
继承性的目的就是要复用代码
1.引入
- 格式
class 父类{ }
class 子类 extends 父类 { }
举例:
class Person { //习惯大写
private int age; //private 只可以在类内访问
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
};
class Student extends Person{ //extends表示继承
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
Person p1 = new Student(); //使用new创建类
p1.setAge(8);
System.out.println(p1.getAge());
}
}
- 关键字extends表示继承
- 构造方法
-
如果一个类没有实现构造方法,java编译器会给它定义一个空的构造方法
-
实例化子类对象时,先调用父类的构造方法,再调用子类的构造方法
-
子类继承父类的属性和方法,也可以覆写
-
super关键字
class Person { //习惯大写
private int age; //private 只可以在类内访问
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 1\n");
}
public Person(int age){
this.age = age;
System.out.println("Person 2\n");
}
}
class Student extends Person{
String school;
public Student(){
//默认是super() 调用父类无参构造函数
this.school = school;
}
public Student(String school){
super(18); // 调用父类有参构造函数
this.school = school;
}
public String getSchool(){
return school;
}
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
Student p1 = new Student("PKU"); //使用new创建类
System.out.println(p1.getAge());
System.out.println(p1.getSchool());
}
}
- 关键字final
- final类不能有子类
- final方法不能被覆写
- final变量不能被修改
2.继承的限制
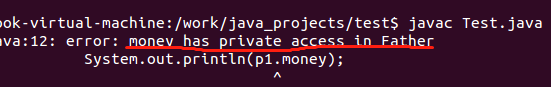
- 看不到父亲的私房钱:私有属性不能被子类访问
class Father { //习惯大写
private int money; //private 只可以在类内访问
}
class Son extends Father{
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
Son p1 = new Son(); //使用new创建类
System.out.println(p1.money);
}
}
结果:
- 看不到父亲的绝招:私有方法不能被子类访问
class Father { //习惯大写
private int money; //private 只可以在类内访问
public void setMoney(int money){
this.money = money;
}
public int getMoney(){
return money;
}
}
class Son extends Father{
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
Son p1 = new Son(); //使用new创建类
p1.setMoney(30);
System.out.println(p1.getMoney());
}
}
- 父类的私有属性和方法,子类是看不到的,但是可以通过父类提供的接口访问私有属性
- 子类调用父类的私有方法出错
- 不能把祖传的招式私吞了:子类覆写的方法不能缩小权限
class Father { //习惯大写
public void printInfo(){
System.out.println("hello world\n");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
private void printInfo(){
System.out.println("hello world\n");
}
}
- 子类不能将父类同名方法权限变小
class Father { //习惯大写
private void printHello(){
System.out.println("hello world\n");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
public void printHello(){
System.out.println("hello world\n");
}
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
Son p1 = new Son(); //使用new创建类
p1.printHello();
}
}
- printHello() 这个方法,父类和子类虽然同名,但是子类不知道父类有,所以不是方法的覆写
3.抽象类
- 语法
abstract class 类名 {
属性;
普通方法 { }
// 抽象方法
访问权限 abstract 返回值类型 方法名 (参数) ; /* 只需要声明,不需要实现 */
}
- 类名前有 abstract 表示抽象类
- 方法名前 abstract 表示抽象方法,只需声明,不需实现
- 举例
abstract class Father { //抽象类不能实例化,起模板作用
public abstract void printHello(); //抽象方法只需声明,不需实现
}
class Son extends Father{
public void printHello(){ //子类必须实现抽象方法
System.out.println("hello world\n");
}
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
Son p1 = new Son(); //使用new创建类
p1.printHello();
}
}
4.接口
- 语法
// 接口由全局常量、公共的抽象方法组成
interface 接口名称 {
全局常量;
抽象方法;
}
interface A {
public static final int i = 10;
public abstract int getNumber( );
}
interface B {
public static final String name = "www.100ask.net";
public abstract int getName( );
}
class C implements A,B {
//覆写A中方法
public int getNumber () { return i; }
//覆写B中方法
public int getName () { return name; }
}
- 举例
interface A { //接口
public static final int i = 10; //全局常量
public abstract int getNumber(); //抽象方法
}
interface B { //接口
public static final String name = "kity"; //全局常量
public abstract String getName(); //抽象方法
}
class C implements A,B{ //C类同时继承A,B接口
public int getNumber(){ //覆写
return i;
}
public String getName(){ //覆写
return name;
}
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
C p1 = new C(); //使用new创建类
System.out.println(p1.getNumber());
System.out.println(p1.getName());
}
}
- 类继承接口中的抽象方法都必须要覆写
同时继承抽象类和接口
abstract class Father{
private int cnt;
public abstract void study(); //抽象方法
}
interface A { //接口
public static final int i = 10; //全局常量
public abstract int getNumber(); //抽象方法
}
interface B { //接口
public static final String name = "kity"; //全局常量
public abstract String getName(); //抽象方法
}
class Son extends Father implements A,B{ //C类同时继承A,B接口
public int getNumber(){ //覆写
return i;
}
public String getName(){ //覆写
return name;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("study");
}
}
public class Test { //必须大写和文件名一致
public static void main(String args[]){
C p1 = new C(); //使用new创建类
System.out.println(p1.getNumber());
System.out.println(p1.getName());
}
}
- 抽象类和接口类似,都起模板作用,子类必须覆写抽象方法
- 抽象类中可以有私有属性,私有方法,抽象方法等,接口中只能有全局变量和抽象方法
- 抽象类比接口容纳更多的内容
- 但是接口突破单继承的限制
