前言
本文是学习《从零开始造Spring》的学习笔记。
为什么要实现AOP
AOP全名Aspect-Oriented Programming,中文直译为面向切面(方面)编程。何为切面,就比如说我们系统中的权限管理,日志,事务等我们都可以将其看成一个个切面。
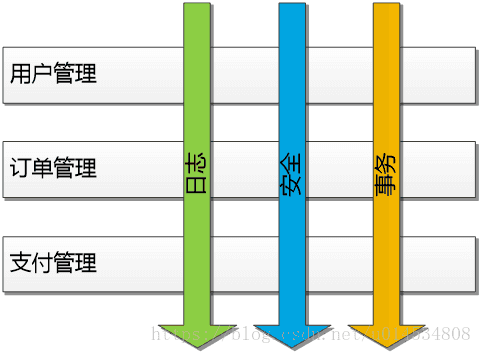
在传统的OOP编程中,一些与业务无关的,日志,安全,事务,性能等代码与业务代码牢牢交织在一起。如下图所示:有订单管理,用户管理,订单管理等业务模块。每个模块都实现了自己的日志,安全,事务,性能统计。
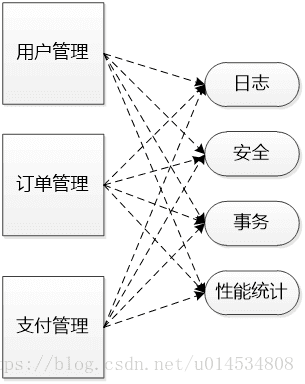
如果我们修改了业务代码就需要修改相应的日志代码。
使用了AOP之后我们可以将日志,安全,事务,性能统计等代码作为一个切面。切入到业务代码中。
AOP的基本概念
- Joint Point (连接点)
被拦截到的点,在Spring AOP中通常是方法类型(a point during the execution of a program, such as the execution of a method or the handling of an exception) - Pointcut(切入点)
对连接点进行拦截的定义,在程序中主要体现为书写的切点表达式
(a predicate that matches join points)
例如:execution(* org.litespring.service.v5.*.placeOrder(..)) - Advice(通知)
AOP在特定的切入点上执行的增强处理,有before,after,afterReturning,afterThrowing,around等通知
(action taken at a particular join point
Many AOP frameworks, including Spring, model an advice as an interceptor, maintaining a chain of interceptors around the join point.
) - Before advice(前置通知)
在连接点之前的通知(Advice that executes before a join point) - After returning advice(后置通知)
在连接点之后的通知,没有抛出异常(Advice to be executed after a join point completes normally: for example, if a method returns without throwing an exception) - After throwing advice(异常通知)
如果方法抛出异常的通知(Advice to be executed if a method exits by throwing an exception) - After (finally) advice (finally 通知)
不过连接点的方法是否正常或者抛出异常,都会执行的通知
(Advice to be executed regardless of the means by which a join point exits (normal or exceptional return) ) - Around advice (环绕通知)
在连接点之前或者之后都可以执行的通知。可以全局的在方法前后自定义行为。
(Advice that surrounds a join point such as a method invocation, Around advice can perform custom behavior before and after the method invocation)
详情参见:spring-framework源码第4弹——Spring AOP的简单实现(学习tiny-spring)
AOP的简单应用
怎么实现AOP
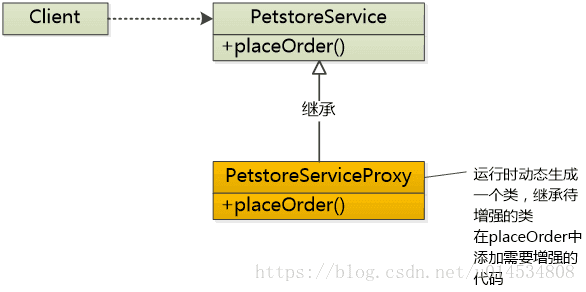
AOP是在运行期通过动态代理生成代理类的方式对方法进行增强的。
首先我们在petstore-v5.xml 中增加如下配置
<bean id="tx" class="com.jay.spring.tx.TransactionManager"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="tx">
<aop:pointcut id="placeOrder" expression="execution(* com.jay.spring.service.v5.*.placeOrder(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="placeOrder" method="start"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="placeOrder" method="commit"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="placeOrder" method="rollback"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>测试代码
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("petstore-v5.xml");
PetStoreService petStore = (PetStoreService)ctx.getBean("petStore");
- CGLib动态代理
在运行时动态生成一个类,继承待增强的类,在placeOrder中添加需要增强的代码,CGLib动态代理实际上是应用于类的代理。如图所示:
- Java 动态代理
Java 动态代理是应用于接口的代理。
—————————————完美的分割—————————————–
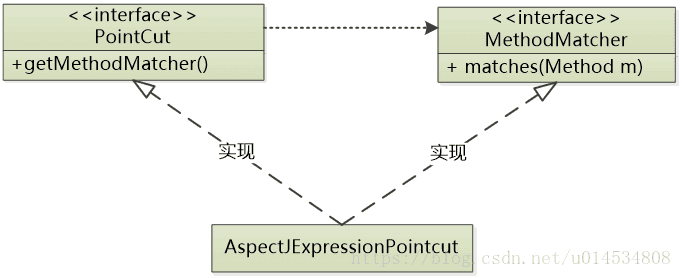
1.实现Pointcut和MethodMatcher
XML中的配置:
<aop:pointcut id="placeOrder"
expression="execution(* org.litespring.service.v5.*.placeOrder(..))" />PointCut 接口依赖于MethodMatcher 接口,MethodMatcher 接口主要是通过给定的类的方法,判断该方法是否符合pointcut的表达式。
关键代码
public void setExpression(String expression){
this.expression = expression;
}
public boolean matches(Method method/*, Class<?> targetClass*/) {
checkReadyToMatch();
ShadowMatch shadowMatch = getShadowMatch(method);
if (shadowMatch.alwaysMatches()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private ShadowMatch getShadowMatch(Method method) {
ShadowMatch shadowMatch = null;
try {
shadowMatch = this.pointcutExpression.matchesMethodExecution(method);
}
catch (ReflectionWorldException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("not implemented yet");
/*try {
fallbackExpression = getFallbackPointcutExpression(methodToMatch.getDeclaringClass());
if (fallbackExpression != null) {
shadowMatch = fallbackExpression.matchesMethodExecution(methodToMatch);
}
}
catch (ReflectionWorldException ex2) {
fallbackExpression = null;
}*/
}
return shadowMatch;
