Description:
Gildong was hiking a mountain, walking by millions of trees. Inspired by them, he suddenly came up with an interesting idea for trees in data structures: What if we add another edge in a tree?
Then he found that such tree-like graphs are called 1-trees. Since Gildong was bored of solving too many tree problems, he wanted to see if similar techniques in trees can be used in 1-trees as well. Instead of solving it by himself, he’s going to test you by providing queries on 1-trees.
First, he’ll provide you a tree (not 1-tree) with n vertices, then he will ask you q queries. Each query contains 5 integers: x, y, a, b, and k. This means you’re asked to determine if there exists a path from vertex a to b that contains exactly k edges after adding a bidirectional edge between vertices x and y. A path can contain the same vertices and same edges multiple times. All queries are independent of each other; i.e. the added edge in a query is removed in the next query.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (3≤n≤105), the number of vertices of the tree.
Next n−1 lines contain two integers u and v (1≤u,v≤n, u≠v) each, which means there is an edge between vertex u and v. All edges are bidirectional and distinct.
Next line contains an integer q (1≤q≤105), the number of queries Gildong wants to ask.
Next q lines contain five integers x, y, a, b, and k each (1≤x,y,a,b≤n, x≠y, 1≤k≤109) – the integers explained in the description. It is guaranteed that the edge between x and y does not exist in the original tree.
Output
For each query, print “YES” if there exists a path that contains exactly k edges from vertex a to b after adding an edge between vertices x and y. Otherwise, print “NO”.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
Example
input
5
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5
1 3 1 2 2
1 4 1 3 2
1 4 1 3 3
4 2 3 3 9
5 2 3 3 9
output
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO

Note
The image below describes the tree (circles and solid lines) and the added edges for each query (dotted lines).
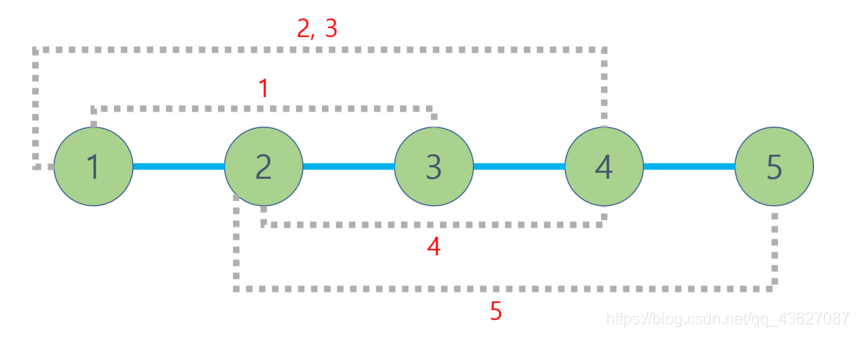
Possible paths for the queries with “YES” answers are:
1-st query: 1 – 3 – 2
2-nd query: 1 – 2 – 3
4-th query: 3 – 4 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 2 – 3
题意:
给定一颗边权都为
的树,接下来
次询问,询问间独立,每次添加一条树中不存在的边,再给定两点询问两点间的路径长度是否可以达到
,两点间的路径可以多次包含相同点,相同边,可以来回走。
比如在
间添加一条边,询问
之间。
就可以分三种情况:
- a->b
- a->x,x->y,y->b
- a->y,y->x,x->b
只需要检查这三种路径长度是否有满足情况即可。
用 处理长度就好。
AC代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define sd(n) scanf("%d", &n)
#define sdd(n, m) scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)
#define sddd(n, m, k) scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k)
#define pd(n) printf("%d\n", n)
#define pc(n) printf("%c", n)
#define pdd(n, m) printf("%d %d\n", n, m)
#define pld(n) printf("%lld\n", n)
#define pldd(n, m) printf("%lld %lld\n", n, m)
#define sld(n) scanf("%lld", &n)
#define sldd(n, m) scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m)
#define slddd(n, m, k) scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &n, &m, &k)
#define sf(n) scanf("%lf", &n)
#define sc(n) scanf("%c", &n)
#define sff(n, m) scanf("%lf%lf", &n, &m)
#define sfff(n, m, k) scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &n, &m, &k)
#define ss(str) scanf("%s", str)
#define rep(i, a, n) for (int i = a; i <= n; i++)
#define per(i, a, n) for (int i = n; i >= a; i--)
#define reps(s) for (int i = head[s]; i; i = e[i].nxt)
#define mem(a, n) memset(a, n, sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << ": " << x << endl
#define pb push_back
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mod(x) ((x) % MOD)
#define gcd(a, b) __gcd(a, b)
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long double ld;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
inline int read()
{
int ret = 0, sgn = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if (ch == '-')
sgn = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
ret = ret * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return ret * sgn;
}
inline void Out(int a)
{
if (a > 9)
Out(a / 10);
putchar(a % 10 + '0');
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b)
{
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b)
{
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
///快速幂m^k%mod
ll qpow(ll a, ll b, ll mod)
{
if (a >= mod)
a = a % mod + mod;
ll ans = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
{
ans = ans * a;
if (ans >= mod)
ans = ans % mod + mod;
}
a *= a;
if (a >= mod)
a = a % mod + mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
// 快速幂求逆元
int Fermat(int a, int p) //费马求a关于b的逆元
{
return qpow(a, p - 2, p);
}
///扩展欧几里得
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
{
if (b == 0)
{
x = 1;
y = 0;
return a;
}
int g = exgcd(b, a % b, x, y);
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t - a / b * y;
return g;
}
///使用ecgcd求a的逆元x
int mod_reverse(int a, int p)
{
int d, x, y;
d = exgcd(a, p, x, y);
if (d == 1)
return (x % p + p) % p;
else
return -1;
}
///中国剩余定理模板0
ll china(int a[], int b[], int n) //a[]为除数,b[]为余数
{
int M = 1, y, x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) //算出它们累乘的结果
M *= a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int w = M / a[i];
int tx = 0;
int t = exgcd(w, a[i], tx, y); //计算逆元
x = (x + w * (b[i] / t) * x) % M;
}
return (x + M) % M;
}
int n, q;
int a, b, x, y, k;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
struct Edge
{
int to, nxt;
} e[N << 1];
int head[N], tote;
void add_edge(int u, int v)
{
e[++tote].to = v, e[tote].nxt = head[u];
head[u] = tote;
}
int maxn, depth[N], dp[N][20];
void dfs(int u, int fa)
{
dp[u][0] = fa, depth[u] = depth[fa] + 1;
rep(i, 1, maxn)
dp[u][i] = dp[dp[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
reps(u) if (e[i].to != fa)
dfs(e[i].to, u);
}
int LCA(int x, int y)
{
if (depth[x] < depth[y])
swap(x, y);
for (int i = maxn; i >= 0; i--)
if ((1 << i) <= (depth[x] - depth[y]))
x = dp[x][i];
if (x == y)
return x;
for (int i = maxn; i >= 0; i--)
if (dp[x][i] != dp[y][i])
x = dp[x][i], y = dp[y][i];
return dp[x][0];
}
int cal(int a, int b)
{
return depth[a] + depth[b] - 2 * depth[LCA(a, b)];
}
void init(int n)
{
rep(i, 0, n)
{
head[i] = 0;
}
tote = 0;
maxn = floor(log(n + 0.0) / log(2.0));
}
int main()
{
sd(n);
init(n);
rep(i, 1, n - 1)
{
int u, v;
sdd(u, v);
add_edge(u, v);
add_edge(v, u);
}
depth[0] = 0;
dp[1][0] = 0, depth[1] = depth[0] + 1;
rep(i, 1, maxn)
dp[1][i] = dp[dp[1][i - 1]][i - 1];
reps(1) if (e[i].to != 0)
dfs(e[i].to, 1);
sd(q);
while (q--)
{
int x, y, a, b, k;
sdd(x, y);
sddd(a, b, k);
int dis = cal(a, b);
if (((k & 1) == (dis & 1)) && dis <= k)
{
puts("YES");
continue;
}
dis = 1 + cal(a, x) + cal(b, y);
if (((k & 1) == (dis & 1)) && dis <= k)
{
puts("YES");
continue;
}
dis = 1 + cal(a, y) + cal(b, x);
if (((k & 1) == (dis & 1)) && dis <= k)
{
puts("YES");
continue;
}
puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
