python3 HTTP请求urllib与requests
一:urllib模块
urllib是Python中内置的发送网络请求的一个库(包),在Python2中由urllib和urllib2两个库来实现请求的发送,但是在Python3中已经不存在urllib2这个库了,已经将urllib和urllib2合并为urllib。
urllib 是标准库,它一个工具包模块,包含下面的模块处理 url:
urllib.request 用于打开和读写url
urllib.error 包含了有urllib.request引起的异常。
urllib.parse 用于解析url
urllib.robotparser 分析robots.txt 文件
1.1 urlopen()
urllib.request.urlopen(url, data=None, [timeout, ]*, cafile=None, capath=None, cadefault=False, context=None)
url参数,可以是一个string,或者一个Request对象。
data一定是bytes对象,传递给服务器的数据,或者为None。
目前只有HTTP requests会使用data,提供data时会是一个post请求,如若没有data,那就是get请求。data在使用前需要使用urllib.parse.urlencode()函数转换成流数据。
from urllib.request import urlopen
url = 'https://www.bing.com'
response = urlopen(url, timeout = 5)
print(response.closed)
with response:
print(type(response)) # from http.client import HTTPResponse
print(response.status, response.reason)
print(response._method)
print(response.read()) # 返回网页内容
print(response.info()) # 获取响应头信息
print(response.geturl()) # 请求的真正url(有的url会被301,302重定向)
print(response.closed)
通过urllib.requset.urlopen 方法,发起一个HTTP的GET请求,web 服务器返回了网页内容,响应的数据被封装到类文件对象中,可以通过read方法,readline方法,readlines方法,获取数据,status,和reason 表示状态码, info方法表示返回header信息等
1.2 User-Agent
urlopen方法通过url 字符串和data发起HTTP请求,如果想修改HTTP头,例如:useragent 就得借助其他方式
urllib.request源码中构造的默认的useragent 如下:
# from urllib.request import OpenerDirector
class OpenerDirector:
def __init__(self):
client_version = "Python-urllib/%s" % __version__
self.addheaders = [('User-agent', client_version)]
自定义构造请求头:
from urllib.request import urlopen, Request
url = 'https://www.bing.com'
user_agent = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50"}
req = Request(url, headers = user_agent) # 也可以通过下面行的代码添加user_agent到请求头
# req.add_header('User-Agent', user_agent)
response = urlopen(req, timeout = 5) # url参数为一个Request对象
print(response.closed)
with response:
print(type(response)) # from http.client import HTTPResponse
print(response.status, response.reason)
print(response._method)
print(response.read()) # 返回网页内容
print(response.info()) # 获取响应头信息
print(response.geturl()) # 请求的真正url(有的url会被301,302重定向)
print(response.closed)
1.3 Request类
Request(url, data=None, headers={} )
# 初始化方法,构造一个请求对象,可添加一个header的字典
# data 参数决定是GET 还是POST 请求(data 为None是GET,有数据,就是POST)
# add_header(key, val) 为header中增加一个键值对。
import random
from urllib.request import urlopen, Request
url = 'http://www.bing.com'
user_agent_list = [
"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.6; rv:2.0.1) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/4.0.1",
"Opera/9.80 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.6.8; U; en) Presto/2.8.131 Version/11.11",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; Maxthon 2.0)",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0; SE 2.X MetaSr 1.0; SE 2.X MetaSr 1.0; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; SE 2.X MetaSr 1.0)",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; 360SE)"
]
user_agent = random.choice(user_agent_list) # 随机选择user_agent
request = Request(url)
request.add_header('User-Agent', user_agent)
response = urlopen(request, timeout = 20)
print(type(response))
with response:
print(1, response.status, response.getcode(), response.reason) # 状态,getcode本质上就是返回status
print(2, response.geturl()) # 返回真正请求的url
print(3, response.info()) # 返回响应头headers
print(4, response.read()) # 读取返回的内容
print(5, request.get_header('User-agent')) # 获取请求头中的User-agent信息
print(6, request.header_items()) # 获取请求头中的信息
1.4 urllib.parse 模块
该模块可以完成对url的编解码
from urllib import parse
d = dict(
id = 1,
name = '张三',
hobby = 'football'
)
u = parse.urlencode(d)
print(u)
# id=1&name=%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89&hobby=football
从运行结果来看冒号。斜杆 & 等号,问号都被编码,%之后实际上是单字节十六进制表示的值
query_param = parse.urlencode({'wd': '中'})
url = 'https://www.baidu.com?{}'.format(query_param)
print(url) # https://www.baidu.com?wd=%E4%B8%AD
print('中'.encode('utf-8')) # b'\xe4\xb8\xad'
print(parse.unquote(query_param)) # 解码:wd=中
print(parse.unquote(url)) # https://www.baidu.com?wd=中
一般来说,url中的地址部分,一般不需要使用中文路径,但是参数部分,不管 GET 还是post 方法,提交的数据中,可能有斜杆等符号,这样的字符表示数据,不表示元字符,如果直接发送给服务器端,就会导致接收方无法判断谁是元字符,谁是数据,为了安全,一般会将数据部分的字符串做url 编码,这样就不会有歧义了。
后来可以传送中文,同样会做编码,一般先按照字符集的encoding要求转化成字节序列,每一个字节对应的十六进制字符串前加上百分号即可。
1.5 提交方法method
最常用的HTTP交互数据的方法是GET ,POST
GET 方法,数据是通过URL 传递的,也就是说数据时候在http 报文的header部分
POST方法,数据是放在http报文的body 部分提交的数据都是键值对形式,多个参数之间使用&符号链接,
GET方法:
连接 bing 搜索引擎官网,获取一个搜索的URL: http://cn.bing.com/search?q=如何学好Python
请写程序需完成对关键字的bing 搜索, 将返回的结果保存到一个网页文件中。
query_param = dict(q = '如何学好Python')
base_url = 'https://cn.bing.com/search'
url = '{}?{}'.format(base_url, parse.urlencode(query_param))
user_agent = "User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1)"
req = Request(url, headers = {'User-agent': user_agent})
result = urlopen(req)
print(type(result))
with result:
with open('bing.html', 'wb+') as f:
f.write(result.read())
f.flush()
POST方法:
url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'
data = urlencode({'name': '张三,@=/$*', 'age': 22})
request = Request(url, headers = {'User-agent': 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; 360SE)'})
with urlopen(request, data = data.encode()) as result:
text = result.read()
d = json.loads(text)
print(d)
print(type(d))
1.6 处理json数据
重要的不是代码,而是在网页上能找到json请求的数据,这里以豆瓣电影为例:
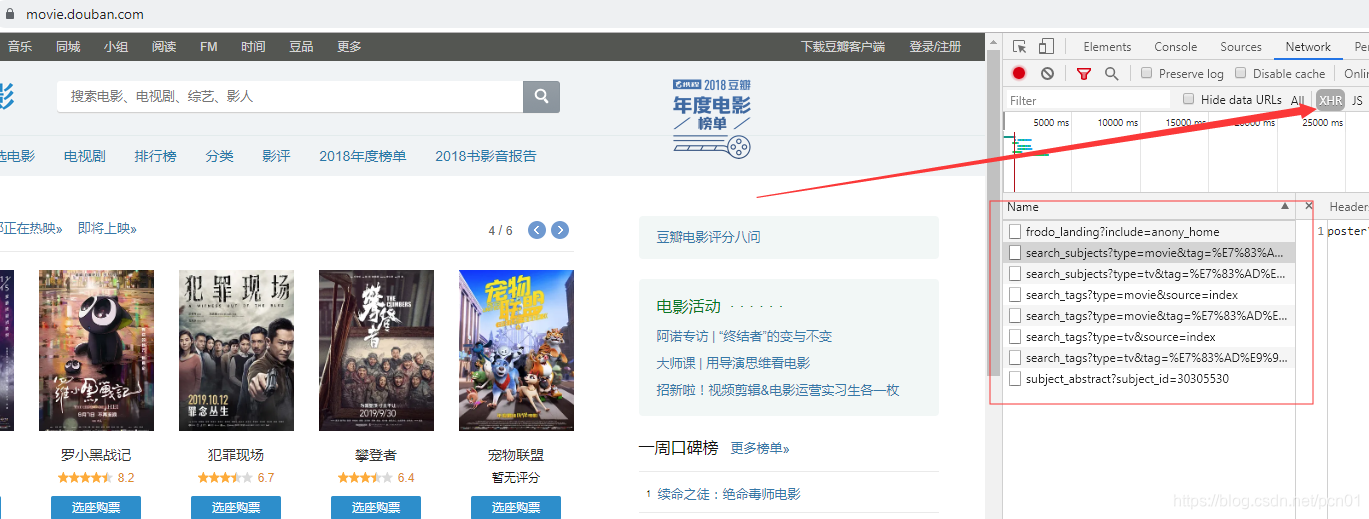
上面箭头指向的就是该页面的json请求,得到json请求数据的url后,代码与上面的写法是一样的
jurl = 'https://movie.douban.com/j/search_subjects'
data = dict(
type= 'movie',
tag = '热门',
page_limit=10,
page_start=10
)
user_agent = {'User-agent': 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; 360SE)'}
req = Request('{}?{}'.format(jurl, urlencode(data)), headers = user_agent)
with urlopen(req) as result:
subjects = json.loads(result.read())
print(len(subjects['subjects']))
print(subjects)
1.7 HTTPS证书忽略
HTTPS使用SSL 安全套接层协议,在传输层对网路数据进行加密,HTTPS 使用的时候,需要证书,而证书需要cA认证
CA(Certificate Authority)是数字证书认证中心的简称,是指发放,管理,废除数据证书的机构。
CA是受信任的第三方,有CA签发的证书具有可信性。如果用户由于信任了CA签发的证书导致的损失可以追究CA的法律责任。
CA是层级结构,下级CA信任上级CA,且有上级CA颁发给下级CA证书并认证。
from urllib.request import urlopen, Request
import ssl
request = Request('https://www.12306.cn/mormhweb/')
print(request)
ua = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3486.0 Safari/537.36'
request.add_header('User-agent', ua)
context = ssl._create_unverified_context() # 忽略不信任的证书(不用校验的上下文)
res = urlopen(request, context=context)
with res:
print(res._method)
print(res.geturl())
print(res.read().decode())
二:urllib3 库
标准库urllib缺少了一些关键的功能,非标准库的第三方库 urlib3 提供了,比如说连接池管理
官方文档:https://urllib3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
pip install urllib3 # 安装
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from urllib3.response import HTTPResponse
import urllib3
jurl = 'https://movie.douban.com/j/search_subjects'
data = dict(
type= 'movie',
tag = '热门',
page_limit=10,
page_start=10
)
user_agent = {'User-agent': 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; 360SE)'}
# 连接池管理器
with urllib3.PoolManager() as http:
response = http.request('GET', '{}?{}'.format(jurl, urlencode(data)), headers = user_agent)
print(type(response))
# response: HTTPResponse = HTTPResponse()
print(response.status)
print(response.data)
三:requests库
requests 使用了 urllib3, 但是 API 更加友好,推荐使用
from urllib.parse import urlencode
import requests
user_agent = {'User-agent': 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; 360SE)'}
jurl = 'https://movie.douban.com/j/search_subjects'
data = dict(
type= 'movie',
tag = '热门',
page_limit=10,
page_start=10
)
url = '{}?{}'.format(jurl, urlencode(data))
response = requests.request('GET', url, headers = user_agent)
print(type(response))
with response:
print(response.text) # Html内容
print(response.status_code)
print(response.url)
print(response.headers) # 响应头
print(response.request.headers) # 请求头
with open('movie.html', 'w', encoding = 'utf-8') as f:
f.write(response.text)
request默认使用Session 对象,是为了在多次 和服务器交互中保留 会话的信息,例如cookie,否则,每次都要重新发起请求
urls = ['https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=Python', 'https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=Java']
session = requests.Session()
with session:
for url in urls:
response = session.get(url, headers = user_agent)
print(type(response))
with response:
print(response.text[:50]) # Html内容
print(response.headers) # 响应头
print(response.request.headers) # 请求头
print('-'*30)
print(response.cookies) # 输入cookie信息
print('-'*30)
print('=' * 100)
第一次发起请求是不带cookie的,第二次请求会带上cookie信息去请求网页
3.1 简单封装
class HTTP:
@staticmethod
def get(url, return_json = True):
r = requests.get(url)
if r.status_code != 200:
return {} if return_json else ''
return r.json() if return_json else r.text
