在ASP.NET MVC 5中,身份验证分别有三种方式。分别为使用FormsAuthentication、MemberShip和Identity进行验证。
(PS:本系列的逻辑代码请勿直接用于生产,请自己多加一层抽象后再投入使用)
为了展示这三种方式,我们先新建一个MVC项目。
为了方便,我们创建一个类用来验证身份。
public class AccountHelper { [Required] public string UserName { get; set; } [Required] public string Password { get; set; } }
方式一:FormsAuthentication
在使用任何一种验证方法之前,我们需要创建一个视图用以进行登录,然后在这个视图中创建一个form用以提交数据
public ActionResult Login() { return View(); }
视图代码:
@model Authority.Models.AccountHelper @{ ViewBag.Title = "Index"; } <h2>Index</h2> <p>Please log in to access the administration area:</p> @using (Html.BeginForm()) { @Html.ValidationSummary() <div class="form-group"> <label>User name</label> @Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.UserName, new { @class = "form-control" }) </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Password</label> @Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.Password, new { @class = "form-control" }) </div> <input type="submit" value="Log In" class="btn-primary" /> }
然后我们需要在Web.config中对验证方式进行配置。

<authentication mode="Forms"> <forms loginUrl="~/FormsAuthentication/Login" timeout="2880"> <credentials passwordFormat="Clear"> <user name="admin" password="secret" /> </credentials> </forms> </authentication>
接着需要创建一个方法用来接收form元素所提交的数据,对数据进行验证并保留Cookie,对验证成功后返回另一个视图。
[HttpPost] public ActionResult Login(AccountHelper helper,string returnUrl) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { if (FormsAuthentication.Authenticate(helper.UserName, helper.Password)) { FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(helper.UserName,false); return Redirect(returnUrl ?? Url.Action("AfterAuthority",helper)); } else { ModelState.AddModelError("", "Error account or password"); return View(); } } return View(); }
对验证成功后的视图进行简单的定义。
[Authorize] public ActionResult AfterAuthority(AccountHelper helper) { return View(helper); }
@model Authority.Models.AccountHelper @{ ViewBag.Title = "AfterAuthority"; } <h2>AfterAuthority</h2> <p>Your Username is: @Model.UserName</p> <p>Your Password is: @Model.Password</p>
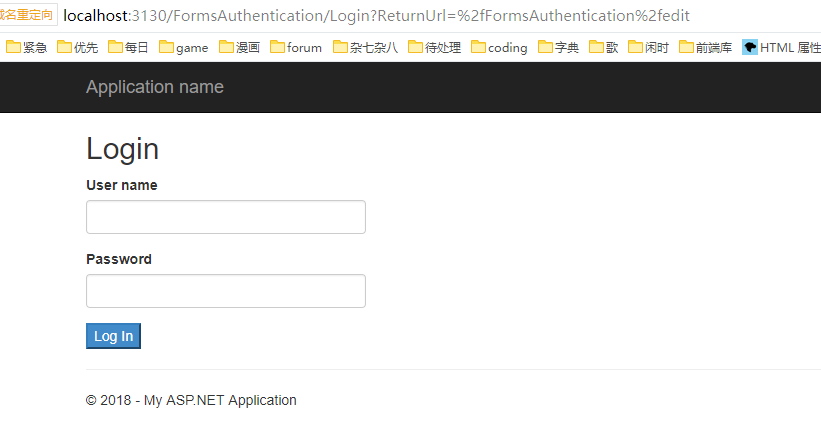
其中Login方法的returnUrl 用于未在 Login 处进行验证而直接访问带有 [Authorize] 修饰的视图时,在验证后可返回原来访问的地址。假如我对一个Edit视图(该视图后面会定义)进行访问它会直接返回至Login方法并带有ReturnUrl字段:
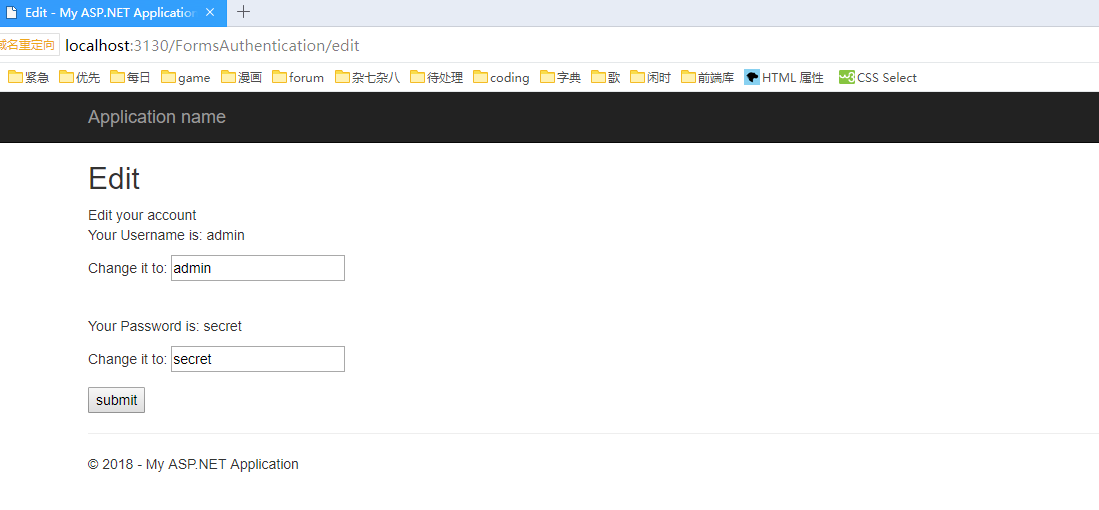
而在验证之后通过returnUrl直接返回至Edit方法。
那么问题来了,要是我想增加更多的用户或者修改现有的账户该怎么办呢?这时候我们就需要对Web.config直接进行修改了。但在这之前我们需要有一个对象用来保存我们现在账户的信息,因此我们需要对Login方法也进行一定的修改:
static AccountHelper account=new AccountHelper(); [HttpPost] //returnUrl 用于未在 Login 处进行验证而直接访问带有 [Authorize] 修饰的视图时,在验证后可返回原来访问的地址。 public ActionResult Login(AccountHelper helper,string returnUrl) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { if (FormsAuthentication.Authenticate(helper.UserName, helper.Password)) { account.UserName = helper.UserName; account.Password = helper.Password; FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(helper.UserName,false); return Redirect(returnUrl ?? Url.Action("AfterAuthority",account)); } else { ModelState.AddModelError("", "Error account or password"); return View(); } } return View(); }
于是,我们可以创建一个用于修改现有账户的视图了。
[Authorize] public ActionResult Edit() { return View(account); }
@model Authority.Models.AccountHelper @{ ViewBag.Title = "Edit"; } <h2>Edit</h2> <p>Your Password is: @Model.Password</p> <div>Edit your account</div> @using (Html.BeginForm()) { <div class="form-group"> <p>Your Username is: @Model.UserName</p> <p>Change it to: @Html.EditorFor(m => m.UserName)</p> </div> <br /> <div class="form-group"> <p>Your Password is: @Model.Password</p> <p>Change it to: @Html.EditorFor(m => m.Password)</p> </div> <input type="submit" value="submit"/> }
[HttpPost] [Authorize] public ActionResult Edit(AccountHelper changedAccount) { XmlDocument doc=new XmlDocument(); //获得配置文件的全路径 string strFileName = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory+"Web.Config"; doc.Load(strFileName); XmlNodeList nodes = doc.GetElementsByTagName("user"); for (int i = 0; i < nodes.Count; i++) { string _name = nodes[i].Attributes["name"]==null? "":nodes[i].Attributes["name"].Value; if (_name==account.UserName) { nodes[i].Attributes["name"].Value = changedAccount.UserName; nodes[i].Attributes["password"].Value = changedAccount.Password;
//清除Cookie FormsAuthentication.SignOut(); break; } } //将修改后的 Web.config 进行保存 doc.Save(strFileName); return View("AfterAuthority",changedAccount); }

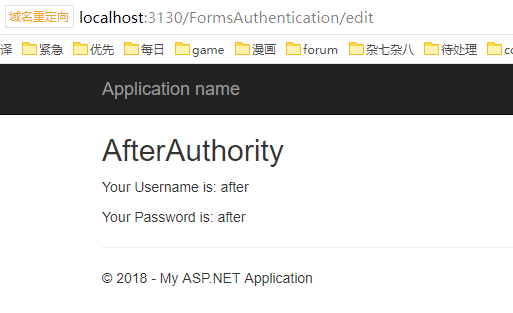
刷新之后:
以修改前的账户登录:
至此修改现有账号的任务完成。
而新增账户不过将XML元素的修改改成插入。
[Authorize] public ActionResult Add() { return View(); } [HttpPost] [Authorize] public ActionResult Add(AccountHelper newAccount) { XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument(); //获得配置文件的全路径 string strFileName = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + "Web.Config"; doc.Load(strFileName); XmlNodeList nodes = doc.GetElementsByTagName("user"); XmlNode credentials = nodes[0].ParentNode; XmlNode child = nodes[0].Clone(); child.Attributes["name"].Value = newAccount.UserName; child.Attributes["password"].Value = newAccount.Password; credentials.AppendChild(child); //将修改后的 Web.config 进行保存 doc.Save(strFileName); return View("Create", newAccount); }
Add视图:
@model Authority.Models.AccountHelper @{ ViewBag.Title = "Add"; } <h2>Create Account</h2> @using (Html.BeginForm()) { <div class="form-group"> <p>UserName: @Html.EditorFor(m => m.UserName)</p> <p>Password: @Html.EditorFor(m => m.Password)</p> </div> <input type="submit" value="submit"/> }
Create视图:
@model Authority.Models.AccountHelper @{ ViewBag.Title = "Create Success"; } <h2>Successfully</h2> <p>UserName: @Model.UserName</p> <p>Password: @Model.Password</p>
但是问题又来了,总不能什么人都可以对账户进行修改或增添用户吧,因此我们需要使用自定义特性,通过继承AuthorizeAttribute获得和AuthorizeAttribute同样的效果,通过继承IAuthenticationFilter对账户进行过滤,在此我们限制Add方法只有admin这一账户可以使用:
public class AdminAccountAttribute : AuthorizeAttribute, IAuthenticationFilter { public void OnAuthentication(AuthenticationContext filterContext) { IIdentity identity = filterContext.Principal.Identity; if (identity.Name!="admin" || !identity.IsAuthenticated) { filterContext.Result = new HttpUnauthorizedResult(); } } public void OnAuthenticationChallenge(AuthenticationChallengeContext filterContext) { if (filterContext.Result == null || filterContext.Result is HttpUnauthorizedResult) { filterContext.Result = new RedirectToRouteResult(new RouteValueDictionary() { {"controller","FormsAuthentication" }, { "action","Login"}, {"returnUrl",filterContext.HttpContext.Request.RawUrl } }); } } }
然后将该修饰用于Add之上:
[AdminAccount] public ActionResult Add() { return View(); } [HttpPost] [AdminAccount] public ActionResult Add(AccountHelper newAccount) {
于是我们便只有admin用户可以对Web.config进行增添用户的操作了。
通过一个非admin用户访问Add页面,返回Login页面。

通过admin用户访问Add页面则返回Add页面。

至此,一个完整的登录系统达成。如果需要什么额外的逻辑也可自行添加。
但是由于使用FormsAuthentication.Authenticate需要使用Web.config,在Web.config直接对账户和密码进行配置,过于繁琐、不安全且扩展性差,对配置文件进行显式的修改更是增添了风险;同时,如果需要对用户的账号或者密码进行限制我们便需要进行硬编码。该方法早已被弃用,之后ASP.NET推出了Membership.ValidateUser方法解决这一情况,而现在更是有了Identity用来更进一步地提高扩展性。
源代码地址:
https://github.com/NanaseRuri/FormsAuthentication