使用python变成实现了六种图像的特殊效果,为:
浮雕、底片、哈哈镜、油画、素描、泛黄
各程序的运行结果均用Lena图像来展示。
一.浮雕特效
大致过程:
使用opencv库的EMBOSS滤波,提取轮廓。
自编写的实现:使用EMBOSS滤波器对应的算子实现。
# 图像特效处理
# 浮雕处理
# 使用opencv函数与自编写函数作效果对比
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageFilter
import cv2
import argparse
import numpy as np
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
def image_filters_test():
im = cv2.imread("Lena.jpg")
# 预定义的图像增强滤波器
im_blur = im.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR) # 模糊滤波
im_contour = im.filter(ImageFilter.CONTOUR) # 轮廓滤波
im_emboss = im.filter(ImageFilter.EMBOSS) # 浮雕滤波
im_min = im.filter(ImageFilter.MinFilter(3)) # 最小值滤波器
im.show()
im_blur.show()
im_contour.show()
im_emboss.show()
im_min.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# image_filters_test()
# read in the image and convert to HSV to extract value channel
img = cv2.imread("Lena.jpg")
horiz = cv2.flip(img, 1) # pressing through the pattern flips the image horizontally
large = cv2.resize(horiz, (0, 0), fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
h, s, v = cv2.split(hsv)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(s, (3, 3), 0)
edge = cv2.Canny(blur, 0, 50) # perform edge detection with a low slope threshold to capture all edges
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
mask = cv2.dilate(edge, kernel, iterations=1)
filt = cv2.bitwise_and(cv2.bitwise_not(mask), s) # filter the noisy edges out by masking off those regions
# get counts of times each value occurs in the filtered parts of the image
G = 3
N = 256 // G + 1
val_count = [0] * N
rows, cols = filt.shape
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
val_count[filt[i, j] // G] += 1
val_count[0] = 0
# detect peaks in the histogram, indicating discrete layers
val_log = np.array([0 if not vc else np.log(vc) for vc in val_count])
val_norm = [0] * N
k = 2 * G
for i in range(N): # use a windowed z-score to find prominent local maxima
lo = max(0, i - k)
hi = min(N, i + k)
window = val_log[lo:hi]
val_norm[i] = (val_log[i] - np.mean(window)) / np.std(window)
val_norm = np.array(val_norm)
colors, _ = find_peaks(val_norm, height=1, distance=15 // G)
# separate into layers by color and apply an edge gradient
# black -> clear to imitate shadows in regions of neg vertical slope
# white -> clear to imitate highlights in regions of pos vert slope
result = np.full_like(v, 128)
upper = np.zeros_like(v)
for i in range(len(colors) - 1, 0, -1):
lowc = np.array([0, G * colors[i] - 15, 0])
highc = np.array([255, G * colors[i] + 15, 255])
layer = cv2.inRange(hsv, lowc, highc)
# don't allow lower layers to overlap upper layers
composite = cv2.bitwise_or(layer, upper)
if i != len(colors) - 1:
composite = cv2.morphologyEx(composite, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
upper = composite
# find the gradient in the y direction
# ypos is positive dY and represents highlights
# yneg is negative dY and represents shadows
sobel_ypos = cv2.Sobel(composite, cv2.CV_8U, 0, 1, ksize=1)
sobel_yneg = cv2.Sobel(cv2.bitwise_not(composite), cv2.CV_8U, 0, 1, ksize=1)
# iteratively add shadows that get lighter and lighter as they shift up
# and add highlights that get darker and darker as thy shift down
S = 5
highlight = np.uint8(sobel_ypos)
shadow = np.uint8(sobel_yneg)
for j in range(1, S):
txlate_down = np.float32([[1, 0, 0], [0, 1, j]])
txlate_up = np.float32([[1, 0, 0], [0, 1, -j]])
hlj = np.uint8(cv2.warpAffine(sobel_ypos, txlate_down, (cols, rows)) / (2 ** j))
sdj = np.uint8(cv2.warpAffine(sobel_yneg, txlate_up, (cols, rows)) / (2 ** j))
highlight = hlj + cv2.bitwise_and(cv2.bitwise_not(hlj), highlight)
shadow = sdj + cv2.bitwise_and(cv2.bitwise_not(sdj), shadow)
mask = cv2.bitwise_not(cv2.threshold(cv2.bitwise_not(result), 128, 256, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1])
mask = cv2.bitwise_and(mask, cv2.bitwise_not(cv2.threshold(result, 128, 256, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]))
result += cv2.bitwise_and(highlight, highlight, mask=mask) // 2
result -= cv2.bitwise_and(shadow, shadow, mask=mask) // 2
# set the hue and saturation to look like paper
# then construct a colored version and display it
h = np.full_like(v, 20)
s = np.full_like(v, 40)
v = cv2.add(result, 100)
hsv = cv2.merge((h, s, v))
bgr = cv2.cvtColor(hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
cv2.namedWindow("output", cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
cv2.imshow("output", bgr) # cv2.resize(bgr, (0,0), fx=.5, fy=.5, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4))
# handle exiting out of the window via the ESC / ENTER key or the X in the corner of the window
while cv2.getWindowProperty("output", cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE):
k = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xFF
if k == 27 or k == 13: # wait for ESC / ENTER key to exit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if k == ord('s'): # wait for 's' key to save and exit
cv2.imwrite("output.png", bgr)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果展示:

二.底片处理
实际效果为图像的反转,即将RGB三值与255作差得到。
# 图像特效处理
# 底片效果
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def films(image):
h, w, d = image.shape[:3]
size = (h, w, d)
iTmp = np.zeros(size, np.uint8)
for i in range(h):
for j in range(w):
iTmp[i, j, 0] = 255 - image[i, j, 0]
iTmp[i, j, 1] = 255 - image[i, j, 1]
iTmp[i, j, 2] = 255 - image[i, j, 2]
return iTmp
if __name__ == "__main__":
img = cv2.imread('Lena.jpg')
cv2.imshow("Offical", img)
output = films(img)
plt.imshow(output)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow("output", output)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果展示:

三.哈哈镜
有局部放大和局部缩小并拉伸或压缩其余部分两种效果。
# 图像特效处理
# 哈哈镜效果
import cv2
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def maxframe(frame):
height, width, n = frame.shape
center_x = int(width / 2)
center_y = int(height / 2)
randius = 400 # 直径
real_randius = int(randius / 2) # 半径
new_data = frame.copy()
for i in range(width):
for j in range(height):
tx = i - center_x
ty = j - center_y
distance = tx ** 2 + tx ** 2
# 为了保证选择的像素是图片上的像素
if distance < randius ** 2:
new_x = tx / 2
new_y = ty / 2
# 图片的每个像素的坐标按照原来distance,之后的distance(real_randius**2)占比放大即可
new_x = int(new_x * math.sqrt(distance) / real_randius + center_x)
new_y = int(new_y * math.sqrt(distance) / real_randius + center_y)
# 当不超过new_data 的边界时候就可赋值
if new_x < width and new_y < height:
new_data[j][i][0] = frame[new_y][new_x][0]
new_data[j][i][1] = frame[new_y][new_x][1]
new_data[j][i][2] = frame[new_y][new_x][2]
return new_data
def MinFrame(frame):
height, width, n = frame.shape[:3]
center_x = int(width/2)
center_y = int(height/2)
new_data = frame.copy()
for i in range(width):
for j in range(height):
tx = i-center_x
ty = j-center_y
theta = math.atan2(ty, tx)
radius = math.sqrt(tx**2+ty**2)
new_x = int(center_x+math.sqrt(radius)*12*math.cos(theta))
new_y = int(center_y+math.sqrt(radius)*12*math.sin(theta))
if new_x < 0 or new_x > width:
new_x = 0
elif new_y < 0 or new_y > height:
new_y = 0
else:
new_data[j][i][0] = frame[new_y][new_x][0]
new_data[j][i][1] = frame[new_y][new_x][1]
new_data[j][i][2] = frame[new_y][new_x][2]
return new_data
if __name__ == '__main__':
image1 = cv2.imread("Lena.jpg")
image2 = cv2.imread("Lena.jpg")
frame1 = maxframe(image1)
frame2 = MinFrame(image2)
cv2.imshow("offical", frame1)
cv2.imshow("max", frame1)
cv2.imshow("min", frame2)
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(frame1, 'gray'), plt.title('max')
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(frame2, 'gray'), plt.title('min')
plt.show()
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果展示:

