_set_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_CHANNELS,
config->channels);
param_set_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIODS, config->period_count);
param_set_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_RATE, config->rate);
...
if (flags & PCM_MMAP)
param_set_mask(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_ACCESS,
SNDRV_PCM_ACCESS_MMAP_INTERLEAVED);
else
param_set_mask(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_ACCESS,
SNDRV_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED);
if (ioctl(pcm->fd, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_HW_PARAMS, ¶ms)) {
oops(pcm, errno, "cannot set hw params");
goto fail_close;
}
/* get our refined hw_params */
config->period_size = param_get_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIOD_SIZE);
config->period_count = param_get_int(¶ms, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIODS);
pcm->buffer_size = config->period_count * config->period_size;
...
//4、根据 input params:config 初始化 sw params 并通过 ioctl 设置 sw params 给 pcm device;
memset(&sparams, 0, sizeof(sparams));
sparams.tstamp_mode = SNDRV_PCM_TSTAMP_ENABLE;
sparams.period_step = 1;
if (!config->start_threshold) {
if (pcm->flags & PCM_IN)
pcm->config.start_threshold = sparams.start_threshold = 1;
else
pcm->config.start_threshold = sparams.start_threshold =
config->period_count * config->period_size / 2;
} else
sparams.start_threshold = config->start_threshold;
/* pick a high stop threshold - todo: does this need further tuning */
if (!config->stop_threshold) {
if (pcm->flags & PCM_IN)
pcm->config.stop_threshold = sparams.stop_threshold =
config->period_count * config->period_size * 10;
else
pcm->config.stop_threshold = sparams.stop_threshold =
config->period_count * config->period_size;
}
else
sparams.stop_threshold = config->stop_threshold;
if (!pcm->config.avail_min) {
if (pcm->flags & PCM_MMAP)
pcm->config.avail_min = sparams.avail_min = pcm->config.period_size;
else
pcm->config.avail_min = sparams.avail_min = 1;
} else
sparams.avail_min = config->avail_min;
sparams.xfer_align = config->period_size / 2; /* needed for old kernels */
sparams.silence_threshold = config->silence_threshold;
sparams.silence_size = config->silence_size;
pcm->boundary = sparams.boundary = pcm->buffer_size;
while (pcm->boundary * 2 <= INT_MAX - pcm->buffer_size)
pcm->boundary *= 2;
if (ioctl(pcm->fd, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_SW_PARAMS, &sparams)) {
oops(pcm, errno, "cannot set sw params");
goto fail;
}
...
pcm->underruns = 0;
return pcm;
fail:
...
fail_close:
close(pcm->fd);
pcm->fd = -1;
return pcm;
}
3.2.2.1 open pcm playback device
在 open /dev/snd/pcmC%uD%up device 时会嵌入到 alsa core,最终会调用 substream->ops->open() 函数。在该函数主要是找到一个空闲 & 可用的 substream,并且为其分配一个 runtime,通过 substream->ops->open() 拿到该 substream 支持的 snd_pcm_hardware,填充给 runtime->hw,又根据该 hw params 填充 runtime->snd_pcm_hw_constraints,以便后面 Setting Hw Params 时使用。该步骤涉及重要的数据结构有:
1)struct snd_pcm_hardware
/*
* Hardware (lowlevel) section
*/
struct snd_pcm_hardware {
unsigned int info; /* SNDRV_PCM_INFO_* */
u64 formats; /* SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_* */
unsigned int rates; /* SNDRV_PCM_RATE_* */
unsigned int rate_min; /* min rate */
unsigned int rate_max; /* max rate */
unsigned int channels_min; /* min channels */
unsigned int channels_max; /* max channels */
size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* max buffer size */
size_t period_bytes_min; /* min period size */
size_t period_bytes_max; /* max period size */
unsigned int periods_min; /* min # of periods */
unsigned int periods_max; /* max # of periods */
size_t fifo_size; /* fifo size in bytes */
};
该结构体主要描述的是 hw 支持的 pcm 能力(各参数详解略)
2)struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints {
struct snd_mask masks[SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_MASK -
SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_MASK + 1];
struct snd_interval intervals[SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_INTERVAL -
SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_INTERVAL + 1];
unsigned int rules_num;
unsigned int rules_all;
struct snd_pcm_hw_rule *rules;
};
该结构体主要是在 alsa core 保存对当前 substream 的 hw capability 描述,详解如下:
masks[]用来描述那些需要使用多个 bits 来描述支持多种能力的参数,如 Access Type(RW/MMAP等),Formats(S16_LE/BE/U16_LE/BE等),每种能力均占用 1 bit,多种能力 ‘|’;intervals[]用来描述那些有大小范围等的参数,如 Sample/Frame Bits,Channels,Rate,Buffer Size/Bytes 等;rules用来为那些依赖其他参数的参数创建 rules,起到限制作用,在snd_pcm_hw_constraints_init()中创建 rules,如 Sample/Frame Bits 依赖于 Format(8/16/24/32等),Buffer Size/Bytes 依赖于 Peroid_size & Period_count 等等,使用 snd_pcm_hw_rule_add() 创建 rules,其中参数有 runtime,var(who’s rules),rule_func,dep…(即依赖的参数,可变参数);rules_nums描述当前创建 rules 的数量;rules_all描述当前分配的可创建 rules 的最大数量(若 rules_nums > rules_all 时,则会重新 + 16).
3.2.2.2 Setting Hw Params
在调用 ioctl(SNDRV_PCM_IOCZTL_HW_PARAMS) 时会传入一个 snd_pcm_hw_params 参数,如前面代码所示,在调用该函数前会先根据 pcm_open() 传入的 pcm_config 转换成相应的 hw_params 中,在 alsa core 中则会利用该 hw_params 与前面 open 时拿到的 substream hw_constraints 进行比较,看 substream 是否支持播放,若支持则会将比较后(masks 相与,intervals 则缩小范围)的结构保存在 hw params,并利用 substream->ops->hw_params(前面已讲解,此处略),若遇到不支持的 hw params 则会直接 return error. 该步骤涉及重要的数据结构有:
1)struct snd_pcm_hw_params
struct snd_pcm_hw_params {
unsigned int flags;
struct snd_mask masks[SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_MASK -
SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_MASK + 1];
struct snd_mask mres[5]; /* reserved masks */
struct snd_interval intervals[SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_INTERVAL -
SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_INTERVAL + 1];
struct snd_interval ires[9]; /* reserved intervals */
unsigned int rmask; /* W: requested masks */
unsigned int cmask; /* R: changed masks */
unsigned int info; /* R: Info flags for returned setup */
unsigned int msbits; /* R: used most significant bits */
unsigned int rate_num; /* R: rate numerator */
unsigned int rate_den; /* R: rate denominator */
snd_pcm_uframes_t fifo_size; /* R: chip FIFO size in frames */
unsigned char reserved[64]; /* reserved for future */
};
该结构体主要保存播放片源 & 硬件支持能力相比较后的结果,参数如下:
- masks[] 如 hw_constraints->masks[];
- intervals[] 如 hw_constraints->intervals[];
3.2.2.3 Setting Sw Params
在调用 ioctl(SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_SW_PARAMS) 时会传入一个 snd_pcm_sw_params 参数,如前面代码所示,在调用该函数前也会先根据 pcm_config 转换成相应的 sw params 中,如 threshold,silence,boundary,tstamp_mode,avail_min(用于在 alsa core 中每次等待唤醒的 free space) 等,在 alsa core 则会根据 sw params 填充到 runtime 相应的参数中,主要涉及的数据结构有:
1)struct snd_pcm_sw_params
struct snd_pcm_sw_params {
int tstamp_mode; /* timestamp mode */
unsigned int period_step;
unsigned int sleep_min; /* min ticks to sleep */
snd_pcm_uframes_t avail_min; /* min avail frames for wakeup */
