任何知识都是用进废退,有段时间没摸linux,这大脑里的知识点仿佛全部消失了,就无语。 索性,再写一篇记录,加强一下记忆,下次需要就看自己的资料好了。
lsof命令
Linux端口查询命令可以通过lsof实现:
lsof : List Open Files的缩写,可列出各种进程打开的文件信息,如下图所示:
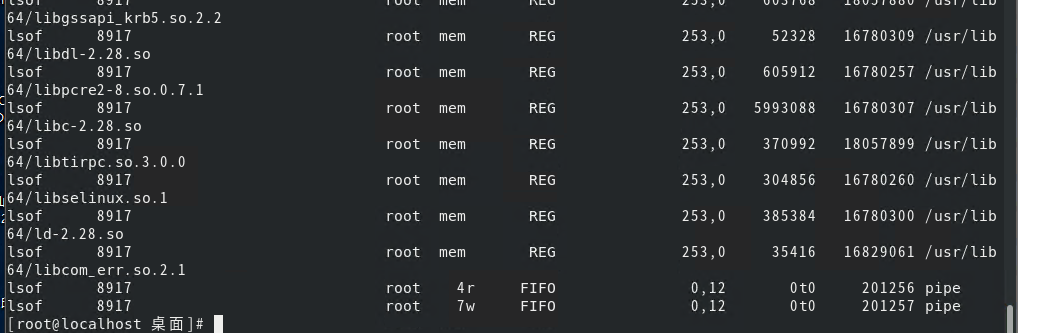
直接使用lsof 命令得出的是当前所有的信息,会有很多,因此一般可以通过结合参数来获取更加精确的信息,命令的具体参数,我们可以通过 --help 命令来查询:
[root@localhost 桌面]# lsof --help
lsof: illegal option character: -
lsof: -e not followed by a file system path: "lp"
lsof 4.91
latest revision: ftp://lsof.itap.purdue.edu/pub/tools/unix/lsof/
latest FAQ: ftp://lsof.itap.purdue.edu/pub/tools/unix/lsof/FAQ
latest man page: ftp://lsof.itap.purdue.edu/pub/tools/unix/lsof/lsof_man
usage: [-?abhKlnNoOPRtUvVX] [+|-c c] [+|-d s] [+D D] [+|-E] [+|-e s] [+|-f[gG]]
[-F [f]] [-g [s]] [-i [i]] [+|-L [l]] [+m [m]] [+|-M] [-o [o]] [-p s]
[+|-r [t]] [-s [p:s]] [-S [t]] [-T [t]] [-u s] [+|-w] [-x [fl]] [--] [names]
Defaults in parentheses; comma-separated set (s) items; dash-separated ranges.
-?|-h list help -a AND selections (OR) -b avoid kernel blocks
-c c cmd c ^c /c/[bix] +c w COMMAND width (9) +d s dir s files
-d s select by FD set +D D dir D tree *SLOW?* +|-e s exempt s *RISKY*
-i select IPv[46] files -K [i] list|(i)gn tasKs -l list UID numbers
-n no host names -N select NFS files -o list file offset
-O no overhead *RISKY* -P no port names -R list paRent PID
-s list file size -t terse listing -T disable TCP/TPI info
-U select Unix socket -v list version info -V verbose search
+|-w Warnings (+) -X skip TCP&UDP* files -Z Z context [Z]
-- end option scan
-E display endpoint info +E display endpoint info and files
+f|-f +filesystem or -file names +|-f[gG] flaGs
-F [f] select fields; -F? for help
+|-L [l] list (+) suppress (-) link counts < l (0 = all; default = 0)
+m [m] use|create mount supplement
+|-M portMap registration (-) -o o o 0t offset digits (8)
-p s exclude(^)|select PIDs -S [t] t second stat timeout (15)
-T qs TCP/TPI Q,St (s) info
-g [s] exclude(^)|select and print process group IDs
-i i select by IPv[46] address: [46][proto][@host|addr][:svc_list|port_list]
+|-r [t[m<fmt>]] repeat every t seconds (15); + until no files, - forever.
An optional suffix to t is m<fmt>; m must separate t from <fmt> and
<fmt> is an strftime(3) format for the marker line.
-s p:s exclude(^)|select protocol (p = TCP|UDP) states by name(s).
-u s exclude(^)|select login|UID set s
-x [fl] cross over +d|+D File systems or symbolic Links
names select named files or files on named file systems
Anyone can list all files; /dev warnings disabled; kernel ID check disabled.
[root@localhost 桌面]#
常用的结合命令使用的参数有:
查看某个端口的对应进程: lsof -i:port:

查看某个协议的某个端口情况:lsof -i 协议:port:

netstat 命令
netstat 命令,查看网络状态情况:

netstat --help :

查看端口的网络状态情况以及进程信息:netstat -a |grep port
-a;显示所有的连接的socket ; grep 在返回的信息中查找后面的内容

一般通过这个命令就可以查询到之后关键字的进程,但是不知道端口的监听情况
telnet命令
除去以上方法可以确认某端口的情况,还可以通过telnet命令去确认某个远程主机上的端口开放情况:
telnet ip port:
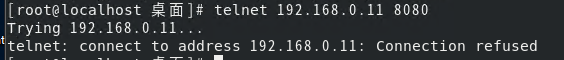
上图的情况,只能确认不能连接,但是不能确认:到底是主机就已经连不上,还是只是端口没开放访问,结合ping命令即可确认:
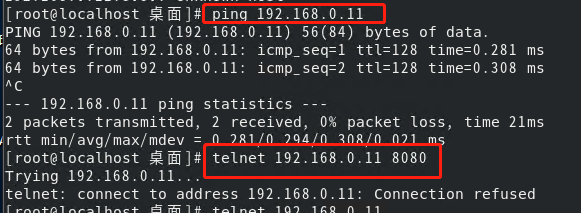
能ping通,不能连上端口,就看看端口对应进程启动没有,端口号开放没有即可。 端口号开放可参考另一篇:https://blog.csdn.net/yeyuningzi/article/details/127546854