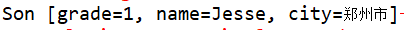一:sutowire属性
1、no:默认值,禁用自动装配;
2、byName:根据属性名称自动装配;
3、byType:根据属性类型自动装配;
4、constructor:通过构造方法自动装配,不推荐使用;
//创建两个类 package com.zzj.vo; public class Student { private int age; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } } package com.zzj.vo; public class School { private Student student; public Student getStudent() { return student; } public void setStudent(Student student) { this.student = student; } }
byName模式(属性的名称必须与之对应否则会报错)
<!--byName模式id与之匹配--> <bean id="student" class="com.zzj.vo.Student"> <property name="age" value="12"></property> </bean> <bean class="com.zzj.vo.School" autowire="byName"></bean>
byType模式(不需要属性名)
<!--byType模式--> <bean class="com.zzj.vo.Student"> <property name="age" value="12"></property> </bean> <bean class="com.zzj.vo.School" autowire="byType"></bean>
//测试 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); System.out.println(context.getBean(School.class).getStudent().getAge());
二:bean的生命周期
通过构造方法或工厂方法创建bean对象——>为bean属性赋值——>调用 bean 的初始化方法,即init-method指定方法——>bean实例化完毕,可以使用——>容器关闭, 调用 bean 的销毁方法,即destroy-method指定方法。
init-method:在设置bean的属性后执行的自定义初始化方法,注意:①、该方法不能有参数;②、对象每创建一次就会执行一次该方法;
destroy-method:该参数中的方法只有bean标签属性scope为singleton且关闭SpringIOC容器时才会被调用,注意:该方法不能有参数
下面我们创建一个类来观察init开始的时间以及destroy结束的时间
//Student类 package com.zzj.vo; public class Student { private int age; static{ System.out.println("静态代码块"); } { System.out.println("非静态代码块"); } public Student(){ System.out.println("构造方法"); } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; System.out.println("set后"); } public void init(){ System.out.println("init"); } public void destroy(){ System.out.println("destroy"); } }
<!--applicaton.xml中的代码--> <bean id="stu" class="com.zzj.vo.Student" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy" p:age="12"></bean>
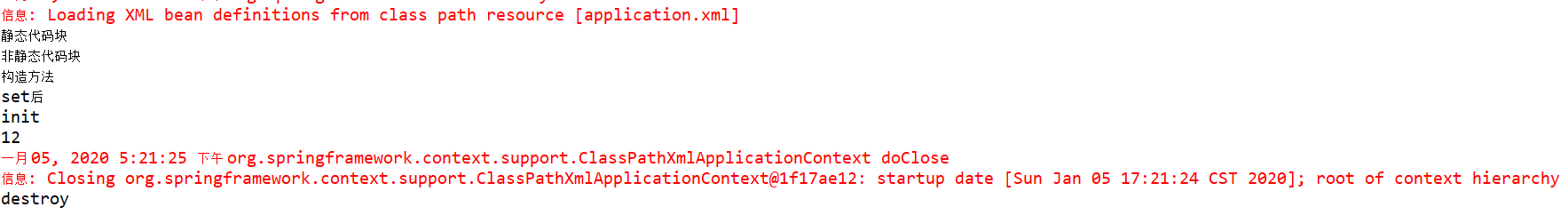
//测试 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); System.out.println(context.getBean(Student.class).getAge()); context.close();
测试结果如下(可见init是在set后开始的):
三:继承 parent属性
parent属性:子bean 从父bean 中继承配置;子bean 也可以覆盖从父bean 继承过来的配置;注意:该属性不允许配置多个值。
//子类(Son)和父类(Parent) package com.zzj.vo; public class Parent { private int grade; private String name; private String city; public int getGrade() { return grade; } public void setGrade(int grade) { this.grade = grade; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } } package com.zzj.vo; public class Son { private int grade; private String name; private String city; public int getGrade() { return grade; } public void setGrade(int grade) { this.grade = grade; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } @Override public String toString() { return "Son [grade=" + grade + ", name=" + name + ", city=" + city + "]"; } }
<!--application.xml--> <bean id="parent" class="com.zzj.vo.Parent"> <property name="grade" value="1"></property> <property name="city" value="郑州市"></property> <property name="name" value="Tom"></property> </bean> <bean id="son" class="com.zzj.vo.Son" parent="parent"> <property name="name" value="Jesse"></property> </bean>
//测试 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); System.out.println(context.getBean(Son.class));
结果如下(可见子类继承了父类的配置,并可作出更改):