文章目录
本节讲解 如何使用OpenMV通过串口来发送数据
OpenMV 是可以直接通过串口发送字符串的。
为什么要用串口呢?因为要时候需要把信息传给其他MCU(单片机),串口简单,通用,基本每一个MCU都会有串口。
TTL串口至少需要3根线:TXD,RXD,GND。TXD是发送端,RXD是接收端,GND是地线。 连线的时候,需要把OpenMV的RXD连到另一个MCU的TXD,TXD连到RXD,GND与GND相连。图示:
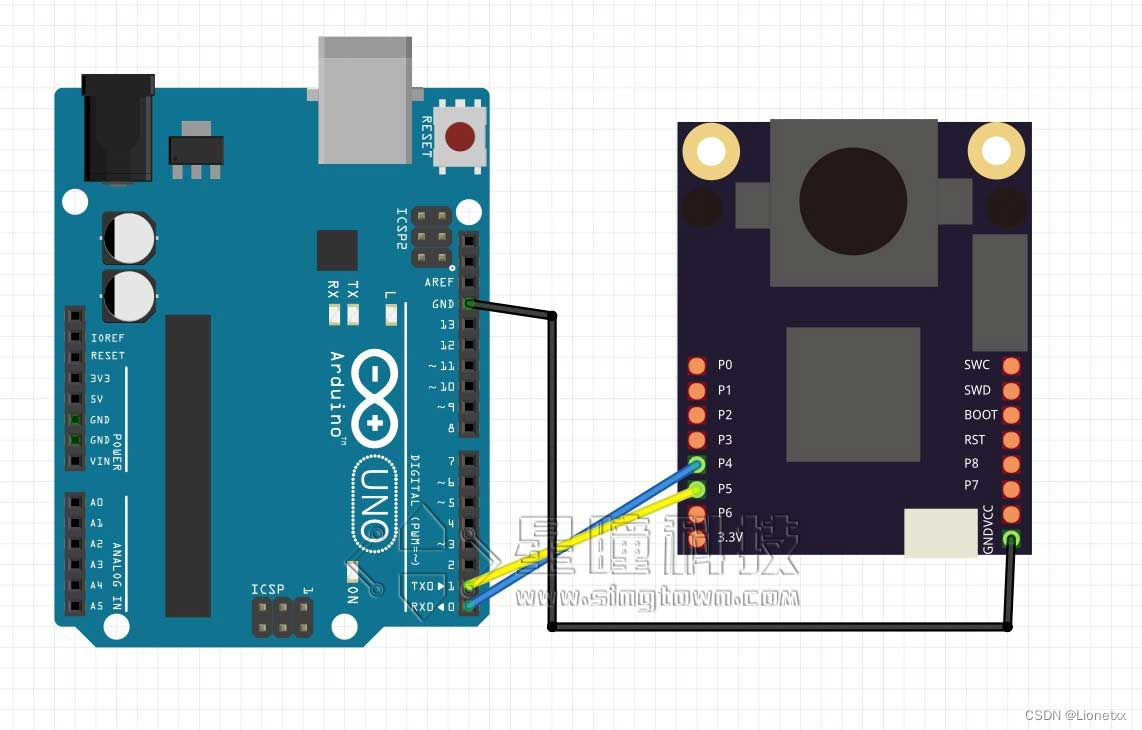
基本上所有单片机都有串口,因此我们可以使用OpenMV的串口来给任何其他的单片机或者是设备来传输信息
如果我们需要查看OpenMV上串口的信息,我们需要额外的设备(示波器或USB转串口模块)
OpenMV有一个扩展板——>串口调试扩展板,它可以直接通过这个USB把数据传到电脑上
产品
打开详细页面,里面有个星瞳串口助手的软件,我们需要下载下来,只有安装了这个软件才能查看上面的数据
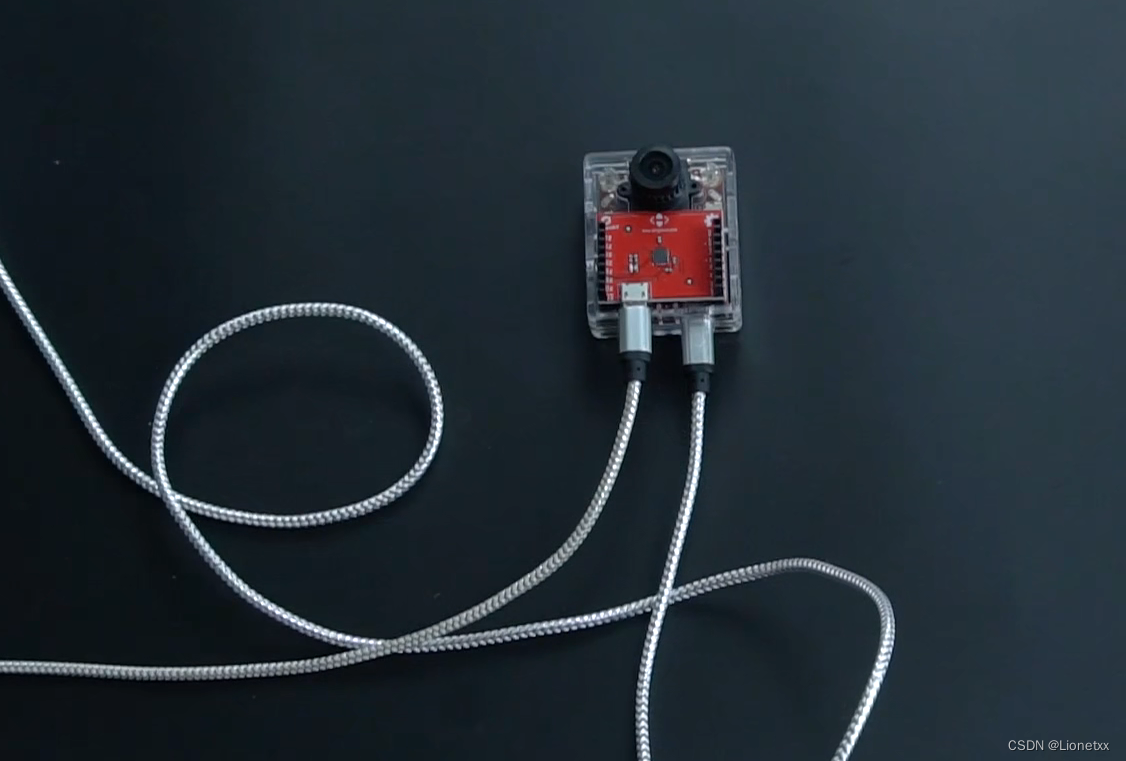

我们把OpenMV连接上扩展板,并且串口的USB数据线要连接到电脑上,OpenMV的数据线也要连接到电脑上
Hello World
运行串口例子
# UART 控制
#
# 这个例子展示了如何使用OpenMV的串口。连接P4到 USB转串口模块 的RX。
# 会显示"Hello World!"
import time
from pyb import UART
# 先实例化一个19200波特率的串口3,然后调用write方法就可以了。
# OpenMV上P4,P5对应的串口3
# 第二个参数是波特率。用来更精细的控制
uart = UART(3, 19200, timeout_char=1000)#
while(True):
uart.write("Hello World!\r")# OpenMV 是可以直接通过串口发送字符串的。
time.sleep_ms(1000)
或者
from pyb import UART
uart = UART(3, 9600)
string = "hello string!"
uart.write(string)
打开星瞳串口助手,选择串口,注意此时的波特率要和代码中的一致
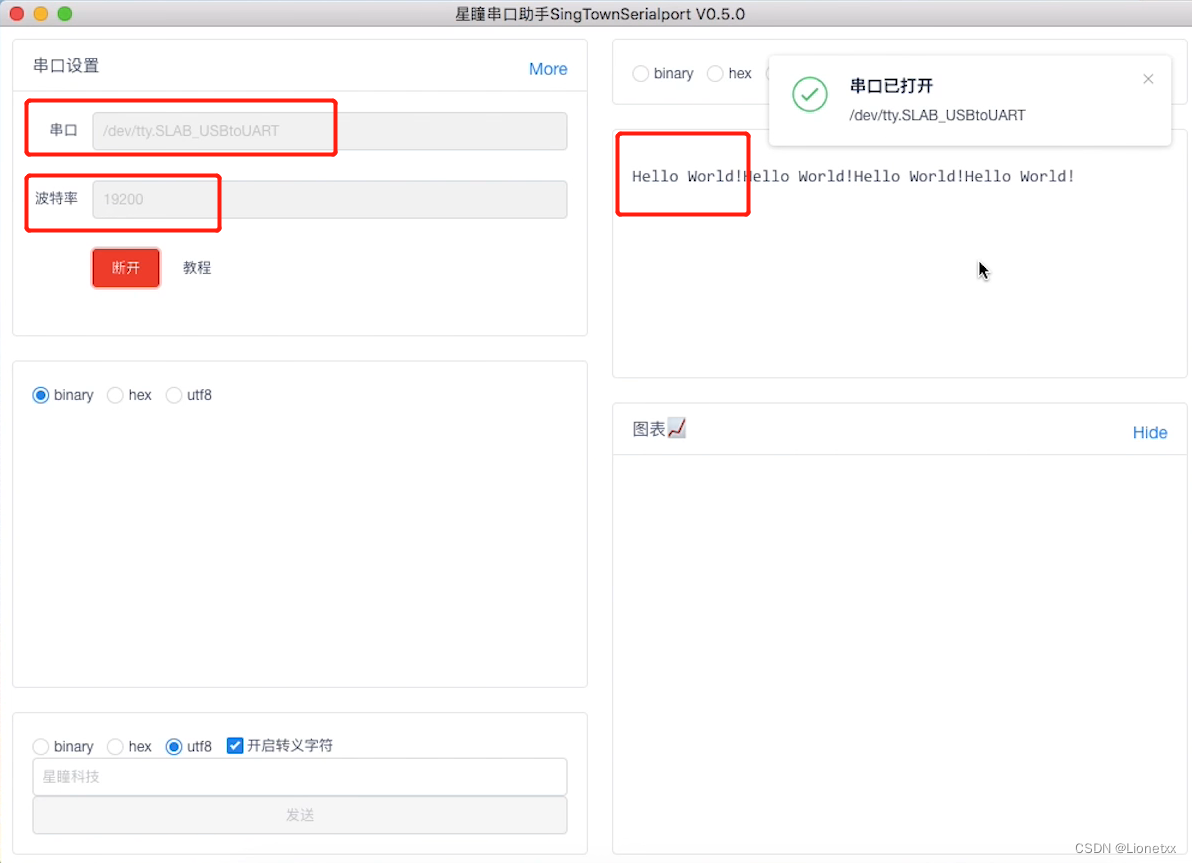
每当有数据传入,OpenMV上的灯就会闪一下
简单的数据发送
但是有时候不想传输一大堆的数据。比如:我只想传输面积最大的色块的x,y中心坐标。
想传输什么数据,就构造一个什么数据。
写一个for循环,再写一个find_max()函数。
以寻找最大色块为例,返回最大色块的中心cx(),cy()
# 色块检测 与 串口通信
import sensor, image, time
# 导入串口类
from pyb import UART
import json
# 为了使颜色跟踪工作得很好,理想情况下,你应该在一个周围因素(亮度等)受控的环境中,那里的照明是恒定的。。。
#
yellow_threshold = (65, 100, -10, 6, 24, 51) # 此处是一个黄色的阈值,我们可以用这个黄色阈值来查找色块
# 您可以按照不同的需要调整以上设置以跟踪其他颜色的内容
# 在帧缓冲区中选择一个区域以复制颜色设置。
sensor.reset() # Initialize the camera sensor.
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # use RGB565.
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) # use QQVGA for speed.
sensor.skip_frames(10) # Let new settings take affect.
sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # turn this off.
clock = time.clock() # Tracks FPS.
# 实例化一个串口对象,设置对应的串口号,设置波特率
uart = UART(3, 115200)
# 在视野中找到最大的一个色块
def find_max(blobs):
max_size=0
for blob in blobs:
if blob.pixels() > max_size:# blob.pixels()返回从属于色块(int)一部分的像素数量。
max_blob=blob
max_size = blob.pixels()
return max_blob
while(True):
img = sensor.snapshot() # Take a picture and return the image.
blobs = img.find_blobs([yellow_threshold])
if blobs:# 如果找到了色块
max_blob=find_max(blobs)
print('sum :', len(blobs))
img.draw_rectangle(max_blob.rect())
img.draw_cross(max_blob.cx(), max_blob.cy())
output_str="[%d,%d]" % (max_blob.cx(),max_blob.cy()) #方式1 把数据(最大色块的中心xy坐标)拼成一个字符串
#output_str=json.dumps([max_blob.cx(),max_blob.cy()]) #方式2
print('you send:',output_str)
# 调用uart.write()把"字符串"传输出去
uart.write(output_str+'\r\n')
else:
print('not found!')
结果:sum表示视野中的小球,you send的内容则是最大小球的cx,cy
sum : 6
you send: [63,45]
sum : 2
you send: [60,50]
sum : 1
you send: [61,51]
Arduino代码
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("来点代码");
}
void loop() {
if(Serial.available())
{
//if(Serial.read()=='[')
char data = Serial.read() ;
Serial.print(data);
if(Serial.read()==',')
Serial.print(',');
if(Serial.read()==']')
Serial.println();
}
}