url结构化/模块化/路径解析
结构化:url.parse(urlString[, parseQueryString[, slashesDenoteHost]])
模块化:url.format(urlObject)
路径解析:url.resolve(from, to)
一个URL字符串是一个结构化的字符串包含多个有意义的组件。在解析时,返回一个URL对象包含每一个组件的属性。
官方手册上面的一张图是这样子的: 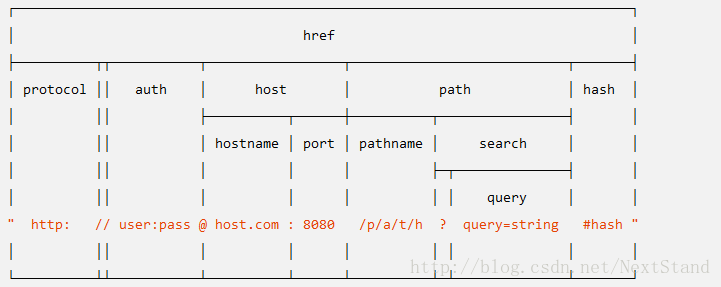
这张图解释了一个url结构化成哪些部分,哪些部分又包含哪些部分
protocol: 使用协议
slashes: true
host: URL主机名已全部转换成小写, 包括端口信息
auth: URL中身份验证信息部分
hostname:主机的主机名部分, 已转换成小写
port: 主机的端口号部分
pathname: URL的路径部分,位于主机名之后请求查询之前
search: URL 的“查询字符串”部分,包括开头的问号。
path: pathname 和 search 连在一起。
query: 查询字符串中的参数部分(问号后面部分字符串),或者使用 querystring.parse() 解析后返回的对象。
hash: URL 的 “#” 后面部分(包括 # 符号)
url结构化
将一个url地址结构化成为拥有上图属性的url对象。url.parse第二个和第三个参数默认为false。
- 第二个参数决定query属性值是字符串还是对象
- 第三个参数如果为true,//后的第一个令牌文字字符串和下一个/之间的文字字符串将被解释为主机
例子如下:
const url = require("url");
var urlstr = "http://localhost:8888/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC";
var urlobj = url.parse(urlstr);
console.log(urlobj);
/*
Url {
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'localhost:8888',
port: '8888',
hostname: 'localhost',
hash: null,
search: '?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
query: 'name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
pathname: '/bb',
path: '/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
href: 'http://localhost:8888/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC' }
*/第二个参数为true时
query: { name: ‘bigbear’, memo: [ ‘helloworld’, ‘helloC’ ] },
例子如下:
const url = require("url");
var urlstr = "http://localhost:8888/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC";
console.log(
url.parse(urlstr, true)
)
/*
Url {
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'localhost:8888',
port: '8888',
hostname: 'localhost',
hash: null,
search: '?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
query: { name: 'bigbear', memo: [ 'helloworld', 'helloC' ] },
pathname: '/bb',
path: '/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
href: 'http://localhost:8888/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC' }
*/第三个参数对比
例子如下:
const url = require("url");
var urlstr = "//foo/bar ";
console.log(
url.parse(urlstr, true,true)
)
/*
输出:Url {
protocol: null,
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'foo',
port: null,
hostname: 'foo',
hash: null,
search: '',
query: {},
pathname: '/bar',
path: '/bar',
href: '//foo/bar' }
*/
const url = require("url");
var urlstr = "//foo/bar ";
console.log(
url.parse(urlstr)
)
/*
输出:
Url {
protocol: null,
slashes: null,
auth: null,
host: null,
port: null,
hostname: null,
hash: null,
search: null,
query: null,
pathname: '//foo/bar',
path: '//foo/bar',
href: '//foo/bar' }
*/url模块化
将一个url对象转换成一个url字符串,url对象中的属性为url.parse()产生的对象的属性。
url.parse()和url.format()互为逆操作。
例子如下:
const url = require("url");
var Urlobj = {
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'localhost:8888',
port: '8888',
hostname: 'localhost',
hash: null,
search: '?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
query: { name: 'bigbear', memo: [ 'helloworld', 'helloC' ] },
pathname: '/bb',
path: '/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC',
}
console.log(
url.format(Urlobj)
)
//输出:http://localhost:8888/bb?name=bigbear&memo=helloworld&memo=helloC路径解析:url.resolve(from, to)
url.resolve()方法解决了目标URL相对于基本URL的方式类似于Web浏览器解决锚标记href。
官方手册例子:
url.resolve('/one/two/three', 'four');
// '/one/two/four'
url.resolve('http://example.com/', '/one');
// 'http://example.com/one'
url.resolve('http://example.com/one', '/two');
// 'http://example.com/two'