文章目录
实验楼实验二 操作系统的引导
bootsec.s文件
编写bootsec.s文件
在 oslab/linux-0.11/boot目录下将原来的bootsect.s改名为bootsect.s.bak,即执行命令
$ mv bootsect.s bootsect.s.bak
并新建一个并编写bootsect.s,命令如下:
$ vim bootsect.s
代码如下:
entry _start
_start:
!读入光标位置
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
!字符串msg1长度
mov cx,#378
!第 0 页,属性 7(正常)
mov bx,#0x0007
!字符串msg1
mov bp,#msg1
!es:bp 是显示字符串的地址
!相比与 linux-0.11 中的代码,需要增加对 es 的处理,因为原代码中在输出之前已经处理了 es
mov ax,#0x07c0
mov es,ax
!写入字符串,移动光标
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10!BIOS中断
! 设置一个无限循环
inf_loop:
jmp inf_loop
msg1:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "## ## # # #### ##### # #### ## #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # # # # # # # # # # #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # #### # # # # # #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # # # # ###### #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # # # # # # # # #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # #### # # #### # # ######"
.byte 13,10,13,10
! boot_flag 必须在最后两个字节
.org 510
! 设置引导扇区标记 0xAA55
! 必须有它,才能引导
boot_flag:
.word 0xAA55
编译
在boot目录下,执行下面的命令:
- 编译
$ as86 -0 -a -o bootsect.o bootsect.s
-0(是数字’0’)以16位代码段运行,当使用了高于8086指令集的指令时警告
-a 使汇编程序部分兼容于Minix asld.交换了[]与()的用法,并且改变了一些16位跳转与调用的语法(“jmp @(bx)” 就成了一个合法的指令),生成与 GNU as 和 ld 部分兼容的代码
- 链接
$ ld86 -0 -s -o bootsect bootsect.o
-0(是数字零)产生具有16bit魔数的头结构,并且对-lx选项使用i86子目录
-s 告诉链接器 ld86 去除最后生成的可执行文件中的符号信息
- 生成文件
-rwxrwxr-x 1 root root 544 Aug 5 18:09 bootsect*
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 511 Aug 5 18:08 bootsect.o
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 862 Aug 5 18:08 bootsect.s
其中 bootsect.o 是中间文件;bootsect 是编译、链接后的目标文件,也就是可执行文件
运行
需要注意的文件是 bootsect 文件大小是 544 字节,而引导程序必须要正好占用一个磁盘扇区,即 512 个字节。多出来的32字节是Minix可执行文件头部,去掉这 32 个字节后就可以放入引导扇区了。可以使用dd命令进行处理
$ dd -bs=1 if=bootsect of=Image skip=32
之后复制该文件到linux-0.11目录下,并运行系统查看显示结果
$ cp ./Image …/Image
运行
!注意目前还位于/oslab/linux-0.11/boot下
$ …/…/run
运行截图:
