1.概述
网络中传输数据总是以字节类型传输,当然传输的方式多种多样,当然效率也参差不齐。常见的BIO、NIO它们之间对比写法在此不做解释,详细可看之前的博客>>IO模型和>>>BIO和NIO+Reactor。本篇这讨论Netty中的传输,然而Netty为他所有的传输实现提供了一个通用的API,这使得我们的开发变得极为简单。
通过Netty使用OIO和NIO
public class NettyDemo {
private int prot;
public NettyDemo(int prot) {
this.prot = prot;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new NettyDemo(9111).satart();
}
public void satart() throws InterruptedException {
final ServerHandller serverHandller = new ServerHandller();
final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello", Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
//创建ServerBootstrap实例
ServerBootstrap boot = new ServerBootstrap();
//为非阻塞模式NioEventLoopGroup
//EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//为阻塞模式OioEventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup group = new OioEventLoopGroup();
//指定实例来接受和处理新的连接。
boot.group(group)
//指定使用NIO Channel传输
//.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.channel(OioSctpServerChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(prot))
//当一个新的连接被接受时,一个新的子Channel会被创建,
// ChannelInitializer会把serverHandller的实例加入到该Channel的ChannelPipeLine
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf.duplicate())
//添加一个Listener,当消息被写完就关闭连接
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
});
}
});
try {
//异步绑定到服务器,调用sync方法阻塞当前线程,直到绑定完成
ChannelFuture future = boot.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}可以看出NIO、OIO传输只有两行代码的变化。正是因为Netty为每种传输的实现提供了相同的API,所以不管选哪种代码几乎不受影响。这都的归功于Channel、ChannelPipeline、ChannelHandler接口。
细节
每个Channel的实现都会被分配一个ChannelPipeline和ChannelConfig。ChannelConfig中包含了该Channel的所有配置,支持热跟新。
2.Netty中的传输
Netty中提供了几种传输,不是所有的传输都支持每一种协议,所以应该在我们的程序中选择适当的传输。
Netty提供的传输
- NIO:使用Java提供的NIO作为基础,基于选择器的方式
- Epoll:由JNI驱动的epoll()和非阻塞IO,只支持Linux
- OIO:Java提供的net包作为基础
- Local:在VM内部通过管道进行通信的本地传输
- Embedded:Embedded传输,一般用于测试
ChannelHandller
2.1.NIO–非阻塞IO
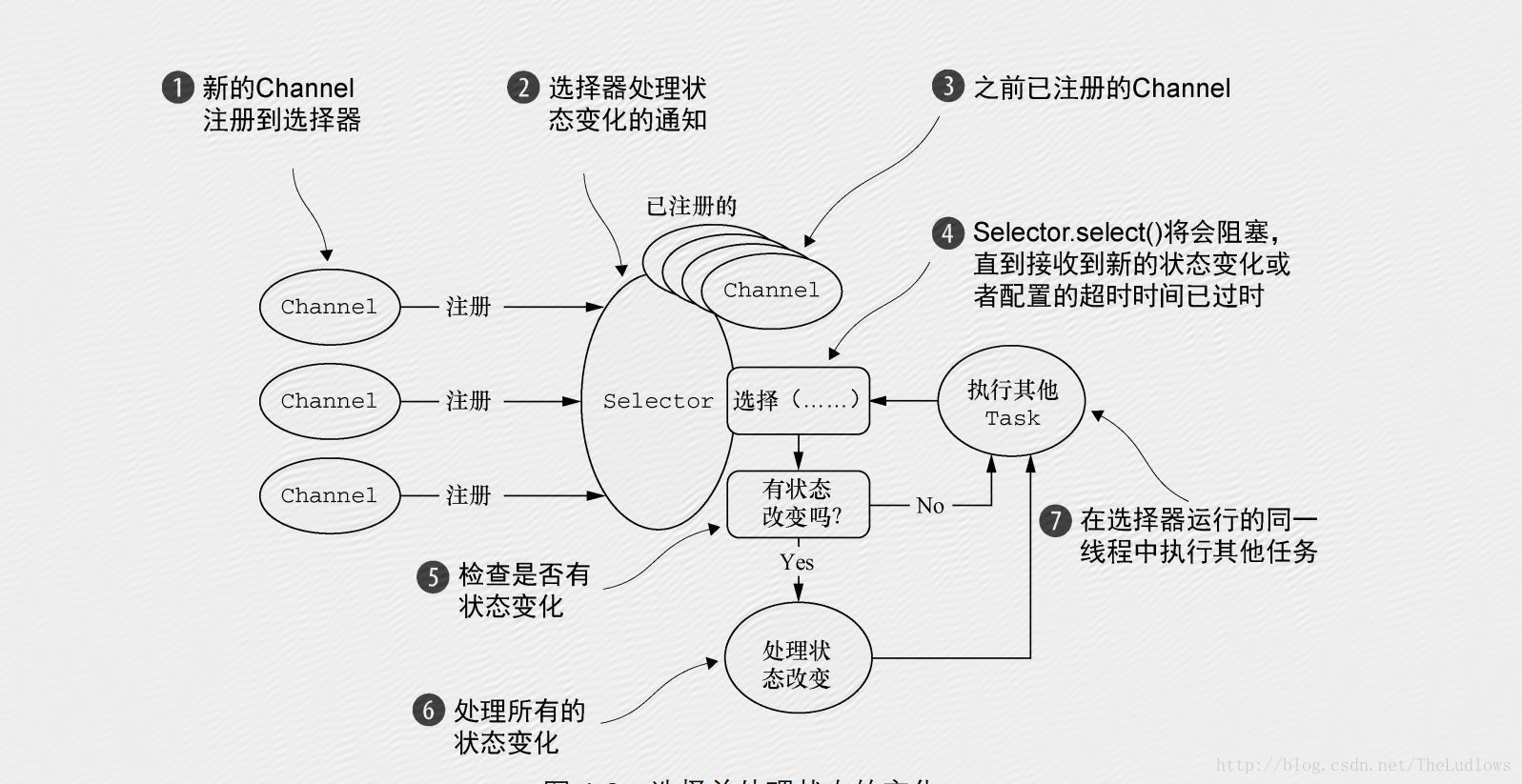
之前的博客说了很多,在这直接上图很清晰的解释了NIO
下一篇:http://blog.csdn.net/theludlows/article/details/79501241