Spike the bounty hunter is tracking another criminal through space. Luckily for him hyperspace travel has made the task of visiting several planets a lot easier. Each planet has a number of Astral Gates; each gate connects with a gate on another planet. These hyperspace connections are, for obvious safety reasons, one-way only with one gate being the entry point and the other gate being the exit point from hyperspace. Furthermore, the network of hyperspace connections must be loop-free to prevent the Astral Gates from exploding, a tragic lesson learned in the gate accident of 20222022 that destroyed most of the moon.
While looking at his star map Spike wonders how many friends he needs to conduct a search on every planet. Each planet should not be visited by more than one friend otherwise the criminal might get suspicious and flee before he can be captured. While each person can start at a planet of their choosing and travel along the hyperspace connections from planet to planet they are still bound by the limitations of hyperspace travel.
Input Format
The input begins with an integer NN specifying the number of planets (0 < N \le 1000)(0<N≤1000). The planets are numbered from 00 to N-1N−1. The following NN lines specify the hyperspace connections.
The i-th of those lines first contains the count of connections KK (0\le K\le N-1)(0≤K≤N−1) from planet ii followed by KK integers specifying the destination planets.
Output Format
Output the minimum number of persons needed to visit every planet.
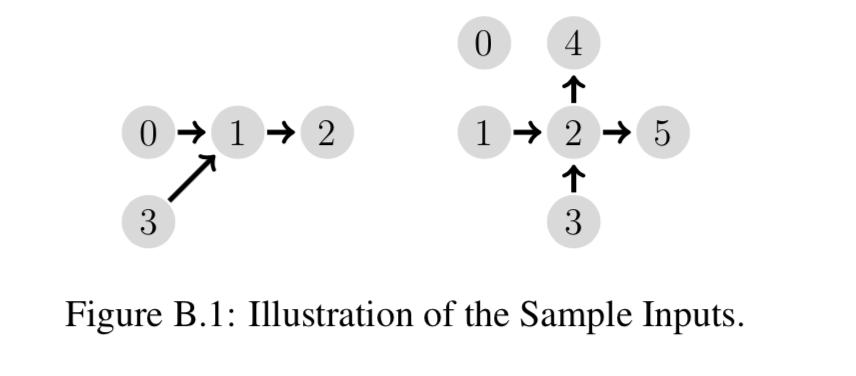
样例输入1
4 1 1 1 2 0 1 1
样例输出1
2
样例输入2
6 0 1 2 2 4 5 1 2 0 0
样例输出2
4
题目来源
German Collegiate Programming Contest 2015
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N =1e3+5;
vector<int >ve[2*N];
int n;
int vis[2*N];
int mat[2*N];
bool hungary(int u)
{
int sz=ve[u].size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++){
int v=ve[u][i];
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=1;
if(mat[v]==-1||hungary(mat[v]))
{
mat[v]=u;
return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
void solve(int n)
{
memset(mat,-1,sizeof(mat));
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
if(hungary(i)) cnt++;
}
cout<<n-cnt<<endl;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int k,v;
cin>>k;
for(int j=1;j<=k;j++){
cin>>v;
v+=n;
ve[i].push_back(v);
}
}
solve(n);
return 0;
}