实验目的
(1) 理解设计模式的基本概念;
(2) 理解设计模式遵循的原则;
(3) 掌握经典设计模式及应用。
实验内容
一、能播放各种声音的软件产品(理解开-闭原则(Open-Closed Principle,OCP–对扩展开放-而对修改关闭)。写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
- 类图:

- Sound.java:
public interface Sound {
public abstract void playSound();
}
- Simulator.java:
public class Simulator {
Sound sound;
public void setSound(Sound sound) {
this.sound=sound;
}
public void play() {
if(sound!=null) {
sound.playSound();
} else {
System.out.println("没有可播放的声音");
}
}
}
- Dog.java:
public class Dog implements Sound {
public void playSound() {
System.out.println("汪汪...汪汪");
}
}
- Violin.java:
public class Violin implements Sound {
public void playSound() {
System.out.println("小提琴.梁祝");
}
}
- Application.java
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Simulator simulator = new Simulator();
simulator.setSound(new Dog());
simulator.play();
simulator.setSound(new Violin());
simulator.play();
}
}
二、简单工厂模式–女娲造人。写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
女娲架起了八卦炉(技术术语:建立工厂),开始造人。
过程如下:先捏泥巴成人形,再放入八卦炉里烤,最后扔到地上成长。时间烤短了,造出了“白种人”;时间烤长了,造出了“黑种人”;时间烤得不长不短,造出了“黄种人”。
- 类图:

- Human.java:
public interface Human {
public void talk();
}
- HumanFactory.java:
public class HumanFactory {
public static Human createHuman(String s) {
Human human=null;
if(s.equals(new String("whiteHuman")))
human=new WhiteHuman();
if(s.equals(new String("yellowHuman")))
human=new YellowHuman();
return human;
}
}
- YellowHuman.java:
public class YellowHuman implements Human {
public void talk() {
System.out.println("您好!");
}
}
- BlackHuman.java:
public class BlackHuman implements Human {
public void talk() {
System.out.println("黑吼!");
}
}
- WhiteHuman.java:
public class WhiteHuman implements Human {
public void talk() {
System.out.println("Hello!");
}
}
- NvWa.java:
public class NvWa {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Human human=HumanFactory.createHuman("yellowHuman");
human.talk();
}
}
三、工厂方法模式–女娲造人。写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
- 类图:

- Human.java:
public interface Human {
public void talk();
}
- HumanFactory.java:
public interface HumanFactory {
public Human createHuman();
}
- YellowHuman.java:
public class YellowHuman implements Human {
public void talk() {
System.out.println("您好!");
}
}
- WhiteHuman.java:
public class WhiteHuman implements Human {
public void talk() {
System.out.println("Hello!");
}
}
- BlackHuman.java:
public class BlackHuman implements Human {
public void talk() {
System.out.println("嘿嘿");
}
}
- YellowHumanF.java:
public class YellowHumanF implements HumanFactory {
public Human createHuman() {
return new YellowHuman();
}
}
- BlackHumanF.java:
public class BlackHumanF implements HumanFactory {
public Human createHuman() {
return new BlackHuman();
}
}
- WhiteHumanF.java:
public class WhiteHumanF implements HumanFactory {
public Human createHuman() {
return new WhiteHuman();
}
}
- NvWa.java:
public class NvWa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HumanFactory humanFactory=null;
humanFactory=new WhiteHumanF();
Human human=humanFactory.createHuman();
human.talk();
}
}
四、适配器模式–交流电转直流电。写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
用户家里现有一台洗衣机,洗衣机使用交流电,现在用户新买了一台录音机,录音机只能使用直流电。由于供电系统供给用户家里的是交流电,因此用户需要用适配器将交流电转化直流电供录音机使用。
- 类图:

- DirectCurrent.java:
public interface DirectCurrent {
public String giveDirectCurrent();
}
- AlternateCurrent.java:
public interface AlternateCurrent {
public String giveAlternateCurrent();
}
- ElectricAdapter.java:
public class ElectricAdapter implements DirectCurrent {
AlternateCurrent out;
ElectricAdapter(AlternateCurrent out) {
this.out=out;
}
public String giveDirectCurrent() {
String m=out.giveAlternateCurrent(); //先由out得到交流电
StringBuffer str=new StringBuffer(m);
for (int i=0; i<str.length(); i++) //将交流电转为直流电
if(str.charAt(i)=='0') str.setCharAt(i,'1');
m=new String(str);
return m; //返回直流电
}
}
- PowerCompany.java:
public class PowerCompany implements AlternateCurrent {
public String giveAlternateCurrent() {
return "10101010101010101010";
}
}
- Application.java
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AlternateCurrent aElectric = new PowerCompany(); //交流电aElectric
Wash wash=new Wash();
wash.turnOn(aElectric); //洗衣机使用交流电aElectric
DirectCurrent dElectric=new ElectricAdapter(aElectric); //将交流电适配成直流电
Recorder recorder=new Recorder();
recorder.turnOn(dElectric); //录音机使用直流电dElectric
}
}
class Wash {
String name;
Wash() { name = "洗衣机"; }
public void turnOn(AlternateCurrent a) {
String s = a.giveAlternateCurrent();
System.out.println(name+"使用交流电:\n"+s);
System.out.println("开始洗衣物。");
}
}
class Recorder { //录音机使用直流电
String name;
Recorder() { name = "录音机"; }
public void turnOn(DirectCurrent a) {
String s=a.giveDirectCurrent();
System.out.println(name+"使用直流电:\n"+s);
System.out.println("开始录音。");
}
}
五、策略模式–评分方案。写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
在多个裁判负责打分的比赛中,每位裁判给选手一个得分,选手的最后得分是根据全体裁判的得分计算出来的。请给出几种计算选手得分的评分方案(策略),对于某次比赛,可以从你的方案中选择一种方案作为本次比赛的评分方案。
- 类图:

- Strategy.java:
public interface Strategy {
public double computerAverage(double []a);
}
- AverageScore.java:
public class AverageScore {
Strategy strategy;
public void setStrategy(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy=strategy;
}
public double getAverage(double []a) {
return strategy.computerAverage(a);
}
}
- StrategyA.java:
public class StrategyA implements Strategy {
public double computerAverage(double []a) {
double score=0,sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
sum=sum+a[i];
}
score=sum/a.length;
return score;
}
}
- StrategyB.java:
public class StrategyB implements Strategy {
public double computerAverage(double []a) {
if(a.length<=2)
return 0;
double score=0,sum=0;
Arrays.sort(a); //排序数组
for (int i=1; i<a.length-1; i++) {
sum=sum+a[i];
}
score=sum/(a.length-2);
return score;
}
}
- Application:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AverageScore game=new AverageScore();
game.setStrategy(new StrategyA());
double []a={9.12,9.25,8.87,9.99,6.99,7.88};
double aver=game.getAverage(a);
System.out.println(aver);
}
}
五、状态模式–自动售货机。写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
咖啡自动售货机共有3种状态,分别是“有咖啡,无人投币”、“有咖啡,有人投币”和“无咖啡”。咖啡自动售货机有两个方法:needAnCoin( )和sellCoffee( )。
咖啡自动售货机的默认初始状态是“有咖啡,无人投币”。当咖啡自动售货机处于“有咖啡,无人投币”状态时,调用sellCoffee( )方法将显示“需投一元硬币,才可以得到一杯咖啡”,并保持当前的状态;调用needAnCoin( )方法将显示“咖啡机里被投入了一元硬币”,然后咖啡自动售货机将处于“有咖啡,有人投币”状态,此时,如果调用sellCoffee( )方法将显示“送出一杯咖啡”,然后咖啡自动售货机将处于“有咖啡,无人投币”状态或“无咖啡”状态;当咖啡白动售货机处于“无咖啡”状态时,调用giveAnCupCoffee( )方法将显示“没有咖啡了,请拨111111服务电话”,调用needAnCoin( )方法将显示“投币无效,退回!”
请使用状态模式模拟咖啡自动售货机。
- 类图
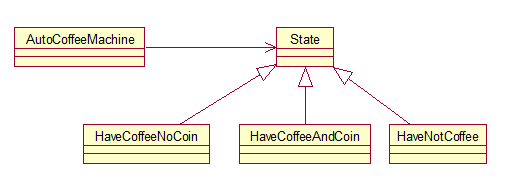
- State.java:
public abstract class State{
int coffeeCount; //记录一共有多少杯咖啡
public abstract void giveAnCupCoffee();
public abstract void comeInCoin();
}
- AutoCoffeeMachine.java:
public class AutoCoffeeMachine {
State haveCoffeeNoCoin,haveCoffeeAndCoin,haveNotCoffee;
State state;
AutoCoffeeMachine( ){
haveCoffeeNoCoin=new HaveCoffeeNoCoin(this);
haveCoffeeAndCoin=new HaveCoffeeAndCoin(this);
haveNotCoffee=new HaveNotCoffee(this);
haveCoffeeNoCoin.coffeeCount=3;
state=haveCoffeeNoCoin; //设置售货机初始状态
}
public void sellCoffee( ){ state.giveAnCupCoffee( ); }
public void needAnCoin( ){ state.comeInCoin( ); }
public void setState(State state){ this.state=state; }
}
- HaveCoffeeAndCoin.java:
public class HaveCoffeeAndCoin extends State{
AutoCoffeeMachine machine;
HaveCoffeeAndCoin(AutoCoffeeMachine machine){
this.machine=machine; }
public void giveAnCupCoffee( ){
int n=machine.haveCoffeeNoCoin.coffeeCount;
if(n>1) { n--;
System.out.println("送出一杯咖啡");
machine.haveCoffeeNoCoin.coffeeCount = n;
machine.setState(machine.haveCoffeeNoCoin);
} else if(n==1) { n--;
System.out.println("送出一杯咖啡");
machine.setState(machine.haveNotCoffee); }
}
public void comeInCoin( ){
System.out.println("目前不允许投币");
}
}
- HaveCoffeeNoCoin.java
public class HaveCoffeeNoCoin extends State{
AutoCoffeeMachine machine;
HaveCoffeeNoCoin(AutoCoffeeMachine machine){
this.machine=machine;
}
public void giveAnCupCoffee(){
System.out.println("需投入一元,才可得一杯");
}
public void comeInCoin(){
System.out.println("投入了一元硬币");
machine.setState(machine.haveCoffeeAndCoin); }
}
- HaveNotCoffee.java:
public class HaveNotCoffee extends State{
AutoCoffeeMachine machine;
HaveNotCoffee(AutoCoffeeMachine machine){
this.machine=machine;
}
public void giveAnCupCoffee( ){
System.out.println("没咖啡了,请拨111111");
}
public void comeInCoin( ){
System.out.println("投币无效,退回!");
}
}
- Application.java:
public class Application{
public static void main(String args[ ]){
AutoCoffeeMachine machine = new AutoCoffeeMachine( );
machine.sellCoffee( ); machine.needAnCoin( );
machine.sellCoffee( ); machine.needAnCoin( );
machine.sellCoffee( ); machine.needAnCoin( );
machine.sellCoffee( ); machine.needAnCoin( );
machine.sellCoffee( );
}
}
体会:策略模式与状态模式极其相似,但是二者有其内在的差别,策略模式将具体策略类暴露出去,调用者需要具体明白每个策略的不同之处以便正确使用。而状态模式状态的改变是由其内部条件来改变的,与外界无关,二者在思想上有本质区别。
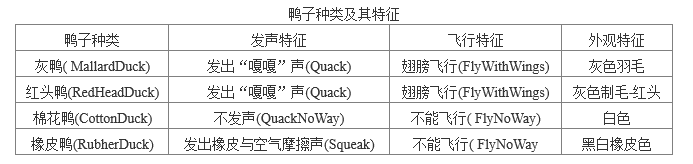
七、某游戏公司现欲开发一款面向儿童的模拟游戏,该游戏主要模拟现实世界中各种鸭子的发声特征、飞行特征和外观特征。游戏需要模拟的鸭子种类及其特征如下表所示。
为了支持将来能够模拟更多种类鸭子的特征,决定采用策略(Strategy)模式。试画出对应的设计模式的类图结构图。并写java文件、编译java文件、执行class文件。
- 类图:

- FlyBehavior.java:
public interface FlyBehavior {
public void fly();
}
- QuackBehavior.java:
public interface QuackBehavior {
public void quack();
}
- Duck.java:
public abstract class Duck {
protected FlyBehavior flyBehavior;
protected QuackBehavior quackBehavior;
public void setFlyBehavior(FlyBehavior flyBehavior) {
this.flyBehavior = flyBehavior;
}
public void setQuackBehavior(QuackBehavior quackBehavior) {
this.quackBehavior = quackBehavior;
}
public void setAppearance(String appearance) {
this.appearance = appearance;
}
private String appearance;
public void fly() { flyBehavior.fly(); }
public void quack() { quackBehavior.quack(); }
public void display(){
System.out.println(appearance);
}
}
- FlyWithWings.java:
public class FlyWithWings implements FlyBehavior {
public void fly() {
System.out.println("使用翅膀飞行");
}
}
- FlyNoWay.java:
public class FlyNoWay implements FlyBehavior {
public void fly() {
System.out.println("不能飞行");
}
}
- Quack.java:
public class Quack implements QuackBehavior {
public void quack() {
System.out.println("发出“嘎嘎”声");
}
}
- QuackNoWay.java:
public class QuackNoWay implements QuackBehavior {
public void quack() {
System.out.println("不能发声");
}
}
- Squeak.java:
public class Squeak implements QuackBehavior {
public void quack() {
System.out.println("发出橡皮与空气摩擦声");
}
}
- CottonDuck.java:
public class CottonDuck extends Duck{
CottonDuck() {
super();
super.setAppearance("白色");
super.setQuackBehavior(new QuackNoWay());
super.setFlyBehavior(new FlyNoWay());
}
}
- MallardDuck.java:
public class MallardDuck extends Duck {
MallardDuck(){
super();
super.setAppearance("灰白羽毛");
super.setQuackBehavior(new Quack());
super.setFlyBehavior(new FlyWithWings());
}
}
- RedHeadDuck.java:
public class RedHeadDuck extends Duck{
RedHeadDuck() {
super();
super.setAppearance("灰色制毛红头");
super.setQuackBehavior(new Quack());
super.setFlyBehavior(new FlyWithWings());
}
}
- RubherDuck.java:
public class RubherDuck extends Duck{
RubherDuck() {
super();
super.setAppearance("黑橡皮白色");
super.setQuackBehavior(new Squeak());
super.setFlyBehavior(new FlyNoWay());
}
}