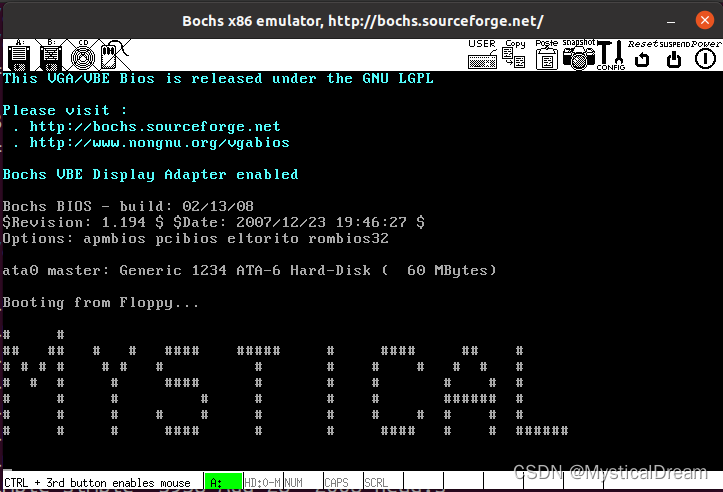
setup.s文件
编写setup.s文件
在
entry _start
_start:
!读入光标位置
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
!字符串msg2长度
mov cx,#25
!第 0 页,属性 7(正常)
mov bx,#0x0007
!字符串msg2
mov bp,#msg2
!es:bp 是显示字符串的地址
!使用cs的值修改es的值
mov ax,cs
mov es,ax
!写入字符串,移动光标
mov ax,#0x1301
!BIOS中断
int 0x10
! 设置一个无限循环
inf_loop:
jmp inf_loop
msg2:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Now we are in SETUP"
.byte 13,10,13,10
! boot_flag 必须在最后两个字节
.org 510
! 设置引导扇区标记 0xAA55
! 必须有它,才能引导
boot_flag:
.word 0xAA55
修改前面写的 bootsect.s
我们需要编写 bootsect.s 中载入 setup.s 的关键代码
load_setup:
! 设置驱动器和磁头(drive 0, head 0): 软盘 0 磁头 0
mov dx,#0x0000
! 设置扇区号和磁道(sector 2, track 0): 0 磁道、2 扇区
mov cx,#0x0002
! 设置读入的内存地址:BOOTSEG+address = 512,偏移512字节
mov bx,#0x0200
! 设置读入的扇区个数(service 2, nr of sectors),
! SETUPLEN是读入的扇区个数,Linux 0.11 设置的是 4,
! 我们不需要那么多,我们设置为 2(因此还需要添加变量 SETUPLEN=2)
mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN
! 应用 0x13 号 BIOS 中断读入 2 个 setup.s扇区
int 0x13
! 读入成功,跳转到 ok_load_setup: ok - continue
jnc ok_load_setup
! 软驱、软盘有问题才会执行到这里。我们的镜像文件比它们可靠多了
mov dx,#0x0000
! 否则复位软驱 reset the diskette
mov ax,#0x0000
int 0x13
! 重新循环,再次尝试读取
jmp load_setup
ok_load_setup:
! 接下来要干什么?当然是跳到 setup 执行。
! 要注意:我们没有将 bootsect 移到 0x9000,因此跳转后的段地址应该是 0x7e0
! 即我们要设置 SETUPSEG=0x07e0
个人理解:
load_setup主要是将指定位置(0磁道2扇区)和数量(这里是SETUPLEN=2)的扇区读入内存(es:bx=07c0H:0200H即地址(07c0H✖10)+200H=07e00H),再将(cs:ip指向07e0:0000)执行setup部分的代码
补充:
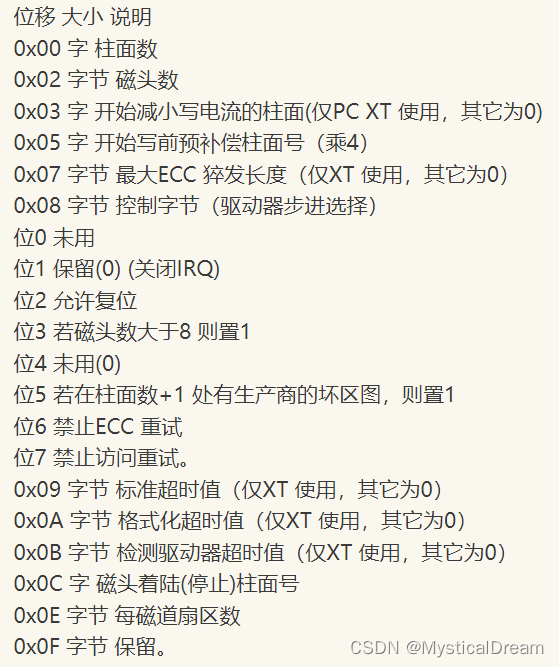
入口参数:
AH=02H(功能号:02H 表示读扇区)AL=扇区数
CH=柱面
CL=扇区
DH=磁头
DL=驱动器,00H ~ 7FH:软盘;80H ~ 0FFH:硬盘
ES:BX=缓冲区的地址(读出数据的缓冲区地址)
出口参数:
若出错则CF示志置位
CF=0——操作成功,AH=00H,AL=传输的扇区数,否则,AH=状态代码,参见下图:
编写完成后的完整代码
SETUPLEN=2
SETUPSEG=0x07e0
entry _start
_start:
!读入光标位置
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
!字符串msg1长度
mov cx,#378
!第 0 页,属性 7(正常)
mov bx,#0x0007
!字符串msg1
mov bp,#msg1
!es:bp 是显示字符串的地址
!相比与 linux-0.11 中的代码,需要增加对 es 的处理,因为原代码中在输出之前已经处理了 es
mov ax,#0x07c0
mov es,ax
!写入字符串,移动光标
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10!BIOS中断
load_setup:
mov dx,#0x0000
mov cx,#0x0002
mov bx,#0x0200
mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN
int 0x13
jnc ok_load_setup
mov dx,#0x0000
mov ax,#0x0000
int 0x13
jmp load_setup
ok_load_setup:
jmpi 0,SETUPSEG
msg1:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "## ## # # #### ##### # #### ## #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # # # # # # # # # # #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # #### # # # # # #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # # # # ###### #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # # # # # # # # # #"
.byte 13,10
.ascii "# # # #### # # #### # # ######"
.byte 13,10,13,10
! boot_flag 必须在最后两个字节
.org 510
! 设置引导扇区标记 0xAA55
! 必须有它,才能引导
boot_flag:
.word 0xAA55
再次编译
借助 Makefile 编译、链接bootsect.s和setup.s
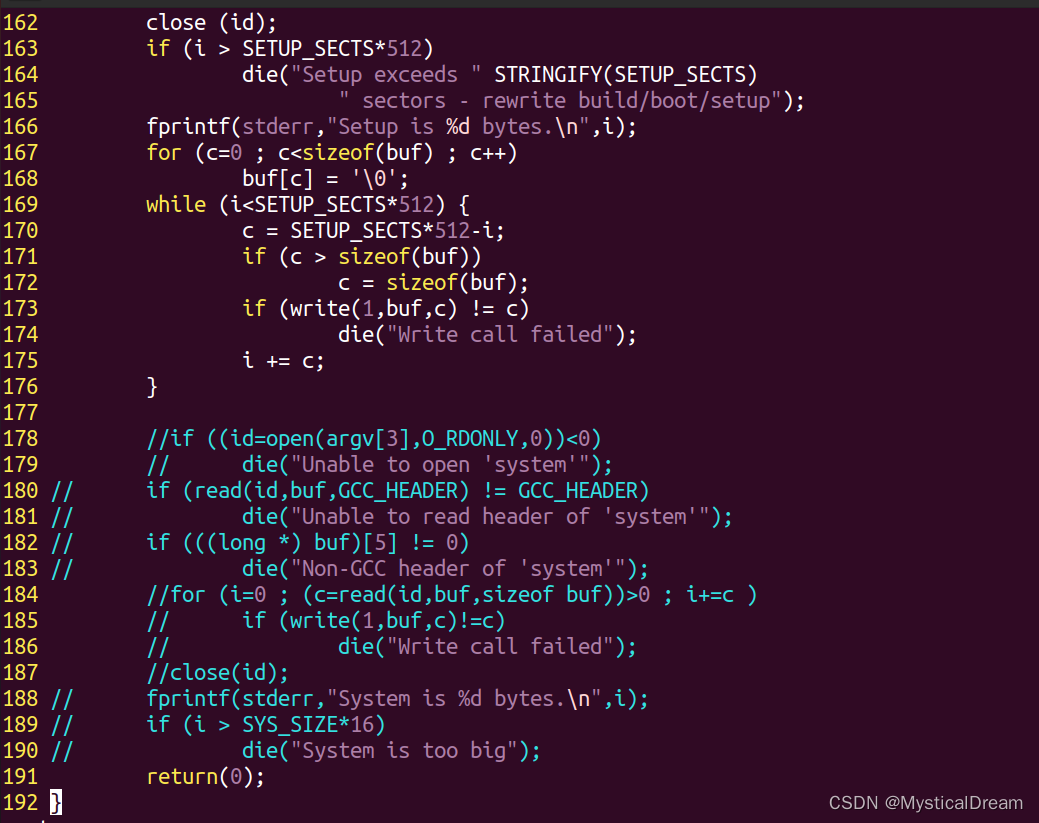
在此之前我们需要修改一下tools/build.c,因为这个是生成整个系统镜像的,我们只需要bootsect.s 和setup.s。
注释掉build.c后面几段代码,如下图所示
最后切换到linux-0.11目录下,执行以下命令:
$ make BootImage
输入以下命令运行:
$ …/run
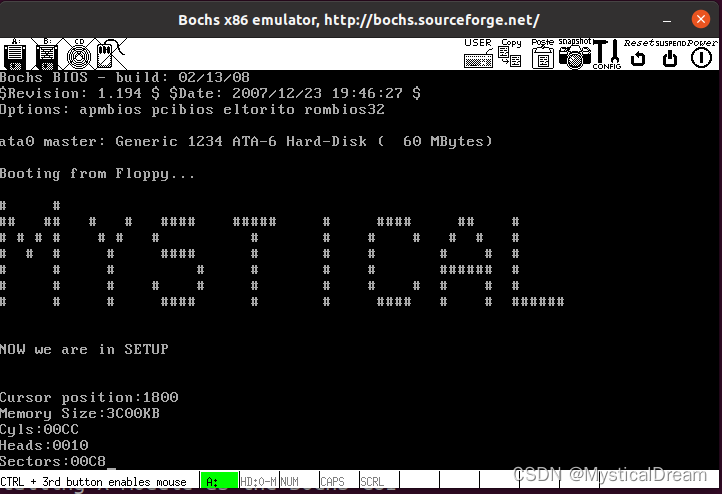
运行截图
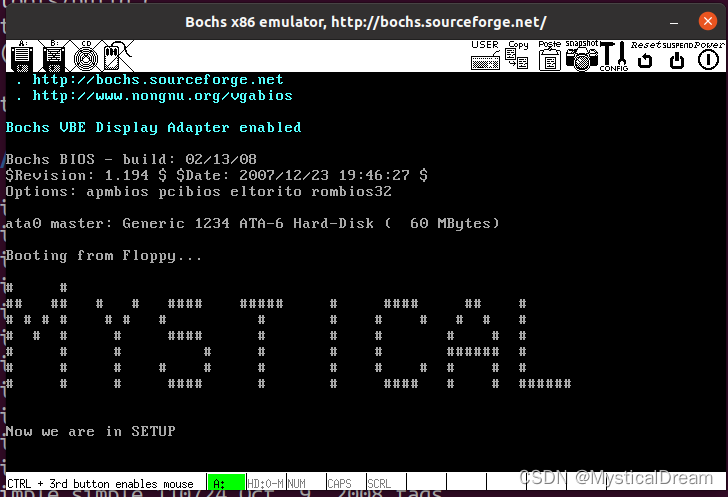
setup.s 获取基本硬件参数
取出硬盘各参数放在了 0x90000 处,并通过十六进制打印在屏幕上
setup.s完整代码:
INITSEG = 0x9000
entry _start
_start:
! 打印 "NOW we are in SETUP"
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#25
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg2
mov ax,cs
mov es,ax
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
mov ax,cs
mov es,ax
! 初始化栈 ss:sp
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov ss,ax
mov sp,#0xFF00
! 获取参数
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov ds,ax
!读取光标坐标
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov [0],dx
!读出内存的大小
mov ah,#0x88
int 0x15
mov [2],ax
!磁盘参数表,复制ds:si->es:di
mov ax,#0x0000
mov ds,ax
lds si,[4*0x41]
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0004
mov cx,#0x10
!重复16次
rep
movsb
! 准备打印
mov ax,cs
mov es,ax
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov ds,ax
! 光标位置
