1、 分发层+应用层 的双层nginx架构,提升缓存命中率
缓存架构图:
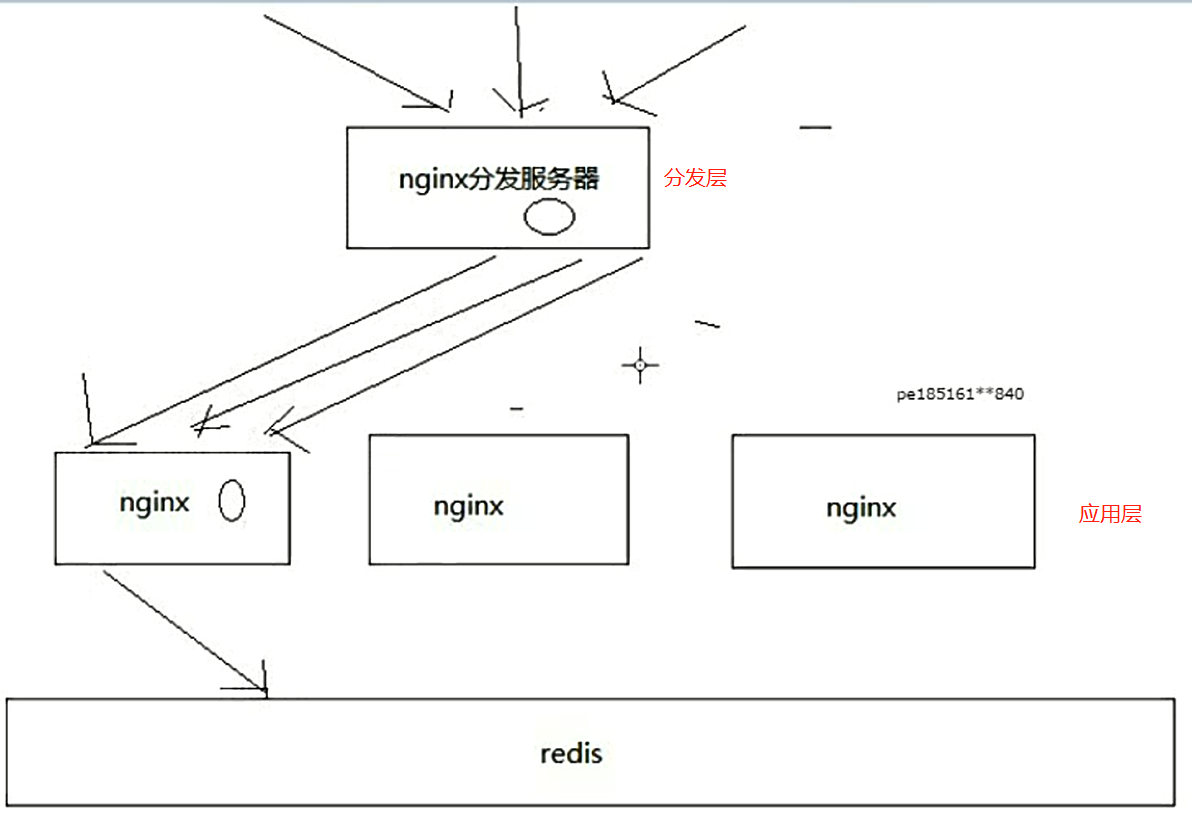
架构图介绍:
1、缓存命中率低
缓存数据生产服务那一层已经搞定了,相当于三层缓存架构中的本地堆缓存+redis分布式缓存都搞定了
就要来做三级缓存中的nginx那一层的缓存了
如果一般来说,你默认会部署多个nginx,在里面都会放一些缓存,就默认情况下,此时缓存命中率是比较低的
2、如何提升缓存命中率
分发层+应用层,双层nginx
分发层nginx,负责流量分发的逻辑和策略,这个里面它可以根据你自己定义的一些规则,比如根据productId去进行hash,然后对后端的nginx数量取模
将某一个商品的访问的请求,就固定路由到一个nginx后端服务器上去,保证说只会从redis中获取一次缓存数据,后面全都是走nginx本地缓存了
后端的nginx服务器,就称之为应用服务器; 最前端的nginx服务器,被称之为分发服务器
看似很简单,其实很有用,在实际的生产环境中,可以大幅度提升你的nginx本地缓存这一层的命中率,大幅度减少redis后端的压力,提升性能
openresty的设计【源码示例】:
local uri_args = ngx.req.get_uri_args() local productId = uri_args["productId"] local hosts = {"192.168.31.187", "192.168.31.19"} local hash = ngx.crc32_long(productId) local index = (hash % 2) + 1 backend = "http://"..hosts[index] local requestPath = uri_args["requestPath"] requestPath = "/"..requestPath.."?productId="..productId local http = require("resty.http") local httpc = http.new() local resp, err = httpc:request_uri(backend,{ method = "GET", path = requestPath }) if not resp then ngx.say("request error: ", err) return end ngx.say(resp.body) httpc:close()
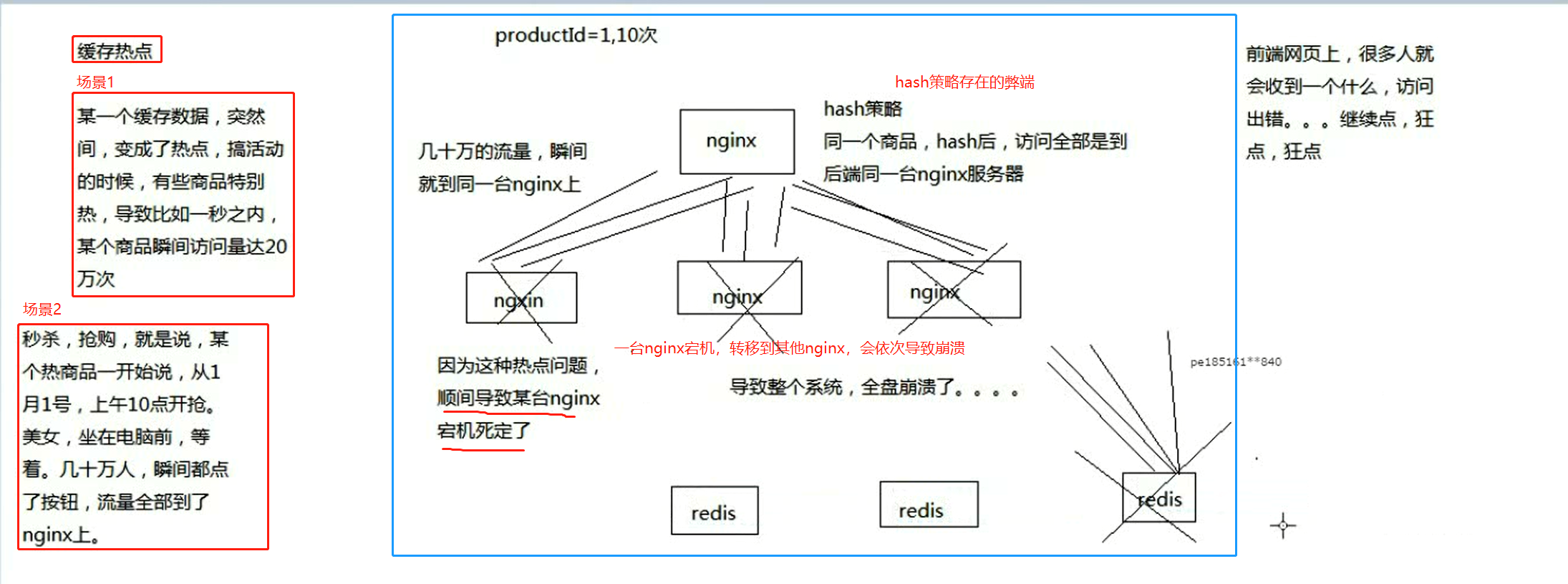
2、热点问题:超级热数据导致系统崩溃的场景: