单链表
链表:
概念:链表是一种物理存储上的非连续、非顺序的存储结构。数据的逻辑顺序通过链表中的指针链接实现的。
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
- 单向、双向
- 带头、不带头
- 循环、非循环
优缺点:
优点:
1.任意位置插入删除时间复杂度为O(1)
2.没有增容问题,插入一个开辟一个空间。
缺点:
以节点为单位存储,不支持随机访问,查找较为麻烦。
链表和顺序表之间优缺点刚好对应互补。
数据结构:
主要由数据域和指针域组成:
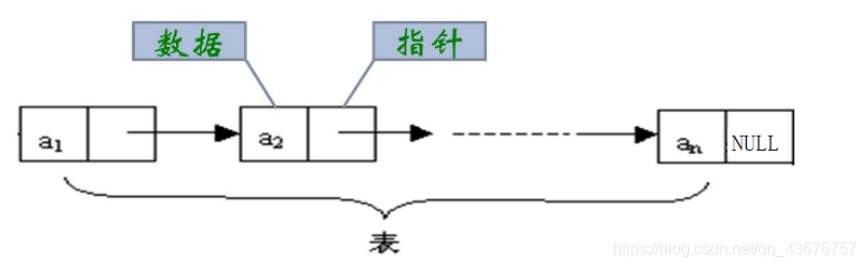
我们主要来看一下笔试面试中出现概率最高的无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结
构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。
代码实现
单向不带头非循环
定义:
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType _data;
struct SListNode* _next;
}SListNode;
typedef struct SList //头指针
{
SListNode* _head;
}SList;
基本操作的实现:
尾插:
1.先申请一个新节点,并初始化内部成员数据域data和指针域_next;
2.判断链表是否为空,为空则直接插入head指针后面,不为空则循环遍历找到链表的尾部插入
代码如下:
void SListPushBack(SList* plt, SLTDataType x)//尾插
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//先申请一个新的节点
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
//判断链表是否为空
if (plt->_head == NULL)
{
plt->_head = newnode;
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
while (cur->_next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
cur->_next = newnode;
}
}
尾删:
1.当链表为空,直接返回
2.当有一个节点时,则直接释放节点,把指向节点的指针置空
3.有多个节点时,需要向后遍历,要找到最后要释放的节点和它的前一个节点(防止释放尾节点后,指向尾节点的指针成为野指针)。
代码如下:
void SListPopBack(SList* plt)//尾删
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
if (plt->_head == NULL)//当为空链表时
{
return;
}
else if (cur->_next == NULL)//有一个节点
{
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
else//有多个节点
{
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
while (cur->_next->_next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
free(cur->_next);
cur->_next = NULL;
}
}
头插:
1.先申请一个新节点newnode,并初始化内部成员数据域data和指针域_next;
2.判断链表是否为空,为空则直接插入head指针后面
3.不为空,则要newnode->next = head;让head 指针指向新结点newnode;
代码如下:
void SListPushfront(SList* plt, SLTDataType x)//头插
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//先申请一个新的节点
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
if (plt->_head == NULL)
{
plt->_head = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->_next = plt->_head;
plt->_head = newnode;
}
}
头删:将头指针指向第一个节点的下个节点,释放第一个节点,第一个节点对应的指针置空。
void SListPopfront(SList* plt)//头删
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
plt->_head = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
下附完成代码:
Slist.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// 单向 不带头 不循环
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType _data;
struct SListNode* _next;
}SListNode;
typedef struct SList //头指针
{
SListNode* _head;
}SList;
void SListInit(SList* plt);
void SListPushBack(SList* plt, SLTDataType x);//尾插
void SListPushfront(SList* plt, SLTDataType x);//头插
void SListPopBack(SList* plt);//尾删
void SListPopfront(SList* plt);//头删
void SListDestory(SList* plt);
SListNode* SListfind(SList* plt, SLTDataType x);//通过值来查找
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x);//任意位置后面插
void SListEraseAfter(SList* plt,SListNode* pos);//任意位置后面删
void TestSList1();
Slist.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Slist.h"
void SListInit(SList* plt){
assert(plt);
plt->_head = NULL;
}
void SListPushBack(SList* plt, SLTDataType x)//尾插
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//先申请一个新的节点
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
//判断链表是否为空
if (plt->_head == NULL)
{
plt->_head = newnode;
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
while (cur->_next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
cur->_next = newnode;
}
}
void SListPushfront(SList* plt, SLTDataType x)//头插
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//先申请一个新的节点
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
if (plt->_head == NULL)
{
plt->_head = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->_next = plt->_head;
plt->_head = newnode;
}
}
void SListPopBack(SList* plt)//尾删
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
if (plt->_head == NULL)//当为空链表时
{
return;
}
else if (cur->_next == NULL)//有一个节点
{
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
else//有多个节点
{
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
while (cur->_next->_next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
free(cur->_next);
cur->_next = NULL;
}
}
void SListPopfront(SList* plt)//头删
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
plt->_head = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
SListNode* SListfind(SList* plt, SLTDataType x)//通过值来查找
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
//void SListDestory(SList* plt);
void Slistprint(SList* plt)
{
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->_data);
cur = cur->_next;
};
printf("NULL\n");
}
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDataType x)//任意位置后面插
{
assert(pos);
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//先申请一个新的节点
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;//申请节点并初始化
newnode->_next = pos->_next;
pos->_next = newnode;
}
void SListEraseAfter(SList* plt,SListNode* pos)//任意位置后面删
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
SListNode* prev = NULL;
while (prev!= pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
prev->_next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
void SListDestory(SList* plt)
{
assert(plt);
SListNode* cur = plt->_head;
SListNode* prev = NULL ;
while (cur != NULL)
{
prev = cur;
free(prev);
prev = prev->_next;
}
plt->_head = NULL;
}
void TestSList1()
{
SList s;
SListInit(&s);
SListPushBack(&s, 1);
SListPushBack(&s, 2);
SListPushBack(&s, 3);
SListPushBack(&s, 4);
SListPushBack(&s, 5);
SListPushfront(&s, 11);
SListPushfront(&s, 12);
SListPushfront(&s, 13);
SListPushfront(&s, 14);
//SListPopBack(&s);
//SListPopBack(&s);
//SListPopfront(&s);
//SListPopfront(&s);
SListNode* pos = SListfind(&s, 4);
SListInsertAfter(pos,2);
SListEraseAfter(&s,pos);//任意位置后面删
Slistprint(&s);
//SListDestory(&s);
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Slist.h"
int main()
{
TestSList1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