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#18
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg_cursor
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
mov dx,[0]
call print_hex
! 内存大小
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#14
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg_memory
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
mov dx,[2]
call print_hex
! 添加 KB
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#2
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg_kb
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
! 柱面
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#7
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg_cyles
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
mov dx,[4]
call print_hex
! 磁头
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#8
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg_heads
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
mov dx,[6]
call print_hex
! 扇区
mov ah,#0x03
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#10
mov bx,#0x0007
mov bp,#msg_sectors
mov ax,#0x1301
int 0x10
mov dx,[12]
call print_hex
inf_loop:
jmp inf_loop
print_hex:
mov cx,#4
print_digit:
rol dx,#4
mov ax,#0xe0f
and al,dl
add al,#0x30
cmp al,#0x3a
jl outp
add al,#0x07
outp:
int 0x10
loop print_digit
ret
print_nl:
mov ax,#0xe0d ! CR
int 0x10
mov al,#0xa ! LF
int 0x10
ret
msg2:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "NOW we are in SETUP"
.byte 13,10,13,10
msg_cursor:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Cursor position:"
msg_memory:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Memory Size:"
msg_cyles:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Cyls:"
msg_heads:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Heads:"
msg_sectors:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Sectors:"
msg_kb:
.ascii "KB"
.org 510
boot_flag:
.word 0xAA55
回到linux-0.11目录下,执行命令:
$ make clean
$ make BootImage
$ …/run
运行截图
补充:
硬盘基本参数表: