Spring Data JPA 是 Spring Boot 体系中约定优于配置的最佳实现,大大简化了项目中数据库的操作。从本课开始将会从 JPA 的由来开始讲解,什么是 JPA、Spring Boot JPA 的实现,以及如何使用。
概念
JPA 由来
ORM 框架能够将 Java 对象映射到关系数据库中,能够直接持久化复杂的 Java 对象。ORM 框架的出现,可以让开发者从数据库编程中解脱出来,把更多的精力放在了业务模型与业务逻辑上。目前比较流行的 ORM 框架有 Hibernate、MyBatis、TopLink、Spring JDBC 等。
在 JPA 规范之前,由于没有官方的标准,使得各 ORM 框架之间的 API 差别很大,使用了某种 ORM 框架的系统会严重受制于该 ORM 的标准。基于此,Sun 引入新的 JPA ORM,主要的原因有:其一,简化现有 Java EE 和 Java SE 应用开发工作;其二,Sun 希望整合 ORM 技术,实现统一的 API 调用接口。
JPA 是什么
JPA(Java Persistence API)是 Sun 官方提出的 Java 持久化规范。它为 Java 开发人员提供了一种对象 / 关联映射工具来管理 Java 应用中的关系数据。它的出现主要是为了简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合 ORM 技术,结束现在 Hibernate、TopLink、JDO 等 ORM 框架各自为营的局面。
值得注意的是,JPA 是在充分吸收了现有的 Hibernate、TopLink、JDO 等 ORM 框架的基础上发展而来的,具有易于使用、伸缩性强等优点。从目前的开发社区的反应上看,JPA 受到了极大的支持和赞扬,其中就包括了 Spring 与 EJB 3.0 的开发团队。
注意:JPA 是一套规范,不是一套产品,那么像 Hibernate、TopLink、JDO 它们是一套产品,如果说这些产品实现了这个 JPA 规范,那么我们就可以称他们为 JPA 的实现产品。
Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA 是 Spring 基于 ORM 框架、JPA 规范的基础上封装的一套 JPA 应用框架,可以让开发者用极简的代码即可实现对数据的访问和操作。它提供了包括增、删、改、查等在内的常用功能,且易于扩展,学习并使用 Spring Data JPA 可以极大提高开发效率。Spring Data JPA 其实就是 Spring 基于 Hibernate 之上构建的 JPA 使用解决方案,方便在 Spring Boot 项目中使用 JPA 技术。
Spring Data JPA 让我们解脱了 DAO 层的操作,基本上所有 CRUD 都可以依赖于它实现。
快速上手
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.Springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加配置文件
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=create
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
#SQL 输出
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
#format 一下 SQL 进行输出
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto 参数的作用主要用于:自动创建、更新、验证数据库表结构,有四个值。
- create:每次加载 Hibernate 时都会删除上一次生成的表,然后根据 model 类再重新来生成新表,哪怕两次没有任何改变也要这样执行,这就是导致数据库表数据丢失的一个重要原因。
- create-drop:每次加载 Hibernate 时根据 model 类生成表,但是 sessionFactory 一关闭,表就自动删除。
- update:最常用的属性,第一次加载 Hibernate 时根据 model 类会自动建立起表的结构(前提是先建立好数据库),以后加载 Hibernate 时根据 model 类自动更新表结构,即使表结构改变了,但表中的行仍然存在,不会删除以前的行。要注意的是当部署到服务器后,表结构是不会被马上建立起来的,是要等应用第一次运行起来后才会。
- validate :每次加载 Hibernate 时,验证创建数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。
其中:
- dialect 主要是指定生成表名的存储引擎为 InneoDB
- show-sql 是否在日志中打印出自动生成的 SQL,方便调试的时候查看
实体类
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String userName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String passWord;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = true, unique = true)
private String nickName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String regTime;
//省略 getter settet 方法、构造方法
}
下面对上面用的注解做一个解释。
@Entity(name="EntityName")必须,用来标注一个数据库对应的实体,数据库中创建的表名默认和类名一致。其中,name 为可选,对应数据库中一个表,使用此注解标记 Pojo 是一个 JPA 实体。@Table(name="",catalog="",schema="")可选,用来标注一个数据库对应的实体,数据库中创建的表名默认和类名一致。通常和 @Entity 配合使用,只能标注在实体的 class 定义处,表示实体对应的数据库表的信息。@Id必须,@Id 定义了映射到数据库表的主键的属性,一个实体只能有一个属性被映射为主键。@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType,generator="")可选,strategy: 表示主键生成策略,有 AUTO、INDENTITY、SEQUENCE 和 TABLE 4 种,分别表示让 ORM 框架自动选择,generator: 表示主键生成器的名称。@Column(name = "user_code", nullable = false, length=32)可选,@Column 描述了数据库表中该字段的详细定义,这对于根据 JPA 注解生成数据库表结构的工具。name: 表示数据库表中该字段的名称,默认情形属性名称一致;nullable: 表示该字段是否允许为 null,默认为 true;unique: 表示该字段是否是唯一标识,默认为 false;length: 表示该字段的大小,仅对 String 类型的字段有效。@Transient可选,@Transient 表示该属性并非一个到数据库表的字段的映射,ORM 框架将忽略该属性。@Enumerated可选,使用枚举的时候,我们希望数据库中存储的是枚举对应的 String 类型,而不是枚举的索引值,需要在属性上面添加 @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING) 注解。
Repository 构建
创建的 Repository 只要继承 JpaRepository 即可,就会帮我们自动生成很多内置方法。另外还有一个功能非常实用,可以根据方法名自动生产 SQL,比如 findByUserName 会自动生产一个以 userName 为参数的查询方法,比如 findAll 会自动查询表里面的所有数据等。
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByUserName(String userName);
User findByUserNameOrEmail(String username,String email);
}
我们只需要在对应的 Repository 中创建好方法,使用的时候直接将接口注入到类中调用即可。在 IDEA 中打开类 UserRepository,在这个类的大括号内的区域右键单击,选择 Diagrams | Show Diagram 选项,即可打开类图,如下:
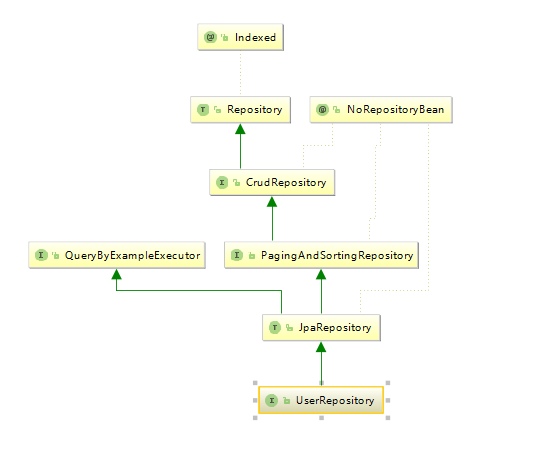
通过上图我们发现 JpaRepository 继承 PagingAndSortingRepository 和 QueryByExampleExecutor,PagingAndSortingRepository 类主要负责排序和分页内容,QueryByExampleExecutor 提供了很多示例的查询方法,如下:
public interface QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
<S extends T> S findOne(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”查找一个对象
<S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”查找一批对象
<S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort); //根据“实例”查找一批对象,且排序
<S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable); //根据“实例”查找一批对象,且排序和分页
<S extends T> long count(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”查找,返回符合条件的对象个数
<S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”判断是否有符合条件的对象
}
因此,继承 JpaRepository 的会自动拥有上述这些方法和排序、分页功能。查看源码我们发现 PagingAndSortingRepository 又继承了 CrudRepository。CrudRepository 的源码如下:
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
<S extends T> Iterable<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);
Optional<T> findById(ID id);
boolean existsById(ID id);
Iterable<T> findAll();
Iterable<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids);
long count();
void deleteById(ID id);
void delete(T entity);
void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
void deleteAll();
}
从 CrudRepository 的源码可以看出 CrudRepository 内置了我们最常用的增、删、改、查的方法,方便我们去使用,因为 JpaRepository 继承了 PagingAndSortingRepository,PagingAndSortingRepository 继承了 CrudRepository,所以继承 JpaRepository 的类也默认拥有了上述方法。
因此使用 JPA 操作数据库时,只需要构建的 Repository 继承了 JpaRepository,就会拥有了很多常用的数据库操作方法。
测试
创建好 UserRepository 之后,当业务代码中需要使用时直接将此接口注入到对应的类中,在 Spring Boot 启动时,会自动根据注解内容创建实现类并注入到目标类中。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserRepositoryTests {
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
public void test() {
Date date = new Date();
DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG, DateFormat.LONG);
String formattedDate = dateFormat.format(date);
userRepository.save(new User("aa", "[email protected]", "aa", "aa123456",formattedDate));
userRepository.save(new User("bb", "[email protected]", "bb", "bb123456",formattedDate));
userRepository.save(new User("cc", "[email protected]", "cc", "cc123456",formattedDate));
Assert.assertEquals(9, userRepository.findAll().size());
Assert.assertEquals("bb", userRepository.findByUserNameOrEmail("bb", "[email protected]").getNickName());
userRepository.delete(userRepository.findByUserName("aa1"));
}
}
上述测试方法简单测试了 JPA 的报错和查询功能,测试用例执行成功表示 JPA 的增、删、改成功。
基本查询
我们可以将 Spring Data JPA 查询分为两种,一种是 Spring Data JPA 默认实现的,另一种是需要根据查询的情况来自行构建。
预生成方法
预生成方法就是我们上面看到的那些方法,因为继承了 JpaRepository 而拥有了父类的这些内容。
(1)继承 JpaRepository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}
(2)使用默认方法
@Test
public void testBaseQuery() {
userRepository.findAll();
userRepository.findById(1l);
userRepository.save(user);
userRepository.delete(user);
userRepository.count();
userRepository.existsById(1l);
// ...
}
所有父类拥有的方法都可以直接调用,根据方法名也可以看出它的含义。
自定义查询
Spring Data JPA 可以根据接口方法名来实现数据库操作,主要的语法是 findXXBy、readAXXBy、queryXXBy、countXXBy、getXXBy 后面跟属性名称,利用这个功能仅需要在定义的 Repository 中添加对应的方法名即可,使用时 Spring Boot 会自动帮我们实现,示例如下。
根据用户名查询用户:
User findByUserName(String userName);
也可以加一些关键字 And、or:
User findByUserNameOrEmail(String username, String email);
修改、删除、统计也是类似语法:
Long deleteById(Long id);
Long countByUserName(String userName)
基本上 SQL 体系中的关键词都可以使用,如 LIKE 、IgnoreCase、OrderBy:
List<User> findByEmailLike(String email);
User findByUserNameIgnoreCase(String userName);
List<User> findByUserNameOrderByEmailDesc(String email);
可以根据查询的条件不断地添加和拼接,Spring Boot 都可以正确解析和执行,其他使用示例可以参考下表。
具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成 SQL 如下表所示
| Keyword | Sample | JPQL snippet |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is,Equals | findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEquals | … where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age ⇐ ?1 |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull | findByAgeIsNull | … where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection<Age> ages) | … where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection<Age> age) | … where x.age not in ?1 |
| TRUE | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true |
| FALSE | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
总结
通过这节课的学习发现使用 JPA 大大解放了我们对数据库的操作,经常使用的 SQL 大部分都已经被预生成,直接使用即可。另外 JPA 还有一个特点,那就是再也不用关心数据库的表结构了,需要更改的时候只需要修改对应 Model 的属性即可。在微服务架构中,因为服务拆分得越来越小,微服务内部只关心自己的业务,需要复杂查询的场景会越来越少,在微服务架构中更推荐使用 JPA 技术。