实例1:适用于非const对象
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:
int m_value;
int m_count;
public:
Test(int value = 0)
{
m_value = value;
m_count = 0;
}
int getValue()
{
m_count++;
return m_value;
}
void setValue(int value)
{
m_count++;
m_value = value;
}
int getCount()
{
return m_count;
}
};
int main()
{
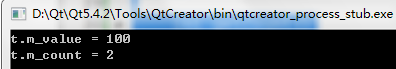
Test t;
t.setValue(100);
cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl;
cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
实例2:适用于const对象和非const对象
mutable是为了突破const函数的限制而设计的
mutable成员变量将永远处于可改变的状态
mutable在实际的项目开发中被严禁滥用
通过mutable来进行修饰,const对象将名存实亡。
mutable的深入分析
-mutable成员变量破坏了只读对象的内部状态
-const成员函数保证只读对象的状态不变性
-mutable成员变量的出现无法保证状态不变性
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:
int m_value;
mutable int m_count;
public:
Test(int value = 0)
{
m_value = value;
m_count = 0;
}
int getValue() const
{
m_count++;
return m_value;
}
void setValue(int value)
{
m_count++;
m_value = value;
}
int getCount() const
{
return m_count;
}
};
int main()
{
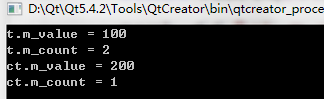
Test t;
t.setValue(100);
cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl;
cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl;
const Test ct(200);
cout << "ct.m_value = " << ct.getValue() << endl;
cout << "ct.m_count = " << ct.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
这种方案不是很完美,因为你适用了mutable,该关键字破坏了const成员函数的特性。
实例3:完美的方案
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:
int m_value;
int * const m_pCount; //一旦指向某片存储空间,那么将不能被改变。但里面的值可以改变
public:
Test(int value = 0): m_pCount(new int(0))
{
m_value = value;
}
int getValue() const
{
*m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1;
return m_value;
}
void setValue(int value)
{
*m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1;
m_value = value;
}
int getCount() const
{
return *m_pCount;
}
};
int main()
{
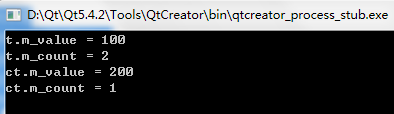
Test t;
t.setValue(100);
cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl;
cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl;
const Test ct(200);
cout << "ct.m_value = " << ct.getValue() << endl;
cout << "ct.m_count = " << ct.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
这个地方很巧妙,就是利用const关键字修饰的指针变量,一旦被初始化后它所指向的存储空间不能被改变,但是这片存储空间中的值是可以改变的。正好对应了const成员函数中,成员变量的值是不能被改变的(在此处指的是指针所指向的存储空间不能改变)