四.油画
类似滑动平均滤波和灰度直方图。
# 图像特效处理
# 油画效果
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def oilPainting(img, templateSize, bucketSize, step): # templateSize模板大小,bucketSize桶阵列,step模板滑动步长
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
gray = ((gray / 256) * bucketSize).astype(int) # 灰度图在桶中的所属分区
h, w = img.shape[:2]
oilImg = np.zeros(img.shape, np.uint8) # 用来存放过滤图像
for i in range(0, h, step):
top = i - templateSize
bottom = i + templateSize + 1
if top < 0:
top = 0
if bottom >= h:
bottom = h - 1
for j in range(0, w, step):
left = j - templateSize
right = j + templateSize + 1
if left < 0:
left = 0
if right >= w:
right = w - 1
# 灰度等级统计
buckets = np.zeros(bucketSize, np.uint8) # 桶阵列,统计在各个桶中的灰度个数
bucketsMean = [0, 0, 0] # 对像素最多的桶,求其桶中所有像素的三通道颜色均值
# 对模板进行遍历
for c in range(top, bottom):
for r in range(left, right):
buckets[gray[c, r]] += 1 # 模板内的像素依次投入到相应的桶中,有点像灰度直方图
maxBucket = np.max(buckets) # 找出像素最多的桶以及它的索引
maxBucketIndex = np.argmax(buckets)
for c in range(top, bottom):
for r in range(left, right):
if gray[c, r] == maxBucketIndex:
bucketsMean += img[c, r]
bucketsMean = (bucketsMean / maxBucket).astype(int) # 三通道颜色均值
# 油画图
for m in range(step):
for n in range(step):
oilImg[m + i, n + j] = (bucketsMean[0], bucketsMean[1], bucketsMean[2])
return oilImg
if __name__ == "__main__":
img = cv2.imread('Lena.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_ANYCOLOR)
oil = oilPainting(img, 4, 8, 2)
cv2.imshow('oil_paintings', oil)
plt.imshow(oil, 'gray'), plt.title('oil_painting')
plt.show()
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果展示:

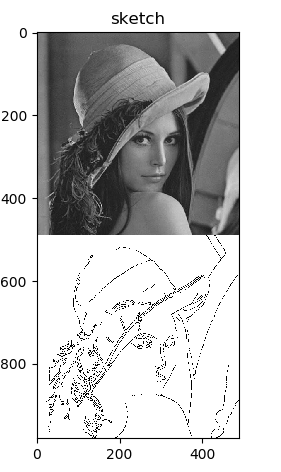
五.素描
基于opencv的轮廓提取实现黑白的效果形成素描,为灰度图像。
# 图像特效处理
# 素描效果
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取原始图像
img = cv.imread('Lena.jpg')
# 图像灰度处理
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 高斯滤波降噪
gaussian = cv.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
# Canny算子
canny = cv.Canny(gaussian, 50, 150)
# 阈值化处理
ret, result = cv.threshold(canny, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv.THRESH_OTSU)
# 显示图像
# cv.imshow('src', img)
# cv.imshow('result', result)
cv.imshow('result', np.vstack((gray, result)))
plt.imshow(np.vstack((gray, result)), 'gray'), plt.title('sketch')
plt.show()
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
结果展示:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
12405255 查看本文章


六.泛黄
改变RGB的值,使三通道均偏黄。
# 图像特效处理
# 泛黄怀旧效果
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取原始图像
img = cv.imread('Lena.jpg')
# 获取图像行和列
rows, cols = img.shape[:2]
# 新建目标图像
dst = np.zeros((rows, cols, 3), dtype="uint8")
# 图像怀旧特效
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
B = 0.272 * img[i, j][2] + 0.534 * img[i, j][1] + 0.131 * img[i, j][0]
G = 0.349 * img[i, j][2] + 0.686 * img[i, j][1] + 0.168 * img[i, j][0]
R = 0.393 * img[i, j][2] + 0.769 * img[i, j][1] + 0.189 * img[i, j][0]
if B > 255:
B = 255
if G > 255:
G = 255
if R > 255:
R = 255
dst[i, j] = np.uint8((B, G, R))
# 显示图像
cv.imshow('result', np.vstack((img, dst)))
plt.imshow(np.vstack((img, dst)), 'gray'), plt.title('yellow')
plt.show()
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
结果展示:
