一、摘自hadoop-example
public class WordCount {
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> [<in>...] <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
for (int i = 0; i < otherArgs.length - 1; ++i) {
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[i]));
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,
new Path(otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}二、核心组件
-
Configuration
- Hadoop 提供了一套独有的配置文件管理系统,并提供API。
- Configuration可以合并多个配置文件,产生一个配置文件。
- Configuration提供属性扩展功能,即可以使用${hadoop.tmp.dir}引用其他配置项
- Configuration构造的一般过程:
- 构造Configuration对象,并通过addResource()方法添加资源,然后可以使用get* 和 set* 方法访问/设置配置项。
- Configuration在构建时,会默认加载core-default.xml,core-site.xml
-
//摘自org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration static{ //print deprecation warning if hadoop-site.xml is found in classpath ClassLoader cL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (cL == null) { cL = Configuration.class.getClassLoader(); } if(cL.getResource("hadoop-site.xml")!=null) { LOG.warn("DEPRECATED: hadoop-site.xml found in the classpath. " + "Usage of hadoop-site.xml is deprecated. Instead use core-site.xml, " + "mapred-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml to override properties of " + "core-default.xml, mapred-default.xml and hdfs-default.xml " + "respectively"); } addDefaultResource("core-default.xml"); addDefaultResource("core-site.xml"); }
-
当DataNode初始化时,会自动加载hdfs-default.xml和hdfs-site.xml
-
// HdfsConfiguration extends Configuration ==> 也会加载core-default.xml core-site.xml // 摘自org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.HdfsConfiguration static { addDeprecatedKeys(); // adds the default resources Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-default.xml"); Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-site.xml"); } -
// 摘自 org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode static{ HdfsConfiguration.init(); }
-
-
同理,YarnConfiguration会加载yarn-default.xml yarn-site.xml
-
InputFormat
我们知道Hadoop可以处理很多类型的数据,从一般的文本文件到数据库,甚至可以自己定义读取任意类型的数据。其核心的抽象就是InputFormat。
InputFormat主要提供两个功能:数据分片,和各个数据分片的读取。InputFormat是为Mapper服务的,即InputFormat会根据分片算法把输入数据切分成若干个Split。对特定的Split会解析成Key/Value对,为Mapper提供输入。
-
Mapper
- 对InputFormat产出的Key/Value进行运算
-
OutputFormat
与InputFormat对应,是Hadoop分析结果的输出,可以是多种类型 -
Reducer
-
Writable
三、MR Job提交流程
以WordCount为例,解析MR Job提交和执行过程
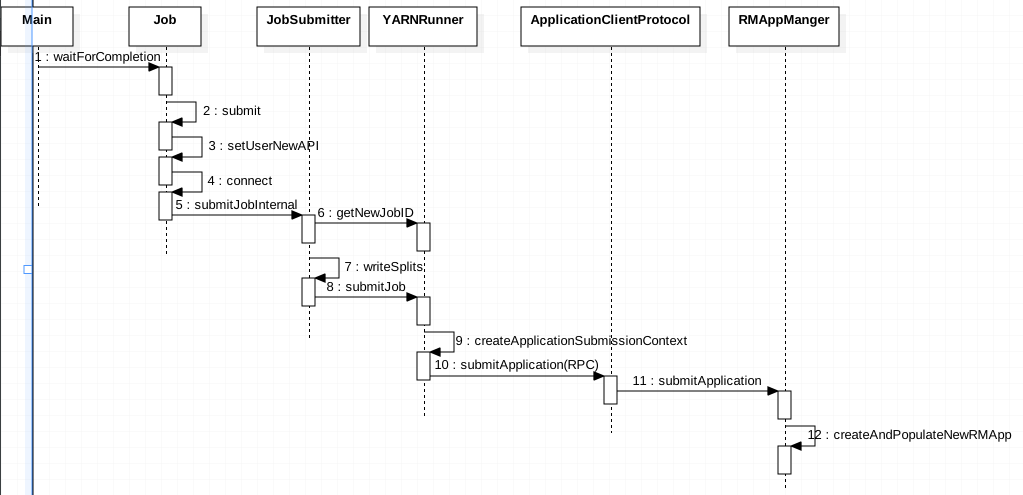
- 构建Configuration,设置必要的参数,
- 构建Job,设置MappClass,ReducerClass,OutputKeyClass,OutputValueClass,InputFormat,OutputFormat.....
- 提交Job
- 根据mapper/reducer API类型,判断是否使用new API
- 根据配置mapreduce.framework.name,采用yarn/local(这里采用SPI模式)即资源平台
- 检查输出
- 调用yarn-client/local-client 申请ApplicationId
- 为该Application构建Hdfs Stage路径
- 上传必要的file、jar、
- 对数据源进行分片来确定Map的个数(这里用到InputFormat的getSplit)
- 配置文件、job的分片信息等写入Application的 Stage路径下
- 根据不同的平台,构建ApplicationSubmissionContext,包含资源以及AppMaster的信息
- 调用submit-client来提交Job到对应的资源调用平台(Yarn/Local)
- Yarn首先申请一个Container来启动AppMaster
- MRAppMaster启动后,会构建Job,Job会根据配置信息,构建Mapper和Reducer Task
- MRAppMaster会根据Mapper和Reducer向Yarn申请对应的Container来运行Mapper和Reducer
- 期间有很多状态的变迁,以及消息Event的处理。各个组件有自己的状态机,有事件Event来驱动状态的变化。
- 当Container启动后,特定的Mapper处理特定的Split的Key-Value,
- Reducer同Shuffle来获取它需要处理的Mapper的输出
- Reducer把Shuffle的数据进行merge sort等,循环处理。最终调用OutputFormat进行结果的输出
注意:
Hadoop MR执行过程中充斥了大量的状态的变迁。各种Event,以及状态机的处理。