}
private void checkReadyToMatch() {
if (getExpression() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Must set property 'expression' before attempting to match");
}
if (this.pointcutExpression == null) {
this.pointcutClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
this.pointcutExpression = buildPointcutExpression(this.pointcutClassLoader);
}
}
private PointcutExpression buildPointcutExpression(ClassLoader classLoader) {
PointcutParser parser = PointcutParser
.getPointcutParserSupportingSpecifiedPrimitivesAndUsingSpecifiedClassLoaderForResolution(
SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES, classLoader);
/*PointcutParameter[] pointcutParameters = new PointcutParameter[this.pointcutParameterNames.length];
for (int i = 0; i < pointcutParameters.length; i++) {
pointcutParameters[i] = parser.createPointcutParameter(
this.pointcutParameterNames[i], this.pointcutParameterTypes[i]);
}*/
return parser.parsePointcutExpression(replaceBooleanOperators(getExpression()),
null, new PointcutParameter[0]);
}代码简单解释:
根据给定的expression字符串表达式,生成一个PointcutExpression 对象,然后,根据这个对象去匹配传入的方法。然后将匹配的结果放入ShadowMatch 对象中。如果匹配成功则返回shadowMatch.alwaysMatches() 为true, 否则为false。
测试代码:
@Test
public void testPointcut() throws Exception{
String expression = "execution(* org.litespring.service.v5.*.placeOrder(..))";
AspectJExpressionPointcut pc = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pc.setExpression(expression);
MethodMatcher mm = pc.getMethodMatcher();
{
Class<?> targetClass = PetStoreService.class;
Method method1 = targetClass.getMethod("placeOrder");
Assert.assertTrue(mm.matches(method1));
Method method2 = targetClass.getMethod("getAccountDao");
Assert.assertFalse(mm.matches(method2));
}
{
Class<?> targetClass = org.litespring.service.v4.PetStoreService.class;
Method method = targetClass.getMethod("getAccountDao");
Assert.assertFalse(mm.matches(method));
}
}- 实现MethodLocatingFactory
<bean id="tx" class="com.jay.spring.tx.TransactionManager"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="tx">
<aop:pointcut id="placeOrder" expression="execution(* com.jay.spring.service.v5.*.placeOrder(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="placeOrder" method="start"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="placeOrder" method="commit"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="placeOrder" method="rollback"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>MethodLocatingFactory 类的主要作用是通过Bean的名称(“tx”)和方法名(“start”)定位到这个Method,然后通过反射调用!
关键代码:
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.targetBeanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetBeanName' is required");
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.methodName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'methodName' is required");
}
Class<?> beanClass = beanFactory.getType(this.targetBeanName);
if (beanClass == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't determine type of bean with name '" + this.targetBeanName + "'");
}
this.method = BeanUtils.resolveSignature(this.methodName, beanClass);
if (this.method == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to locate method [" + this.methodName +
"] on bean [" + this.targetBeanName + "]");
}
} public Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
BeanDefinition bd = this.getBeanDefinition(name);
if (bd == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(name);
}
resolveBeanClass(bd);
return bd.getBeanClass();
}public void resolveBeanClass(BeanDefinition bd) {
if (bd.hasBeanClass()) {
return;
} else {
try {
bd.resolveBeanClass(this.getBeanClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("can't load class:"+bd.getBeanClassName());
}
}
}源码下载:
https://github.com/XWxiaowei/spring-learn/tree/testcase-v6-aop-1/liu-spring-demo