snd_pcm_uframes_t xfer_align; /* obsolete: xfer size need to be a multiple */
snd_pcm_uframes_t start_threshold; /* min hw_avail frames for automatic start */
snd_pcm_uframes_t stop_threshold; /* min avail frames for automatic stop */
snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_threshold; /* min distance from noise for silence filling */
snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_size; /* silence block size */
snd_pcm_uframes_t boundary; /* pointers wrap point */
unsigned int proto; /* protocol version */
unsigned int tstamp_type; /* timestamp type (req. proto >= 2.0.12) */
unsigned char reserved[56]; /* reserved for future */
};
该结构体主要描述播放片源时的各种 sw params,如 threshold,silence,boundary,tstamp_mode,avail_min(用于在 alsa core 中每次等待唤醒的 free space) 等,详细略。
在上述中针对 pcm_open() 函数中调用到 alsa core 都仅仅描述其重要功能,并未描述详细 flow,其 flow 基本如下时序图,
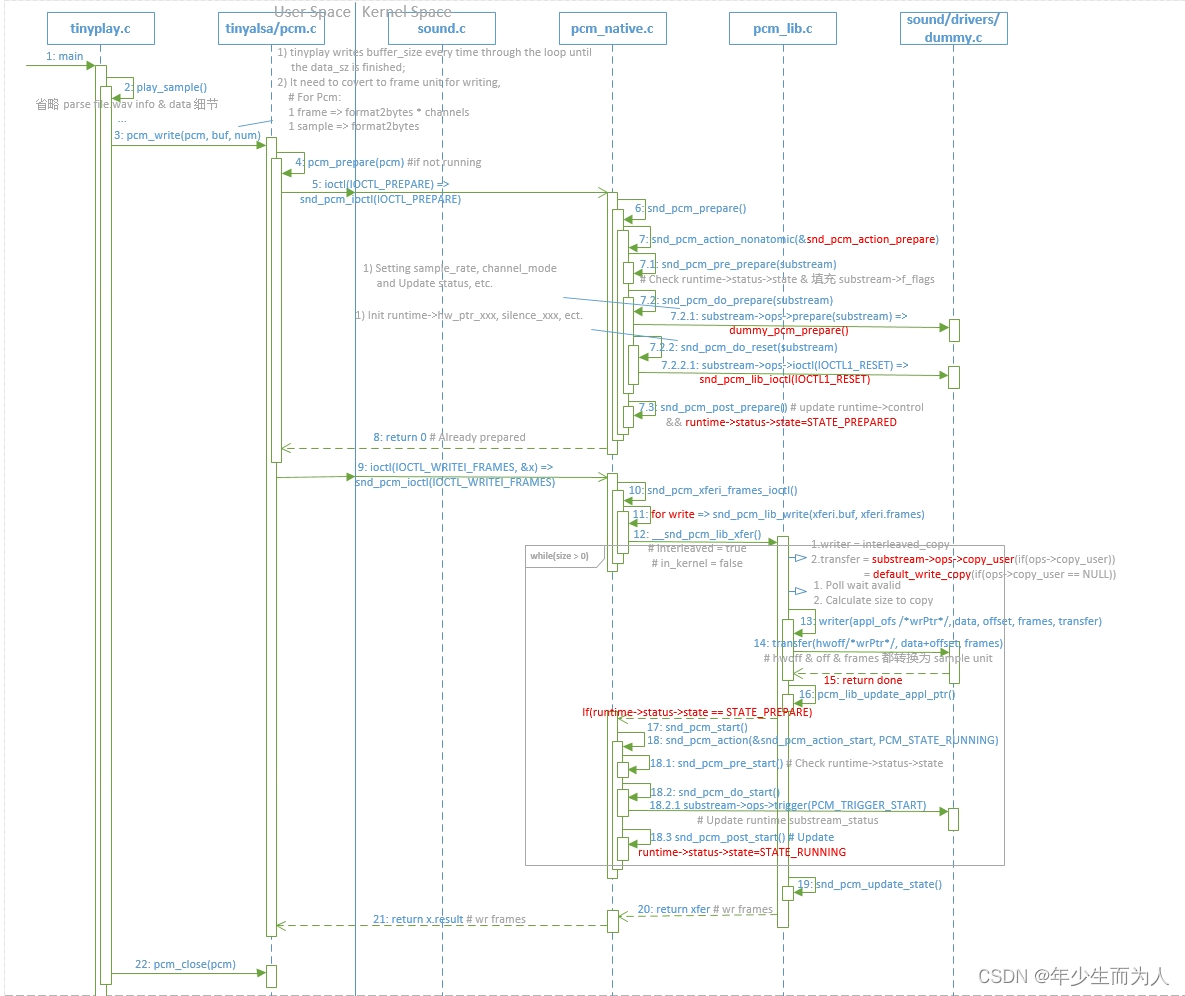
3.2.3 通过 pcm_write 写 pcm 数据到 Pcm 设备
在前面调用 pcm_open() 函数创建并分配好 pcm handle 后,此时就可以利用 pcm handle 调用 pcm_write 将 pcm 数据循环写入到 pcm device 中。
3.2.3.1 Setting Pcm Prepare Once
在 pcm_write() 中如果前面为非 running 状态时,先需要下 pcm_prepare(),即 ioctl(SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_PREPARE),内部会调用 substream->ops->prepare(),用于设置采样率、格式等,并且最后会 do_reset(),即调用 substream->ops->ioctl(IOCTL1_RESET) 实现对 runtime hw_ptr & appl_ptr 做 reset 动作;
3.2.3.2 Write Pcm Data to pcm Dev Loop
在有做 pcm_prepare() 之后就会循环调用 pcm_write(),即 ioctl(SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_WRITEI_FRAMES) 每次写不超过 buffer_size=period_count*period_size pcm data,直到写完。在 alsa core 中,会循环等待 avail_min freespace 后唤醒去 copy pcm data 到 dma 缓冲区中,其中 wrptr=>runtime->control->appl_ptr(在每次 copy data 之后由 alsa core 更新),rdptr=>runtime->status->hw_ptr(在 alsa driver 中会有个 period_size timer interrupt call snd_pcm_period_elapsed() 更新),并且在第一次 write 之后会下 snd_pcm_start(substream),即 substream->ops->trigger(SNDRV_PCM_TRIGGER_START),update runtime substream_status.
在上述描述 pcm_write() 中针对 alsa core 的详细 flow 如下时序图: