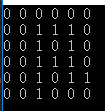
迷宫问题是栈的应用的一个难点问题,通常迷宫问题分为三类:


单通路不带环 多通路不带环 通路间带环
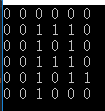
(其中1代表通路,0代表墙)
—————————————————————————————————————————————
单通路不带环 :
此类问题是迷宫问题最为简单的类型我们采用非递归循环遍历来完成
规定右边为出口,规定下边为入口,将每一个走过的位置的坐标入栈,当遇到死胡同时进行回溯,也就是将当前的的栈顶坐标出栈,此时一直回退,当检测到周围有通路时,继续进栈,当检测到右边出口时记录下来出口坐标,然后继续回溯,直到回到起点。此时便实现了一个简单迷宫找出口的问题。
这里我们将回溯过的位置标记为2,方便查看。
代码如下:
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define STACKINCREMENT 10
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct Pos //入口
{
int _row; //行
int _col; //列
}Pos;
typedef struct Stack
{
Pos *_st;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack *s, size_t capacity);
void StackPush(Stack *s, Pos x);
void StackPop(Stack*s);
Pos StackTop(Stack *s);
size_t StackSize(Stack *s);
size_t StackEmpty(Stack *s);
void StackInit(Stack *s, size_t capacity)
{
assert(s && capacity>0);
s->_st = (Pos *)malloc(sizeof(Pos)*capacity);
assert(s->_st);
s->_size = 0;
s->_capacity = capacity;
}
void StackPush(Stack *s, Pos x)
{
assert(s);
if (s->_size == s->_capacity) //栈空间满了
{
s->_capacity *= 2;
s->_st = (Pos*)realloc(s->_st, sizeof(Pos)*s->_capacity);
}
s->_st[s->_size++] = x;
}
void StackPop(Stack*s)
{
assert(s && s->_size > 0);
--s->_size;
}
Pos StackTop(Stack *s)
{
assert(s && s->_size > 0);
return s->_st[s->_size - 1];
}
size_t StackSize(Stack *s)
{
assert(s);
return s->_size;
}
//为空
size_t StackEmpty(Stack *s)
{
return s->_size;
}
Maze.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Stack.h"
#define N 6
int _mz[N][N];
Pos _entry; //入口
void MazeInit(int a[][N]);
void MazeGetPath();
void MazeGetShortPath();
void MazePrint();
void TestMaze();
void MazeInit(int a[][N])
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
_mz[i][j] = a[i][j];
}
}
_entry._row = 5; //定义入口点
_entry._col = 2;
}
int CheckIsAccess(Pos pos) //检测通路,存在边界情况
{
if (pos._row >= 0 && pos._row<N
&&pos._col >= 0 && pos._col<N
&&_mz[pos._row][pos._col] == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void MazeGetPath() //得到路径
{
Stack s;
StackInit(&s, 10); //栈里面是走过路径的坐标,先给栈初始化
StackPush(&s, _entry); //把入口给栈
_mz[_entry._row][_entry._col] = 2; //先把入口标记为2
while (StackEmpty(&s) != 0) //栈为空就表示结束,坐标全出栈了,没路可走了
{
Pos cur, next;
cur = StackTop(&s); //cur此时三种可能 1.入口 2.下一个可以走的位置 3.回溯的上一个位置
if (cur._col == N - 1) //规定右边为出口,此时找到出口
{
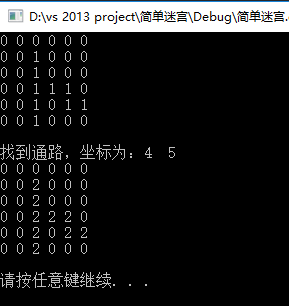
printf("找到通路,坐标为:%d %d\n", StackTop(&s)._row, StackTop(&s)._col);
return;
}
//探测周围可通路径
next = cur;
next._row -= 1;//上
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue; //直接到while循环判断条件
}
next = cur;
next._row += 1;//下
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._col -= 1;//左
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._col += 1;//右
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
//到这里表示四个方向都不可以通,就要回溯
StackPop(&s);
}
printf("没有通路\n");
}
void MazePrint()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
printf("%d ",_mz[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void TestMaze()
{
int a[N][N] =
{
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }
};
MazeInit(a);
MazePrint();
MazeGetPath();
MazePrint();
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Maze.h"
int main()
{
TestMaze();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
—————————————————————————————————————————————
多通路不带环:
这次使用递归实现检测坐标周围的通路,因为存在不知一条通路,所以要求最短路径。
首先定义两个栈,path和shortpath,通过递归将坐标入栈,当遇到第一个出口时开始回溯,出栈,此时path栈存储第一次出口坐标,然后回溯,经过第二个出口时比较两个栈的size,将size小的栈赋值给shortpath栈。程序结束后,shortpath里面存储的就是路径最短的坐标,栈顶就是最短路径出口坐标。
stack .h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define STACKINCREMENT 10
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct Pos //入口
{
int _row; //行
int _col; //列
}Pos;
typedef struct Stack
{
Pos *_st;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack *s, size_t capacity);
void StackDestory(Stack *s);
void StackPush(Stack *s, Pos x);
void StackPop(Stack*s);
Pos StackTop(Stack *s);
size_t StackSize(Stack *s);
size_t StackEmpty(Stack *s);
void StackPush(Stack *s, Pos x);
void StackCopy(Stack* s1, Stack* s2);
void StackCopy(Stack* s1, Stack* s2) //栈内容拷贝,要有一样多空间
{
assert(s1&&s2);
if (s1->_size == 0)
{
s2->_size = 0;
}
else
{
if (s1->_size > s2->_capacity)
{
s2->_st = (Pos *)realloc(s2->_st, s1->_size);
s2->_capacity = s1->_size;
}
s2->_size = s1->_size;
memcpy(s2->_st, s1->_st, sizeof(Pos)*s1->_size);
}
}
void StackInit(Stack *s, size_t capacity)
{
assert(s && capacity>0);
s->_st = (Pos *)malloc(sizeof(Pos)*capacity);
assert(s->_st);
s->_size = 0;
s->_capacity = capacity;
}
//
//void StackDestory(Stack *s)
//{
//
//}
void StackPush(Stack *s, Pos x)
{
assert(s);
if (s->_size == s->_capacity)
{
s->_capacity *= 2;
s->_st = (Pos*)realloc(s->_st, sizeof(Pos)*s->_capacity);
}
s->_st[s->_size++] = x;
}
void StackPop(Stack*s)
{
assert(s && s->_size > 0);
--s->_size;
}
Pos StackTop(Stack *s)
{
assert(s && s->_size > 0);
return s->_st[s->_size - 1];
}
size_t StackSize(Stack *s)
{
assert(s);
return s->_size;
}
//0为空
size_t StackEmpty(Stack *s)
{
return s->_size;
}
void Teststack()
{
Stack s;
/*StackInit(&s, 3);
StackPush(&s, 1);
StackPush(&s, 2);
StackPush(&s, 3);
StackPush(&s, 4);
StackPush(&s, 5);
StackPush(&s, 6);*/
while (StackEmpty(&s) != 0)
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&s));
StackPop(&s);
}
printf("\n");
}
Maze.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Stack.h"
#define N 6
//typedef struct Pos DataType; //Pos就是一个坐标类型
int _mz[N][N];
Pos _entry; //入口
Stack path;
Stack shortpath;
void MazeInit(int a[][N]);
void MazeGetPath();
void MazeGetShortPath();
void MazePrint();
void TestMaze();
void MazeInit(int a[][N])
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
_mz[i][j] = a[i][j];
}
}
_entry._row = 5;
_entry._col = 1;
}
int CheckIsAccess(Pos pos) //检测通路,存在边界情况
{
if (pos._row >= 0 && pos._row<N
&&pos._col >= 0 && pos._col<N
&&_mz[pos._row][pos._col] == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void MazeGetPath()
{
Stack s;
StackInit(&s, 10); //栈里面是走过路径的坐标,先给栈初始化
StackPush(&s, _entry); //把入口给栈
_mz[_entry._row][_entry._col] = 2; //走过的路径标记为2,先标记在遍历防止死循环
while (StackEmpty(&s) != 0) //栈为空就表示结束,坐标全出栈了,没路可走了
{
Pos cur, next, prev;
cur = StackTop(&s); //cur此时三种可能 1.入口 2.下一个可以走的位置 3.回溯的上一个位置
if (cur._col == N - 1) //规定右边为出口,此时找到出口
{
printf("找到通路\n");
return;
}
next = cur;
//探测周围可通路径
next._row -= 1;//上
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._row += 1;//下
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._col -= 1;//左
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._col += 1;//右
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
//到这里表示四个方向都不可以通,就要回溯
prev = StackTop(&s);
_mz[prev._row][prev._col] = 3;
StackPop(&s);
}
printf("没有通路\n");
}
void MazeGetShortPath(Pos cur)
{
Pos next;
StackPush(&path, cur);
_mz[cur._row][cur._col] = 2;
if (cur._col == N - 1)
{
if (StackSize(&shortpath) == 0 || StackSize(&path) < StackSize(&shortpath))
{
StackCopy(&path, &shortpath); //更新shortpath
}
/*StackPop(&path);
return;*/
}
next = cur;
next._row -= 1; //上
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
next = cur;
next._row += 1; //下
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
next = cur;
next._col -= 1; //左
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
next = cur;
next._col += 1; //右
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
StackPop(&path);
}
void MazePrint()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
printf("%d ", _mz[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void TestMaze()
{
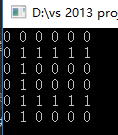
int a[N][N] =
{
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
StackInit(&path, 10);
StackInit(&shortpath, 10);
MazeInit(a);
MazePrint();
MazeGetShortPath(_entry);
//MazeGetPath();
MazePrint();
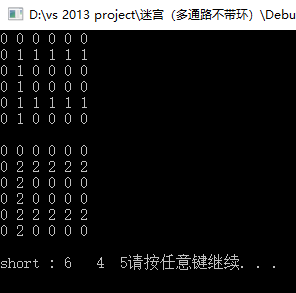
printf("short : %d %d %d", StackSize(&shortpath), StackTop(&shortpath)._row, StackTop(&shortpath)._col);
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Maze.h"
int main()
{
TestMaze();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
—————————————————————————————————————————————
通路间带环
当解决着这种带环迷宫时就不能用上面的方法,若仅仅将走过的路径标记为2时,回溯时就会出现部分路径不会通过的情况,所以最好的解决方法就是将回溯的坐标再标记为1,这样就会把环走完。代码和上一种类似,只是Maze.h改变了。
Maze.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Stack.h"
#define N 6
//typedef struct Pos DataType; //Pos就是一个坐标类型
int _mz[N][N];
Pos _entry; //入口
Stack path;
Stack shortpath;
void MazeInit( int a[][N]);
void MazeGetPath();
void MazeGetShortPath();
void MazePrint();
void TestMaze();
void MazeInit( int a[][N])
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
_mz[i][j] = a[i][j];
}
}
_entry._row = 5;
_entry._col = 2;
}
int CheckIsAccess(Pos pos) //检测通路,存在边界情况
{
if (pos._row>=0 && pos._row<N
&&pos._col>=0 && pos._col<N
&&_mz[pos._row][pos._col]==1)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void MazeGetPath()
{
Stack s;
StackInit(&s, 10); //栈里面是走过路径的坐标,先给栈初始化
StackPush(&s, _entry); //把入口给栈
_mz[_entry._row][_entry._col] = 2; //走过的路径标记为2,先标记在遍历防止死循环
while (StackEmpty(&s) != 0) //栈为空就表示结束,坐标全出栈了,没路可走了
{
Pos cur, next,prev;
cur =StackTop(&s); //cur此时三种可能 1.入口 2.下一个可以走的位置 3.回溯的上一个位置
if (cur._col == N - 1) //规定右边为出口,此时找到出口
{
printf("找到通路\n");
return;
}
next = cur;
//探测周围可通路径
next._row -= 1;//上
if (CheckIsAccess( next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._row += 1;//下
if (CheckIsAccess( next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._col -= 1;//左
if (CheckIsAccess( next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
next._col += 1;//右
if (CheckIsAccess( next) == 1) //可通就一直走
{
StackPush(&s, next);
_mz[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
//到这里表示四个方向都不可以通,就要回溯
prev = StackTop(&s);
_mz[prev._row][prev._col] = 3;
StackPop(&s);
}
printf("没有通路\n");
}
void MazeGetShortPath(Pos cur)
{
Pos next, pos;
StackPush(&path, cur);
_mz[cur._row][cur._col] = 2;
if (cur._col == N - 1)
{
if (StackSize(&shortpath) == 0 || StackSize(&path) < StackSize(&shortpath))
{
StackCopy(&path, &shortpath); //更新shortpath
}
}
next = cur;
next._row -= 1; //上
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
next = cur;
next._row += 1; //下
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
next = cur;
next._col -= 1; //左
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
next = cur;
next._col += 1; //右
if (CheckIsAccess(next) == 1)
{
MazeGetShortPath(next);
}
pos = StackTop(&path);
_mz[pos._row][pos._col] = 1;
StackPop(&path);
}
void MazePrint()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
printf("%d ", _mz[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void TestMaze()
{
int a[N][N] =
{
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }
};
StackInit(&path, 30);
StackInit(&shortpath, 30);
MazeInit(a);
MazePrint();
MazeGetShortPath(_entry);
//MazeGetPath();
MazePrint();
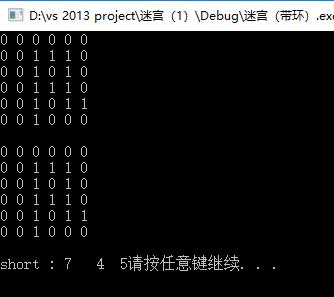
printf("short : %d %d %d", StackSize(&shortpath), StackTop(&shortpath)._row, StackTop(&shortpath)._col);
}
运行结果