源码:https://github.com/tfwcn/AI
Word.txt为用到的字符集,本文用的只包含训练集里的字。
ai.txt为训练素材,格式:问题1\t回答1\n问题2\t回答2\n
LSTM原理图:
σ代表:sigmoid函数
训练过程图:
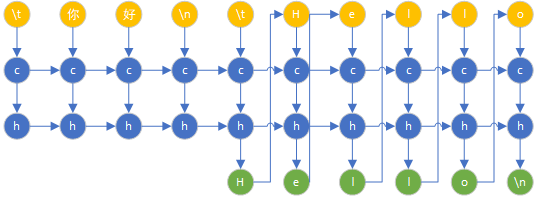
代码如下:
import keras as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import math
import os
batch_size = 50 # Batch size for training. 训练批次大小
epochs = 1000 # Number of epochs to train for. 训练多少回
latent_dim = 128 # Latent dimensionality of the encoding space. 隐藏神经元数量
num_samples = 10000 # Number of samples to train on. 训练数量
max_encoder_seq_length = 256 # 句子最大长度
word_file = open('word.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
alphabet = word_file.read() # 2500
# alphabet += 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789' # 英文数字
# alphabet += ',./;\'[]\\-=`<>?:"{+}|_)(*&^%$#@!~` ' # 标点
# alphabet += ',。《》?;‘’:“”【】—()…¥!·' # 中文标点
# alphabet += '\t\n' # 开头结束标志
word_file.close()
print('word', len(alphabet), alphabet)
# 训练数据集
train_file = open('ai.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
sentences = train_file.read().split('\n')
train_file.close()
question_texts = []
answer_texts = []
for senterce in sentences:
if len(senterce) == 0:
continue
# 补全缺失文字,需重新运行
for t, char in enumerate(senterce):
if alphabet.find(char) == -1:
f2 = open('word.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
f2.truncate() # 清空文件
alphabet += char
f2.write(alphabet)
f2.close()
print('senterce', senterce.split('\t'))
question_text, answer_text = senterce.split('\t')
# \t 作为开头标识
# \n 作为结尾标识
question_text = '\t' + question_text + '\n'
answer_text = '\t' + answer_text + '\n'
# question_text = question_text.ljust(max_encoder_seq_length, '\0')
# answer_text = answer_text.ljust(max_encoder_seq_length, '\0')
question_texts.append(question_text)
answer_texts.append(answer_text)
# print('question_texts', question_texts)
# print('answer_texts', answer_texts)
# 字符与序号对应的字典
char_to_int = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(alphabet))
int_to_char = dict((i, c) for i, c in enumerate(alphabet))
# print('char_to_int', char_to_int)
# print('int_to_char', int_to_char)
# 编码器字符数量
num_encoder_tokens = len(alphabet)
# 解码器字符数量
num_decoder_tokens = len(alphabet)
# 样本数
print('Number of samples:', len(question_texts))
# 输入
encoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(len(question_texts), max_encoder_seq_length, num_encoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
# 输出
decoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(len(question_texts), max_encoder_seq_length, num_decoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
# 下一个时间点的输出
decoder_target_data = np.zeros(
(len(question_texts), max_encoder_seq_length, num_decoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
# enumerate返回下标与元素,zip把两个列表打包成一个个元组组成的列表
# 下面循环生成训练数据,转one hot
for i, (input_text, target_text) in enumerate(zip(question_texts, answer_texts)):
# print('input_text', input_text)
# print('target_text', target_text)
for t, char in enumerate(input_text):
encoder_input_data[i, t, char_to_int[char]] = 1.
for t, char in enumerate(target_text):
# decoder_target_data is ahead of decoder_input_data by one timestep
decoder_input_data[i, t, char_to_int[char]] = 1.
# 翻译时下一个时间点的输入数据
if t > 0:
# decoder_target_data will be ahead by one timestep
# and will not include the start character.
decoder_target_data[i, t-1, char_to_int[char]] = 1.
print('encoder_input_data', len(encoder_input_data))
print('decoder_input_data', len(decoder_input_data))
# ==================编码器=====================
# Define an input sequence and process it.
# 输入一句话
encoder_inputs = K.Input(shape=(None, num_encoder_tokens))
# return_state返回状态,用于状态保持
encoder = K.layers.LSTM(latent_dim, return_sequences=True,
return_state=True, activation=K.activations.tanh)
encoder2 = K.layers.LSTM(latent_dim, return_sequences=False,
return_state=True, activation=K.activations.tanh)
encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = encoder(encoder_inputs)
encoder_outputs2, state_h2, state_c2 = encoder2(encoder_outputs)
# We discard `encoder_outputs` and only keep the states.
encoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
encoder_states2 = [state_h2, state_c2]
# ==================编码器 end=====================
# ==================解码器=====================
# Set up the decoder, using `encoder_states` as initial state.
# 预测正确答案作为输入
decoder_inputs = K.Input(shape=(None, num_decoder_tokens))
# We set up our decoder to return full output sequences,
# and to return internal states as well. We don't use the
# return states in the training model, but we will use them in inference.
# return_sequences返回完整序列
decoder_lstm = K.layers.LSTM(
latent_dim, return_sequences=True, return_state=True, activation=K.activations.tanh)
decoder_lstm2 = K.layers.LSTM(
latent_dim, return_sequences=True, return_state=True, activation=K.activations.tanh)
decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder_lstm(decoder_inputs,
initial_state=encoder_states)
decoder_outputs2, _, _ = decoder_lstm2(decoder_outputs,
initial_state=encoder_states2)
decoder_dense = K.layers.Dense(
num_decoder_tokens, activation=K.activations.softmax)
# 输出值,真正答案
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs2)
# ==================解码器 end=====================
# 编码 解码
# \t h i \n \t 你 好 \n
# LSTM LSTM
# 你 好 \n
# Define the model that will turn
# `encoder_input_data` & `decoder_input_data` into `decoder_target_data`
model = K.Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], decoder_outputs)
if os.path.exists('s2s.h5'):
print('加载模型')
model.load_weights('s2s.h5')
# Run training
# 训练
# encoder_input_data:输入要翻译的语句
# decoder_input_data:输入解码器的结果\t开头
# decoder_target_data:真正的翻译结果
model.compile(K.optimizers.RMSprop(),
loss=[K.losses.categorical_crossentropy],
metrics=[K.metrics.categorical_crossentropy])
# model.fit([encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data], decoder_target_data,
# batch_size=batch_size,
# epochs=epochs,
# validation_split=0.2)
model.fit([encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data], decoder_target_data,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs)
# Save model
model.save_weights('s2s.h5')
# Next: inference mode (sampling). 下一步,推理模式(抽样),识别
# Here's the drill:
# 1) encode input and retrieve initial decoder state
# 2) run one step of decoder with this initial state
# and a "start of sequence" token as target.
# Output will be the next target token
# 3) Repeat with the current target token and current states
# Define sampling models
# 编码模型,encoder_states
encoder_model = K.Model(encoder_inputs, encoder_states + encoder_states2)
# 解码模型
# 状态输入
decoder_state_input_h = K.Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_state_input_c = K.Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_state_input_h2 = K.Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_state_input_c2 = K.Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_states_inputs = [decoder_state_input_h, decoder_state_input_c]
decoder_states_inputs2 = [decoder_state_input_h2, decoder_state_input_c2]
# 训练后的LSTM,
decoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = decoder_lstm(
decoder_inputs, initial_state=decoder_states_inputs)
decoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
decoder_outputs2, state_h2, state_c2 = decoder_lstm2(
decoder_outputs, initial_state=decoder_states_inputs2)
decoder_states2 = [state_h2, state_c2]
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs2)
# 输入[decoder_inputs, decoder_state_input_h, decoder_state_input_c]
# 输出[decoder_outputs, state_h, state_c]
decoder_model = K.Model(
[decoder_inputs] + decoder_states_inputs + decoder_states_inputs2,
[decoder_outputs] + decoder_states + decoder_states2)
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# Encode the input as state vectors.
# 编码,抽象概念
states_value = encoder_model.predict(input_seq)
# Generate empty target sequence of length 1.
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
# Populate the first character of target sequence with the start character.
target_seq[0, 0, char_to_int['\t']] = 1.
# Sampling loop for a batch of sequences
# (to simplify, here we assume a batch of size 1).
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
while not stop_condition:
output_tokens, h, c, h2, c2 = decoder_model.predict(
[target_seq] + states_value)
# 对应字符下标,把预测出的字符拼成字符串
# Sample a token
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
sampled_char = int_to_char[sampled_token_index]
decoded_sentence += sampled_char
# 句子结束
# Exit condition: either hit max length
# or find stop character.
if (sampled_char == '\n' or
len(decoded_sentence) > max_encoder_seq_length):
stop_condition = True
# Update the target sequence (of length 1).
# 当前字符,传递到下一次预测
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
target_seq[0, 0, sampled_token_index] = 1.
# Update states
# 当前状态,传递到下一次预测
states_value = [h, c, h2, c2]
return decoded_sentence
for seq_index in range(10):
# Take one sequence (part of the training set)
# for trying out decoding.
input_seq = encoder_input_data[seq_index: seq_index + 1]
decoded_sentence = decode_sequence(input_seq)
print('-')
print('Input sentence:', question_texts[seq_index])
print('Decoded sentence:', decoded_sentence)
执行命令:
python seq2seq.py参考资料:
