TDD的Demo
M:什么是TDD?
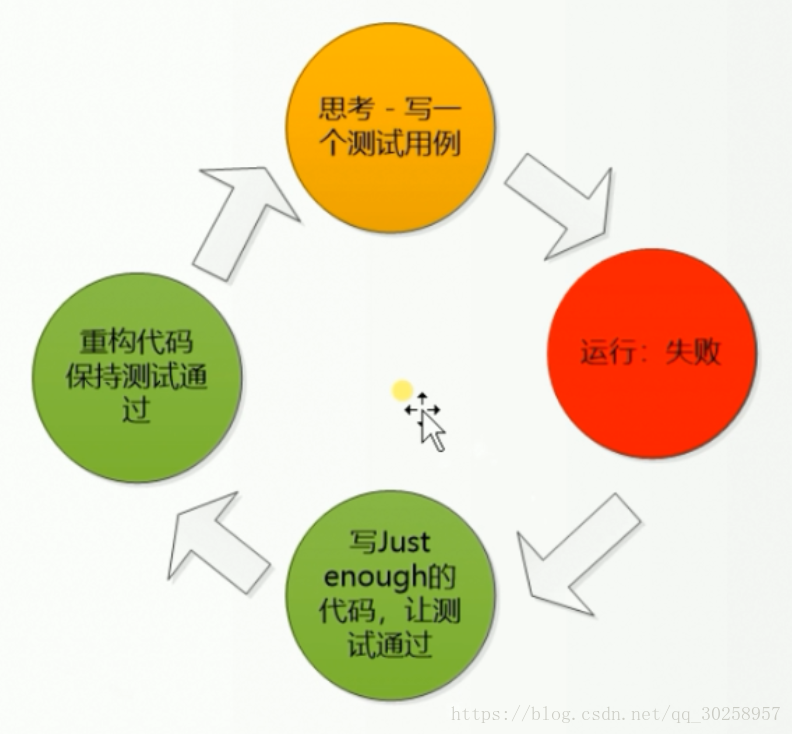
Z:TDD是测试驱动开发(Test-Driven Development)的英文简称,是敏捷开发中的一项核心实践和技术,也是一种设计方法论。TDD的原理是在开发功能代码之前,先编写单元测试用例代码,测试代码确定需要编写什么产品代码。
M:那具体要怎么做呢?
Z: 如下
M:能写一个Demo么?
Z:TDD开发Demo:测试会返回所有素数数组的方法(边界版)
测试案例可能有哪些:边界数据 , 正常数据
边界数据:0,-1,2
正常数据:9,17,30
创建测试用例:测试边界条件
@Test public void testGetPrimesForEmptyResult() { int[] expected = {}; Assert.assertArrayEquals(expected, PrimeUtil.getPrimes(2)); Assert.assertArrayEquals(expected, PrimeUtil.getPrimes(0)); Assert.assertArrayEquals(expected, PrimeUtil.getPrimes(-1)); }运行失败尝试:写一个有问题的测试对象,保证案例具有判断能力
public class PrimeUtil { public static int[] getPrimes(int i){ return null; } }编写功能代码,通过测试案例
public static int[] getPrimes(int max){ if(max <= 2){ return new int[]{}; } return null; }重构,这里代码很简洁,无需再进行重构。
Z:TDD开发Demo:测试会返回所有素数数组的方法(正常版)
编写测试案例:
@Test public void testGetPrimes(){ Assert.assertArrayEquals(new int[]{2,3,5,7}, PrimeUtil.getPrimes(9)); Assert.assertArrayEquals(new int[]{2,3,5,7,11,13}, PrimeUtil.getPrimes(17)); Assert.assertArrayEquals(new int[]{2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29}, PrimeUtil.getPrimes(30)); }运行失败尝试,没有代码,返回失败
编写功能代码,通过测试案例
public static int[] getPrimes(int max){ if(max <= 2){ return new int[]{}; }else{ int[] newArray = new int[max]; int size = 0; int j = 0; for(int i=2 ; i < max ; i++){ for (j = 2; j < i/2+1; j++) { if(i % j == 0){ break; } } if(j == i/2+1){ newArray[size++] = i; } } newArray = Arrays.copyOf(newArray, size); return newArray; } }重构,虽然这段代码通过了测试案例,但是其编写很复杂,可以重构如下:
- 重命名(无需测试)
public static int[] getPrimes(int max){ if(max <= 2){ return new int[]{}; }else{ int[] primes = new int[max]; int count = 0; int j = 0; for(int num=2 ; num < max ; num++){ for (j = 2; j < num/2+1; j++) { if(num % j == 0){ break; } } if(j == num/2+1){ primes[count++] = num; } } primes = Arrays.copyOf(primes, count); return primes; } }- 提取函数(测试)
public static int[] getPrimes(int max){ if(max <= 2){ return new int[]{}; }else{ int[] primes = new int[max]; int count = 0; for(int num=2 ; num < max ; num++){ if(isPrime(num)){ primes[count++] = num; } } primes = Arrays.copyOf(primes, count); return primes; } } private static boolean isPrime(int num) { for (int j = 2; j < num/2+1; j++) { if(num % j == 0){ return false; } } return true; }- 分支进行调整(测试)
public static int[] getPrimes(int max){ if(max <= 2){ return new int[]{}; } int[] primes = new int[max]; int count = 0; for(int num=2 ; num < max ; num++){ if(isPrime(num)){ primes[count++] = num; } } primes = Arrays.copyOf(primes, count); return primes; } private static boolean isPrime(int num) { for (int i = 2; i < num/2+1; i++) { if(num % i == 0){ return false; } } return true; }
M:到这里,边界条件和正常输入的测试用例就都通过了。总结一下,TDD开发方式:
- 分析,编写不同方面的测试用例
- 每个测试用例之前先确保Junit具有报错能力,做个错误的返回测试
- 编写实现代码
- 对代码进行重构:先重构名称,提取方法,修改结构