一. AXI 有5个通道:
1.写地址通道信号;
2.写数据通道信号;
3.写响应通道;
4.读地址通道;
5.读数据通道;
二. 什么是支持 outstanding
Outstanding 支持的多少是需要设定的。举个例子,如果 outstanding设为5,对于写来说,可以连续发送5个写操作而不用等待bresponse的响应,否则必须等待有一个responese回来才能发送下一个写操作,对于读来说,是通过rlast信号来看是否有respone,也类似于写操作;也就是说,如果没有respone的操作超过了outstanding的值,则会通过拉低响应的ready信号,从而不能发送有效操作;
三、 各个通道的时序关系:
1、读地址通道:
output [0: 0] master_axi_arid; // axi read command ID
output [35: 0] master_axi_araddr; // axi read command address
output [3:0] master_axi_arlen; // axi encoded read command length
output [2:0] master_axi_arsize; // axi encoded read command size
output [1:0] master_axi_arburst; // axi read command burst type.
output [1:0] master_axi_arlock; // axi atomic access indicator
output [3:0] master_axi_arcache; // axi cache control os for the read.
output [2:0] master_axi_arprot; // axi read command protection type.
output master_axi_arvalid; // axi read command valid indicator.
input master_axi_arready; // indicates that axi is ready to accept the read command.
2、读数据通道:
Input [0:0] master_axi_rid; // axi read data ID.
Input [255:0] master_axi_rdata ; // axi read data.
Input [1:0] master_axi_rresp ; // aix read data response a response is sent with each burst indicating the status of the burst.
input master_axi_rlast; // Indicates that this is the final world of the data for the command.
input master_axi_rvalid; // axi read data valid indicator.
output master_axi_rready; // indicates that the axi master is ready to accept read data.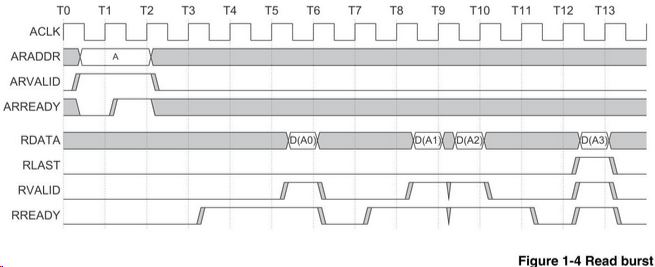
4.写地址通道:
output [ 0: 0] master_axi_awid; // axi write command ID
output [35: 0] master_axi_awaddr; // axi write command address
output [ 3:0] master_axi_awlen; // axi encoded write command length
output [ 2:0] master_axi_awsize; // axi encoded write command size
output [ 1:0] master_axi_awburst; // axi write command burst type.
output [ 1:0] master_axi_awlock; // axi atomic access indicator
output [ 3:0] master_axi_awcache; // axi cache control os for the read.
output [ 2:0] master_axi_awprot; // axi read command protection type.
output master_axi_awprot; // axi read command valid indicator.
input master_axi_awready; // indicates that aix is ready to accept the read command.
5.写数据通道:
output [ 0:0] master_axi_wid; // axi write data ID.
output [255:0] master_axi_wdata ; // axi write data.
output [ 31:0] master_axi_wstrb ; // axi write data strobe.
output master_axi_wlast; // Indicates that this is the final world of the data for the command.
output master_axi_wvalid; // axi write data valid indicator.
input master_axi_0_wready; // indicates that the axi master is ready to accept write data.
6.写响应通道:
input [0:0] master_axi_bid; // AXI write respone ID.
input [1:0] master_axi_bresp; // AXI write respone A responese is sent for the entire burst.
input master_axi_bvalid; // AXI write response valid indicator.
input master_axi_bready; // Indicates that the AXI master is ready to accepta write respone.