最近假期在家闲来无事,天天吃了喝,喝了睡,突然想起年前手写了个spring和springmvc。废话不多说,直接上代码。
插入链接与图片
git地址 https://github.com/985391294/spring-demo

1.创建一个maven项目,然后在pom文件里面添加servlet的jar包以及jetty服务器,如果对tomcat熟悉,也可以使用tomcat启动。
<!--servlet的依赖-->
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jetty-plugin</artifactId>
<version>6.1.26</version>
<configuration>
<webAppSourceDirectory>${basedir}/src/main/webapp</webAppSourceDirectory>
<scanIntervalSeconds>3</scanIntervalSeconds>
<contextPath>/</contextPath>
<connectors>
<connector implementation="org.mortbay.jetty.nio.SelectChannelConnector">
<port>8080</port>
</connector>
</connectors>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2.在webapp下面新建一个文件夹为WEB-INF,在WEB-INF新建web.xml文件。此处需要说的是idea开发工具不同于eclipse,刚开始新创建完项目之后,可能会没有webapp,需要自动手动创建,结构目录下图。
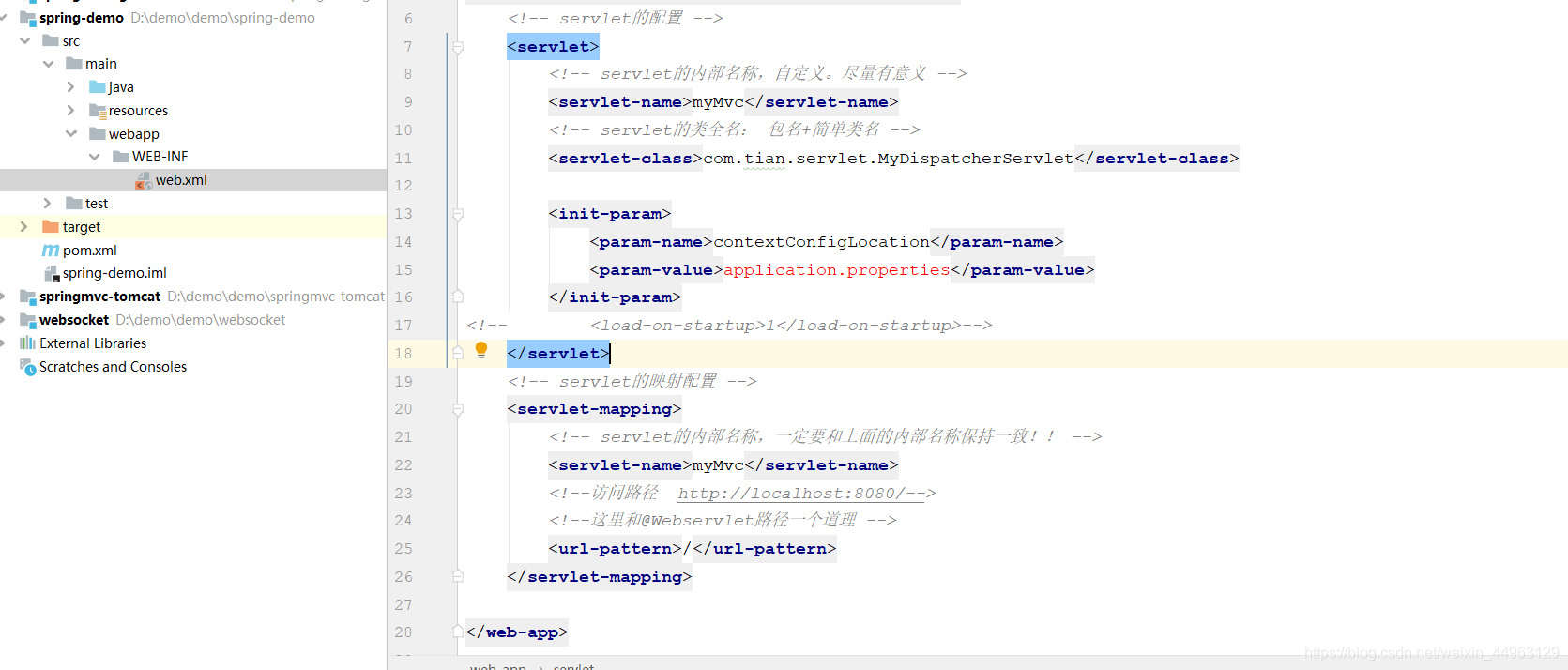
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0" metadata-complete="true">
<!-- servlet的配置 -->
<servlet>
<!-- servlet的内部名称,自定义。尽量有意义 -->
<servlet-name>myMvc</servlet-name>
<!-- servlet的类全名: 包名+简单类名 -->
<servlet-class>com.tian.servlet.MyDispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>application.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>-->
</servlet>
<!-- servlet的映射配置 -->
<servlet-mapping>
<!-- servlet的内部名称,一定要和上面的内部名称保持一致!! -->
<servlet-name>myMvc</servlet-name>
<!--访问路径 http://localhost:8080/-->
<!--这里和@Webservlet路径一个道理 -->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
3.在resources下面新建一个application.properties配置文件,里面只需要写上一行包名的路径即可,稍后会读取当前配置文件里面的报名的路径,此处的代码就不往上面贴了。

4.配置工作都完成之后,开始我们的代码编写,首先自定义我们自己的注解,稍后我们的控制层就是由这些注解去实现请求路径的跳转。
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:11
* desc:
**/
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyAutowired {
String value() default "";
}
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:12
* desc:
**/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyController {
String value() default "";
}
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:14
* desc:
**/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyRequestMapping {
String value() default "";
}
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:11
* desc:
**/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyService {
String value() default "";
}
5.手动实现我们自定义的DispatcherServlet,先编写一个类去实现HttpServlet,然后重写里面的三个方法,init()、doGet()、doPost()。然后在doGet()里面,调用doPost()方法,如果是get请求也去交给post。在初始化的方法里面完成spring所做的事情,里面包含了扫描当前项目的类、解析类、DI、初始化映射器。这里要重复的是,主要的功能都在3、4、5里面实现了。
package com.tian.servlet;
import com.tian.annotation.MyAutowired;
import com.tian.annotation.MyController;
import com.tian.annotation.MyRequestMapping;
import com.tian.annotation.MyService;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:30
* desc:
**/
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private Properties contextConfig = new Properties();
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// ioc容器
private Map<String,Object> ioc = new HashMap<String,Object>();
// 用来存放requestMapping的值和方法名
private Map<String,Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String, Method>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// get请求也去交给post解决
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 6.调用
try {
doDispatch(req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
// 1.加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
// 2.扫描相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
// 3.实例化相关的类
doInstance();
// 4.依赖注入
doAutowied();
// 5.初始化handlerMapping
doInitHandlerMapping();
// 6.调用
System.out.println("servlet初始化了。。。");
}
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:44
* desc: 主核心做的事情
**/
// 1.加载配置文件
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try {
contextConfig.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != is){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 2.扫描相关的类
private void doScanner(String scanPackage) {
// 把要扫描的包名转换为一个文件路径
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.","/"));
File classPath = new File(url.getFile());
// 递归遍历这个文件夹下面所有的文件
for(File file : classPath.listFiles()){
if(file.isDirectory()){ // 如果得到的是还是一个文件夹,就继续往下找
doScanner(scanPackage + "." + file.getName());
}else {
// 如果不是class文件结尾的就调出当前循环层,因为可能会有xml properties 等文件
if (!file.getName().endsWith(".class")) { continue; }
// 得到当前类的报名和类名,
String className = scanPackage + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", "");
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
// 3.实例化相关的类
private void doInstance() {
// 如果没有得到文件,就return
if(classNames == null){
return;
}
// 利用反射机制动态创建对象
for(String className : classNames){
try {
// 根据文件名得到类名
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 如果这个类不是注解类,就不放到ioc容器中去new
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
// spring的原始配置文件 <bean id="" class="">
// beanName 默认是类名的首字母小写加上其余所有的字母 clazz.getSimpleName()方法为得到文件的类名
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
// 反射机制动态创建对象
ioc.put(beanName,clazz.newInstance());
}else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyService.class)){ // 如果是service层的话情况比较复杂
// 第一种情况,默认类型首字母小写加其余字母
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
// 第二种情况,自定义的名字
MyService myService = (MyService)clazz.getAnnotation(MyService.class);
// 如果是自定义的,也让首字母小写加上其余字母
if(!"".equals(myService.value())){
beanName = myService.value();
}
ioc.put(beanName,clazz.newInstance());
// 第三种情况,接口不能被new,实例化出来的是他的实现类
for(Class i : clazz.getInterfaces()){
if(ioc.containsKey(i.getName())){ // 如果一个接口有两个实现类,抛出一个异常
throw new Exception("当前实现类的id已经存在!!!");
}
ioc.put(i.getName(),clazz.newInstance());
}
}else {
continue;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 4.依赖注入
private void doAutowied() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){ // 如果容器中没有对象就return
return;
}
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()){
// 拿到这个容器中所有的字段
Field[] declaredFields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : declaredFields){
// 如果加了autowired注解的字段才给他赋值
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)){
continue;
}
MyAutowired annotation = field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class);
String beanName = annotation.value();
//如果不是自定义,就默认根据类型注入
if("".equals(beanName)){
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
// 如果使用自动注入的对象的作用域为private,直接强制访问
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(),ioc.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 5.初始化handlerMapping
private void doInitHandlerMapping() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){ return; }
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> i : ioc.entrySet()){
Class clazz = i.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){ continue; } // 如果不是controller就跳出当前循环层
// 如果controller类里面有requestMapping注解的话
String baseUrl = "";
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
MyRequestMapping myRequestMapping = (MyRequestMapping) clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = myRequestMapping.value();
}
// 得到controller中所有的方法
for(Method method : clazz.getMethods()){
// 如果方法上面没有加requestMapping注解的话也跳出
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){ continue; }
MyRequestMapping myRequestMapping = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
// 得到requestMapping注解里面的值 replace是为了防止类上面的requestMapping结尾的 / 和方法上面的requestMapping的 / 拼接之后重复,全部替换成一个
String url = ("/" + baseUrl + "/" + myRequestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+","/");
handlerMapping.put(url,method);
}
}
}
// 6.调用
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
String url = request.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
url = url.replaceAll(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/", "/");
if(!handlerMapping.containsKey(url)){
response.getWriter().write("<h1 align='center'>404 Not Found</h1>");
return;
}
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
Method method = this.handlerMapping.get(url);
System.out.println("得到的类名:"+method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("request:"+request);
System.out.println("response:"+response);
System.out.println("参数:"+parameterMap.get("userName")[0]); // 此处的 userName 字段要和controller里面方法的参数保持一致
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName());
method.invoke(ioc.get(beanName),new Object[]{request,response,parameterMap.get("userName")[0]});
}
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 18:25
* desc: 首字母小写加上其余字母
**/
private String toLowerFirstCase(String beanName){
char [] chars = beanName.toCharArray();
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
}
6.在控制层去使用我们完成的注解。
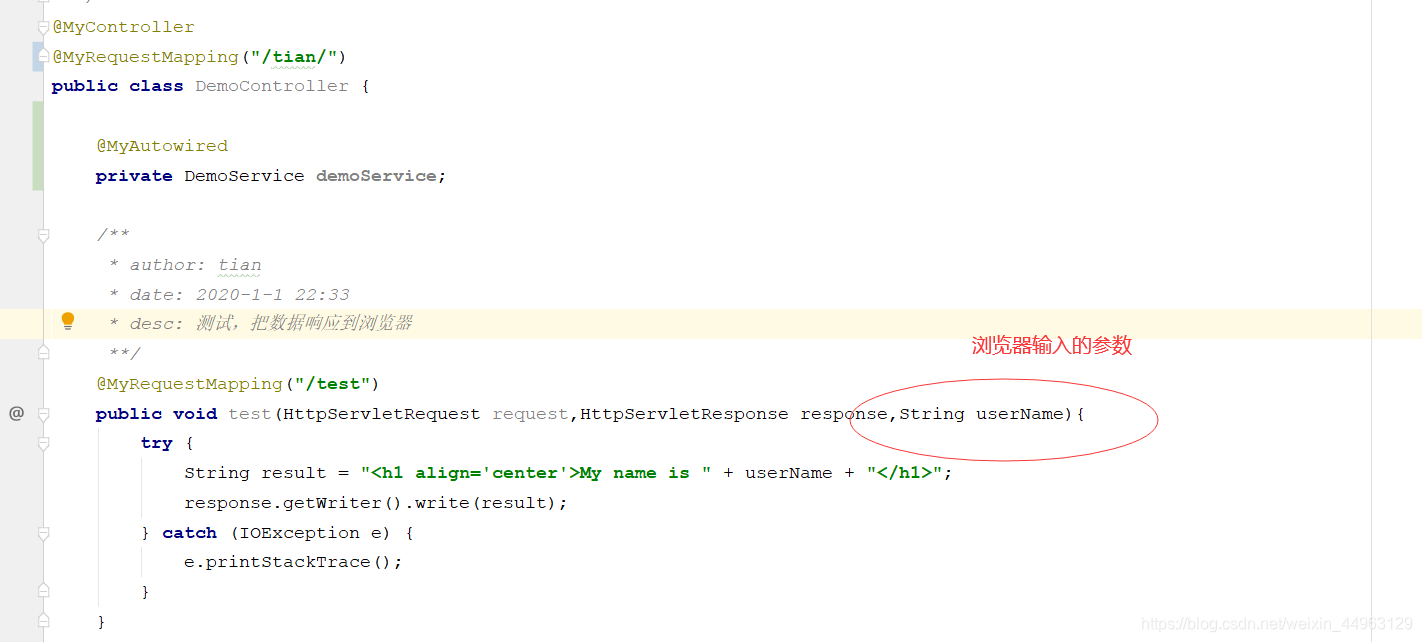

package com.tian.controller;
import com.tian.annotation.MyAutowired;
import com.tian.annotation.MyController;
import com.tian.annotation.MyRequestMapping;
import com.tian.entity.User;
import com.tian.service.DemoService;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 17:17
* desc:
**/
@MyController
@MyRequestMapping("/tian/")
public class DemoController {
@MyAutowired
private DemoService demoService;
/**
* author: tian
* date: 2020-1-1 22:33
* desc: 测试,把数据响应到浏览器
**/
@MyRequestMapping("/test")
public void test(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,String userName){
try {
String result = "<h1 align='center'>My name is " + userName + "</h1>";
response.getWriter().write(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@MyRequestMapping("/user")
public void selectAll(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,String name){
try {
User user = demoService.selectByName(name);
response.getWriter().write(user.toString());
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
7.启动jetty,测试!总结:始终站在一个设计者的角度去看待问题。
我们要生产代码,不做代码的搬运工!
