一、 计算机概述
1.1 计算机组成部分
计算机的组成主要分为两大类:硬件,软件
硬件:是由许多不同功能模块化的部件组合而成的,并在软件的配合下完成输入、处理、储存、和输出等4个操作步骤,主要是一些电子元器件。
软件:是一系列按照特定顺序组织的电脑数据和指令,是电脑中的非有形部分。
常见的硬件:
- 运算器:计算机的运算系统,负责数据的运算工作;相当于计算机的大脑。
- 控制器:计算机的控制系统,协调控制个部件间的工作。
- 控制器 + 运算器 = 中央处理器(CPU)
- 存储器:计算机存储系统,分为内存(临时性存储数据的存储设备ROM,断电后数据消失)和外存(永久性存储设备RAM),存储形式都为二进制形式存储,RAM如下:机械硬盘、固态硬盘、光盘、U盘。
- 输入设备:键盘、鼠标、麦克风、摄像头、触摸屏、扫描仪等。
- 输出设备:显示器、音响、打印机。
- 网络设备:网卡
软件的分类:
系统软件:是负责管理计算机系统中各种独立的硬件,使得它们可以协调工作。系统软件使得计算机使用者和其他软件将计算机当作一个整体而不需要顾及到底层每个硬件是如何工作的,主要是用来控制和管理底层硬件的一套指令。
户提供最基本的计算机功能。
具体包括以下四类:
- 各种服务性程序,如诊断程序、排错程序、练习程序等
- 语言程序,如 汇编程序、 编译程序、 解释程序
- 操作系统
- 数据库管理系统
应用软件:基于系统软件之上的,为了某种特定的用途而被开发的软件。它可以是一个特定的程序,比如一个图像浏览器。也可以是一组功能联系紧密,可以互相协作的程序的集合,比如微软的Office软件。也可以是一个由众多独立程序组成的庞大的软件系统,比如 数据库管理系统。
1.2 人机交互方式
- 图形化界面操作方式:操作简单,表现直观,容易上手操作,步骤繁琐,占用空间大(显示图标等资源文件)
- 命令行操作方式 CMD(Command win+R 输入cmd回车)窗口:操作复杂,命令较多,不容易上手,步骤简单,占用空间小,适合远程操作
常见的DOS命令:
- cd:改变当前目录
格式:cd [/D] [drive:][path]
如果省略路径和子目录名则显示当前目录
c: 进入C盘根目录
cd / 进入到当前所在盘符的根目录;
cd .. 返回上一级目录
- dir:显示磁盘目录命令
格式:dir [ 盘符][路径][文件名][/p][/w][/A[[:]属性]][/O[:]排列顺序]][/S] - cls:清屏
- md:建立子目录
格式:md[ 盘符:][路径名]〈子目录名〉
盘符:指定要建立子目录的 磁盘驱动器字母,若省略,则为当前驱动器
路径名:要建立的子目录的上级目录名,若缺省则建在当前目录下
md c:\ fox (在当前驱动器c盘下创建子目录fox)
md c:\ fox\user (在fox 子目录下再创建user子目录)
- rd:删除子目录命令
子目录在删除前必须是空的,也就是说需要先进入该子目录,不能删除根目录和当前目录 - copy:文件复制命令
格式:copy [源盘][路径](源文件名) [目标盘][路径](目标文件名) - ren:文件改名命令
格式:ren[盘符:][路径]〈旧文件名〉〈新文件名〉 - del:删除文件命令
格式:del[ 盘符:][路径]〈文件名〉[/p]
选用/p参数,系统在删除前询问是否真要删除该文件,若不使用这个参数,则自动删除
在文件名称中可以使用 通配符
若要删除磁盘上的所有文件(del*·*或del·),则会提示:(arey ou sure?)(你确定吗?)若回答y,则进行删除,回答n,则取消此次删除作业
1.3 计算机语言
计算机本身就是有一系列物理硬件组成的,它们之间的沟通方式就是电信号,高低电压——二进数据,所以和计算机之间打交道,就得通过二进制来做,早期的编程语言/命令都是以二进制形式存在
计算机语言的种类非常的多,总的来说可以分成机器语言,汇编语言,高级语言三大类。

- 静态编译语言:C,C++ ,Java
编译是指在应用源程序执行之前,就将程序源代码“翻译”成目标代码(机器语言),因此其目标程序可以脱离其语言环境独立执行,使用比较方便、效率较高。但应用程序一旦需要修改,必须先修改源代码,再重新编译生成新的目标文件才能执行,只有目标文件而没有源代码,修改很不方便。(翻译一本书) - 动态解释语言:Python,JS
执行方式类似于我们日常生活中的“同声翻译”,应用程序源代码一边由相应语言的解释器“翻译”成目标代码(机器语言),一边执行,因此效率比较低,而且不能生成可独立执行的可执行文件,应用程序不能脱离其解释器,但这种方式比较灵活,可以动态地调整、修改应用程序。(同声翻译)
1.4 Java语言介绍
Java语言的前身Oak(橡树),1994年詹姆斯高斯林和他的团队开发出来的嵌入式编程语言。随着互联网的发展,紧随潮流编程互联网应用程序开发语言(面向对象),一直到2010年Sun公司被Oracle收购,Java就属于Oralce的子产品。
java技术架构:
- JavaSE Java Standard Edition Java标准版:桌面型应用程序
- JavaEE Java Enterprise Edition Java企业版:服务器应用程序
- JavaME Java Micro Edition Java微型版:嵌入式应用程序
Java最大的特点——跨平台
跨平台的意思就是说,一个软件可以在多个平台上运行,而不用更改软件的内容。
是因为JVM的功劳:JVM(Java Virtual Machine)Java虚拟机。
Java源代码文件后缀名为xxx.java 所编译出来的二进制文件后缀名为xxx.class
JVM主要负责将java语言的字节码文件转换为本地操作系统指令的一个工具软件。
所以,最终是字节码文件在跨平台!
1.5 Java开发环境搭建
JRE与JDK
JRE(Java Runtime Environment)Java运行环境:如果我们的计算机仅仅想运行Java程序的话,装这个软件即可。JRE = JVM + 核心类库。
JDK(Java Development Kit)Java开发工具包:如果我们的计算机想要去开发一个Java程序的话,装这个软件即可。JDK = 开发工具 + JRE。
二、基本数据类型与运算
2.1 关键字
关键字是指被高级编程语言赋予特殊含义的一些单词,关键字一般都是由小写字母组成。
- 用于定义数据类型的关键字:byte short int long float double char boolean void class interface
- 用于定义数据类型值的关键字:true false null
- 用于定义流程控制语句的关键字:if else switch case default while do for break continue return
- 用于定义访问权限修饰符的关键字:public protected private
- 用于定义继承关系的关键字:extends implements
- 用于定义实例对象的关键字:new this super instanceof
- 用于定义函数类型的关键字:static final abstract synchronized
- 用于处理异常的关键字:try catch finally throw throws
- 用于包的关键字:package import
- 其他的一些修饰关键字:native assert volatile transient
2.2 标识符
标识符指的是我们在程序中对变量、函数、类、接口、常量所定义的名称,也就是说这些名称是我们自定义的。
规则如下:
- 标识符可以由数字、字母、下划线 _ 、美元符 $ 组成
- 标识符不能以数字开头,当然下划线和美元符其实是可以开头的,但不推荐
- 标识符不能是关键字
- 标识符严格区分大小写
- 标识符可以为任意长度,但必须是一个连续的词
- 标识符也不能是Java内置类的名称
标识符命名的规范:
- 大驼峰式:主要针对类名,接口名。所有单词的首字母大写
- 小驼峰是:主要针对于变量名,函数名。除了第一个单词之外,其他单词首字母大写
- 常量规范:所有单词字母大写,单词与单词之间用下划线分隔
- 包名规范:所有单词字母小写,单词与单词之间用句号 .分隔
2.3 注释
注释是用于注解和说明程序的一些程序中的内置文本信息的,但这些内置文本不属于代码的范畴。所以在对含有注释的源代码进行编译时,所生成的字节码中不含有注释。
- 单行注释: //注释内容 直到换行为止
- 多行注释: /* 注释内容 内部可以进行换行 */
- 文档注释:/** 注释内容 内部可以进行换行 */ :文档注释可以被编译器识别,并生成相应的程序说明书。对某一个类进行文档生成时,该类必须是public型
多行注释中,不能再出现多行注释
2.4 常量与进制
常量就是指在程序中直接出现的一些数据,也叫字面量。
- 整数常量
- 小数常量
- 字符常量:由一个字母、数字、符号被单引号( ‘’ )标识的数据
- 字符串常量:由若干个字母、数字、符号被双引号( “” )标识的数据
- 布尔类型常量
- null常量
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//整数常量
System.out.println(10); //十进制整数
System.out.println(0b1001); //二进制整数 打印出来是十进制
System.out.println(0123); //八进制整数
System.out.println(0xAF3); //十六进制整数
//小数常量
System.out.println(3.14);
System.out.println(5.234e3);
System.out.println(1.2e-3);
//字符常量
System.out.println('a');
//System.out.println('ab'); ERROR
System.out.println('9');
//System.out.println('12'); ERROR
System.out.println('我');
System.out.println(' ');
//System.out.println(''); ERROR
//System.out.println('''); ERROR
System.out.println('\''); //打印 '
System.out.println('\n'); //打印 换行
System.out.println('\t'); //打印 缩进
//字符串常量
System.out.println("abcd");
System.out.println("a");
System.out.println(""); //字符串空串 vs null真空
System.out.println("\"");
//布尔常量
System.out.println(true);
System.out.println(false);
}
}
二进制转十进制
规律就是:1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 - 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
10010101 十进制是 128 + 16 + 4 + 1 = 149
十进制149 = 9 * 10^0 + 4 * 10^1 + 1 * 10 ^2
二进制1011 = 1 * 2^0 + 1 * 2^1 + 0 * 2^2 + 1 * 2^3 = 1 + 2 + 0 + 8 = 11
一个二进制位称之为是一个比特 bit;八个比特称之为一个字节 byte;字节是计算机当中的最小计数单元。
- 1 byte = 8 bit
- 1 kb = 1024 byte
- 1 mb = 1024 kb
- 1 gb = 1024 mb
十进制转二进制
- 53 ÷ 2 = 26 ~ 1
- 26 ÷ 2 = 13 ~ 0
- 13 ÷ 2 = 6 ~ 1
- 6 ÷ 2 = 3 ~ 0
- 3 ÷ 2 = 1 ~ 1
- 1 ÷ 2 = 0 ~ 1
余数从下到上 110101 = 1 + 4 + 16 + 32 = 53
二进制转八进制
10010101 => 010-010-101 => 0225 = 5 * 8^0 + 2 * 8^1 + 2 * 8^2 =5 + 16 + 128 = 149
二进制转十六进制
10010101 => 1001-0101 => 0x95 = 5 * 16^0 + 9 * 16^1 = 5 + 144 = 149
负数的二进制
-29的二进制 将正数部分的二进制先取反 再加1 即为负数的二进制
00011101 =>取反 11100010 =>加1 11100011
2.5 变量
- 变量的本质就是在内存中程序所处的进程中的一个临时存储区域
- 该区域的存储值有限制的
- 该区域值的变化必须是同类型的或向下兼容的
- 该区域有其自身的物理内存地址-指针
该区域中 存储值的限制 和 数据的变化类型 由 数据类型 来决定
该区域中 其空间的分配 和 空间的物理内存地址 由计算机底层来决定
#include<stdio.h>
void main() {
int a = 3; //创建一个普通的整型变量 存3这个常量
int* b; //创建一个一重指针变量 存的是a变量的地址
b = &a;
int** c; //创建一个二重指针变量 存的是b变量的地址
c = &b;
printf("a的地址:%d\n",&a); //打印a的地址 0x123
printf("a的内容:%d\n",a); //打印a空间的内容 3
printf("b的地址:%d\n",&b); //0x456
printf("b的内容:%d\n",b); //0x123
printf("拿着b的内容去找变量a:%d\n",*b); //3
printf("c的地址:%d\n",&c); //0x789
printf("拿着c的内容去找变量b:%d\n",*c); //0x123
printf("拿着c的内容去找变量b,拿着b的内容去找变量a:%d\n",**c); //3
//printf("%d\n",*a);
printf("%d\n",*&*c); //0x123
printf("%d\n",&*&**&c); //0x456
//结果如下
a的地址:6422300
a的内容:3
b的地址:6422296
b的内容:6422300
拿着b的内容去找变量a:3
c的地址:6422292
拿着c的内容去找变量b:6422300
拿着c的内容去找变量b,拿着b的内容去找变量a:3
6422300
6422296
}
2.6 数据类型
在Java当中,数据类型主要分为两大类基本数据类型和引用数据类型
基本数据类型:在变量的空间中存储数据
- 整型
- byte 1字节 2^8 256 -128~127 -2^7 ~ 2^7 - 1
- short 2字节 2^16 65536 -32768~32767 -2^15 ~ 2^15 - 1
- int 4字节
- long 8字节
- 浮点型
- float 4字节
- double 8字节
- 字符型
- char 2字节
- 布尔型
- boolean 不确定
在常量中,整型常量默认int类型,小数常量默认是double类型。
布尔类型,如果是单一变量的话,在JVM中true被认为是1 false被认为是0 所以是4字节存如果是布尔类型数组的话,在JVM中true和false被认为是byte类型 1字节
引用数据类型:数据是在堆内存中存储,变量仅仅存放的是数据在堆内存中的地址
- 字符串
- 数组
- 数组
在Java中,但凡存储在堆内存中的数据,统称为对象
2.7 运算符
| 算术运算符 | 含义 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| + | 加法 | 如果加号左右有字符串 则加号为连接符 |
| - | 减法 | 6-3=9 |
| * | 乘法 | 6*6+36 |
| / | 除法 | 3/2=1 3.0/2=1.5 如果除号两边都是整数 结果为整数;有小数 结果为小数 |
| % | 取余 | 9%5=4,x%-y=x%y,-x%y=-(x%y),-x%-y=-(x%y) |
| a++ | 后置自增 | a自身加一,使用原来的值 |
| ++a | 前置自增 | a自身加一,使用加之后的值 |
| a– | 后置自减 | a自身减一,使用原来的值 |
| –a | 前置自减 | a自身减一,使用加之后的值 |
赋值运算符
-
+=
-
-=
-
*=
-
/=
-
%=
比较运算符 -
> -
< -
>= -
<= -
!=
逻辑运算符
&!^!&&||
位运算符
&与|或^异或(相异为1,相同为0)>>右移(减小*2^x)<<左移(增大*2^x)(x为偏移量)
三目运算符
数据类型 变量名 = 布尔表达式?值1:值2;
int number = 10 % 2 == 0? 10 : 2;
变量的交换问题:
int a = 3;int b = 7;
//方法一
int c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
//方法二
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
//方法三
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
三、流程控制语句
3.1 if条件语句
单分支if语句
...CodeA
if (布尔表达式) {
语句组;
}
...CodeB
双分支if-else语句
...CodeA
if (布尔表达式) {
语句组A;
} else {
语句组B;
}
....CodeB
多分支if-else-if语句
...CodeA
if (布尔表达式1) {
语句组A;
} else if (布尔表达式2) {
语句组B;
} else if (布尔表达式3) {
语句组C;
} else {
语句组D;
}
...CodeB
3.2 switch分支语句
与if分支语句一样,都是对条件的判断。switch一般用在条件较多的情况下,但是有一个重要的细节,if语言可以对区间值或固定值进行判断,switch只能对固定值进行判断。
switch (变量) {
case 值1: //if (变量==值1) {语句组A;}
语句组A;
break;
case 值2:
语句组B;
break;
...
case 值n: //if (变量==值n) {语句组N;}
语句组N;
default: // else {语句组N+1;}
语句组N+1;
break;
}
switch的一些使用细节
- switch所传入的变量,char,byte,short,int,String或者枚举类型
- 值1,值2,一直到值n,这几个值必须是同一个数据类型的
- 当变量匹配的相关case的值的时候,执行case中的语句,直到遇到break结束;如果该case语句中没有break,则继续向下执行,直到遇到另外一个break结束
3.3 for循环语句
循环主要解决具有规律性的且具有重复性的代码问题,避免程序冗余
循环四要素
- 1循环的初始化:循环的第1次执行从哪里开始
- 2循环的继续条件:循环从当前轮是否向后执行下一轮
- 3循环体:需要被循环执行的部分
- 4循环的步长、周期:当前循环到下一轮循环之间的变化
常见的循环问题可以分为两大类:
- 已知循环次数的 一般用for语句做
- 未知循环次数但是已知循环结束条件 一般用while语句做
for (1循环的初始化;2.循环的继续条件;4.循环的步长) {
3.循环体
}
1-2-3-4-2-3-4-2-3-4-2不满足则结束循环
3.4 while循环语句
while循环主要用于解决循环次数未知,但循环结束条件已知的情况。
while其实和for循环是可以相互转换的,是因为都逃不开循环四要素
1.循环的初始化
while (2.循环继续条件) {
3.循环体
4.循环的步长、周期
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
可以转换为while循环
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
3.5 break、continue跳转语句
break在循环语句中叫做终止语句,终止的是break最近的一层循环
continue在循环语句中叫做跳过语句,跳过本次循环开启下一轮循环
3.6 编程题练习

思路: 后台随机产生一个两位数,获取产生两位数的十位和个位,将其与用户输入的数字做比较,得出奖金。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo19{
public static void main(String[] args){
//产生[10,100)的随机数,分别获取该数的十位和个位
int number = (int)(Math.random()*90 + 10);
int numberShi = number / 10;
int numberGe = number % 10;
//获取用户输入的数字,分别获取该数的十位和个位
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个两位数:");
int guess = input.nextInt();
int guessShi = guess / 10;
int guessGe = guess % 10;
//分情况进行判断用户所赢得的奖金
if(number == guess){
System.out.println("奖金10 000美元");
}else if(numberShi == guessGe && numberGe == guessShi){
System.out.println("奖金3 000美元");
}else if(numberShi==guessShi || numberGe == guessGe){
System.out.println("奖金1 000美元");
}else{
System.out.println("没中奖");
}
System.out.println("中奖号码是:" + number);
}
}

思路: 根据用户输入的数据,判断ad-bc是否等于0,为0就结束程序,输出提示信息,否则就将数据带入公式进行计算。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo21{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a,b,c,d,e,f: ");
double a=scanner.nextDouble();
double b=scanner.nextDouble();
double c=scanner.nextDouble();
double d=scanner.nextDouble();
double e=scanner.nextDouble();
double f=scanner.nextDouble();
//判断用户输入的数据是否有值,有值就带入公式计算
if((a * d - b * c)==0){
System.out.println("The equation has no solution");
}
else{
double x=(e * d - b * f) / (a * d - b * c);
double y=(a * f - e * c) / (a * d - b * c);
System.out.println("x is "+x+" and y is "+y);
}
}
}

思路: 根据用户输入的星期和天数做一个相加,并对7取余数,根据余数判断将来天数的星期。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo22{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
//获取用户输入的今天日期的星期和,过后的天数
System.out.print("Enter today's day: ");
int day=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the number of days elapsed since today: ");
int latter=scanner.nextInt();
//将用户输入的数据进行一个相加并对7取余后根据余数判断星期
int finall=(day + latter) % 7;
String today=process(day);
//输入数字超出范围提示用户输入无效
if(today=="error"){
System.out.println("Check the nubmer you jiust hava input!");
}
else{
System.out.println("Today is "+process(day)+" and the future day is "+process(finall));
}
}
public static String process(int day){
String week="";
switch(day)
{
case 0:
week="Sunday";
break;
case 1:
week="Monday";
break;
case 2:
week="Tuesday";
break;
case 3:
week="Wednesday";
break;
case 4:
week="Thursday";
break;
case 5:
week="Friday";
break;
case 6:
week="Saturday";
break;
default:
week="error";
}
return week;
}
}

思路: 思路基本与上一题相似,将用户输入的数据,带入公式计算即可。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo25{
public static void main(String[] args){
//获取用户输入的数据
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter year: (e.g..2012): ");
int year=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter month: (1-12): ");
int month=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the day of month: (1-31): ");
int day=scanner.nextInt();
//如果月份为1或2就将月份分别变成 13,14,并将年-1
if(month==1 || month==2){
month+=12;
year-=1;
}
//带入公式计算
int j=year / 100;
int k=year % 100;
int weekInt=(day + 26 * (month + 1) / 10 + k + k / 4 + j / 4 + 5 * j) % 7;
String week=process(weekInt);
System.out.println("Day of the week is "+week);
}
public static String process(int day){
String week="";
switch(day)
{
case 0:
week="Sunday";
break;
case 1:
week="Monday";
break;
case 2:
week="Tuesday";
break;
case 3:
week="Wednesday";
break;
case 4:
week="Thursday";
break;
case 5:
week="Friday";
break;
case 6:
week="Saturday";
break;
default:
week="error";
}
return week;
}
}

思路: 获取用户输入点的坐标,判断该坐标与矩形宽高的关系,得出该点是否在矩形内。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo27{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a point with two coordinates: ");
double i=scanner.nextDouble();
double j=scanner.nextDouble();
//对用户输入的坐标求绝对值
double x=Math.abs(i);
double y=Math.abs(j);
//判断该点和矩形宽高的距离关系
if((x < (10 / 2)) && (y < (5.0 / 2))){
System.out.println("Point ("+i+", "+j+") is in the rectangle");
}
else{
System.out.println("Point ("+i+", "+j+") is not in the rectangle");
}
}
}

思路: 画图早出两矩形的临界值得出,临界值的数据关系即可。

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo29{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("Enter r1's center x-,y-coordinates,width, and height: ");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
double x1=scanner.nextDouble();
double y1=scanner.nextDouble();
double w1=scanner.nextDouble();
double h1=scanner.nextDouble();
//获取用户输入两个矩形中心点的坐标,和矩形的宽高
System.out.print("Enter r2's center x-,y-coordinates,width, and height: ");
double x2=scanner.nextDouble();
double y2=scanner.nextDouble();
double w2=scanner.nextDouble();
double h2=scanner.nextDouble();
//判断临界值的关系得出结论
if(y2 -y1 <= (h1 - h2) / 2 && y1 -y2 <= (h1 - h2) / 2 &&
x2 -x1 <= (w1 - w2) / 2 && x1 -x2 <= (w1 -w2) / 2) {
System.out.println("r2 is inside r1");
}else if(y2 -y1 >= (h1 + h2) / 2 || y1 -y2 >= (h1 + h2) / 2 ||
x2 -x1 >= (w1 + w2) / 2 || x1 -x2 >= (w1 + w2) / 2) {
System.out.println("r2 does not voerlap r1");
}else {
System.out.println("r2 overlaps r1");
}
}
}

思路: 用户输入坐标和圆心后计算两圆之间的圆心距,在将圆心距和两半径进行比较,得出两圆的位置关系。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo30{
public static void main(String[] args){
//获取输入的坐标和圆心数据
System.out.print("请输入圆1心的坐标和半径:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double ox1=input.nextDouble();
double oy1=input.nextDouble();
double r1=input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入圆2心的坐标和半径:");
double ox2=input.nextDouble();
double oy2=input.nextDouble();
double r2=input.nextDouble();
//计算圆心距
double distant=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(ox1 - ox2,2) + Math.pow(oy1 -oy2,2));
//判断距离
if(distant <= r1 - r2){
System.out.println("圆2在圆1内");
}else if(distant < r1 +r2){
System.out.println("圆2和圆1相交");
}else{
System.out.println("圆2在圆1外");
}
}
}

思路: 获取输入的两个数字,比较这两个数字的大小,取最小的值作为循环的初始值,倒序遍历,每次遍历判断该数是否可以被输入的两个数字整除,若可以则该数就是最大公约数,结束循环,进行输出,否则继续遍历查找。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo33{
public static void main(String[] args){
//输入两个数字,取出其中的最小值,
System.out.print("请输入两个整数:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int num1=input.nextInt();
int num2=input.nextInt();
//获取两值的较小值
int min=num1 < num2 ? num1 : num2;
int gcd=1;
//以最小值,倒序挨个找那个数既可以被num1和num2的数找到就退出输出该值
for(int i=min;i>0;i--){
if(num1 % i == 0 && num2 % i == 0){
gcd=i;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("最大公约数为:"+gcd);
}
}

思路: 对于字符串中的字符可以通过String.charAt(index),方法来获取字符串中index角标的值,于是可以通过比较字符串首尾的值,来判断该字符串是否为回文字符串,设左边为l,l从0开始l=0,右边为r=str.length()-1,判断结束的条件为l<r,即左边的下标大于右边时结束循环。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo35{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("请输入一段话:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String str = input.nextLine();
int l=0;
int r=str.length()-1;
boolean flag=true;
//头尾判断该字符串是否回文
while(l < r){
if(str.charAt(l) == str.charAt(r)){
l++;
r--;
}else{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println(str + "这段话是一个回文");
}else {
System.out.println(str + "这段话不是一个回文");
}
}
}

思路: 5行显示50个素数,以50作为循环的条件,定义一个计数器变量,每10个就换行,从2开始,循环判断该数是否可以被该数的一半的每个数整除,可以就不做处理,在循环下一个数,否则就输出这个数,并且计数器加1。
public class Demo36{
public static void main(String[] args){
int count=0;
int number=2;
while(count < 50){
//标志该数是否为素数
boolean flag=true;
for(int i=2; i<=number / 2; i++) {
if(number % i ==0){
flag=false;
break;
}
}
//计数器加1,输出素数,每十个换行
if(flag) {
System.out.print(number + "\t");
count++;
if(count % 10 ==0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
number++;
}
}
}

思路:
第4行 4 3 2 1 2 3 4
3 2 1 0 1 2 3
y = |x| + 1 x∈[-3,3]
第5行 5 4 3 2 1 2 3 4 5
4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4
y = |x| + 1 x∈[-4,4]
第i行 y = |x| + 1 x∈[-(i-1),i-1]
public class Demo41{
public static void main(String[] args){
//一共循环7次
for(int i=1; i <= 7; i++) {
//每次先打印空格,空格规律为7-i
for(int k=1; k<= 7-i; k++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j=-(i-1); j<=i-1; j++) {
System.out.print(Math.abs(j)+1+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

思路: 循环进行一个累加,分母是分子+2
public class Demo45{
public static void main(String[] args){
double sum=0;
//循环累加步长为2
for(int i=1; i<=97; i+=2) {
sum += i * 1.0 / (i+2);
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}

思路: 循环累加,并求每次的阶乘,每次阶乘为前一个阶乘在乘以当前循环的数。(题中阶乘数太大了,大于int和double的范围,结果为infinite,所以这里缩小了范围)
public class Demo47{
public static void main(String[] args){
double sum = 1;
//值不可为10000,阶乘范围超出int范围,结果会为infinite
int max = 10;
//阶乘数从1开始
int temp = 1;
for(int i=1; i < max; i++) {
temp=temp * i;
sum += 1.0 / temp;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}

思路: 从1开始循环到10000,内循环每次从1开始到该数的半值,判断当前内循环的数是否可以被外循环的数整除,可以的话就加入总和,内循环循环完后就判断总和和当前的值是否相等,相等就输出,否则就继续循环。
public class Demo48{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1; i<=10000; i++) {
int sum=0;
//判断当前数否可以被,从1到自己一半的数整除可以的话就加入总和
for(int j=1; j<=i / 2; j++) {
if(i % j == 0) {
sum +=j;
}
}
//如果总和和当前的数相等的话就输出该结果
if(sum == i) {
System.out.print(i+"\t");
}
}
}
}

思路: 将用户或计算机赢的次数为2作为循环的退出的条件,只要用户或计算机谁赢了2次就退出循环,每次进入循环,接收用户输入的数字并产生内部的随机数,在对两个数进行比较判断输赢,进入用户和电脑的计数器中,达到两次后就结束循环判断用户赢还是电脑赢。
import java.util.*;
public class Demo49{
public static void main(String[] args){
//定义一个字符串数组
String[] arry={
"剪刀","石头","布"};
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
//定义用户和电脑赢的次数的计数器
int userCount = 0;
int comCount = 0;
//只要用户和电脑赢的次数不为2就继续循环
while(userCount != 2 && comCount != 2){
System.out.print("剪刀(0),石头(1),布(2):");
int user=input.nextInt();
Random random=new Random();
//随机产生一个[0,3)的数字
int com=random.nextInt(3);
//判断用户和电脑谁赢,记录到计数器中
if(user == com) {
System.out.println("用户:"+arry[user]+" , 电脑:"+arry[com]+", 平局!");
}else if(user - com == -2 || user - com == 1 ) {
System.out.println("用户:"+arry[user]+" , 电脑:"+arry[com]+", 用户赢!");
userCount++;
}else {
System.out.println("用户:"+arry[user]+" , 电脑:"+arry[com]+", 电脑赢!");
comCount++;
}
}
if(userCount == 2) {
System.out.println("用户最终胜利!");
} else {
System.out.println("电脑最终胜利!");
}
}
}

思路: 每次循环对2取余,将余数存入字符串的第一位,然后除2去掉最后一位数,直到为0为止。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo50{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("请输入一个数字:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = input.nextInt();
String str="";
//每次对2取余,并将该数存放到字符串的第一位
while(number != 0){
str = number % 2 + str;
number /= 2;
}
System.out.println(str);
}
}

思路: 与求二进制思路相同。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo51{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = input.nextInt();
String o = "";
//每次对8取余,并将该数存放到字符串的第一位
while(number != 0) {
o = number % 8 +o;
number /= 8;
}
System.out.println(o);
}
}

思路: 死循环,每次获取一串数字的一个值,对初始最大值0,进行比较,如果大于就将该值赋给最大值,并将计数器置为1,如果与最大值相等就将计数器加一,循环到输入为0 为止,最后输出结果。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo52{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("请输入一串整数数字:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int max=0;
int count=0;
while(true) {
//死循环,每次获取一个数字,以0结束
int num=input.nextInt();
if(num == 0){
break;
}
//判断当期数是否大于最大数,是的话将改值赋给最大值,将计数器置为1
if(num > max){
max=num;
count=1;
//相等的话就先加
}else if(num == max){
count++;
}
}
//最后输出结果
if(max == 0){
System.out.println("none");
}else {
System.out.println("max number is "+max+" is count is "+count);
}
}
}

思路: 基本逻辑思路
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo31{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter an integer: ");
int num=scanner.nextInt();
//与判断,即能被5和6整除
if(num % 5 == 0 && num % 6 == 0){
System.out.println("Is "+num+"divisible by 5 and 6?"+" true");
}else{
System.out.println("Is "+num+"divisible by 5 and 6?"+" false");
}
//或判断,能被5或6整除
if(num % 5 == 0 || num % 6 == 0){
System.out.println("Is "+num+"divisible by 5 or 6?"+" true");
}else{
System.out.println("Is "+num+"divisible by 5 or 6?"+" false");
}
//异或判断不能同时被5或6整除
if(num % 5 == 0 ^ num % 6 == 0){
System.out.println("Is "+num+"divisible by 5 and 6, but not both?"+" true");
}else{
System.out.println("Is "+num+"divisible by 5 and 6, but not both?"+" false");
}
}
}

思路: 对输入十进制数循环对16取余数,如果得余数小于10就直接将该数转为字符数字,否则就变为对应的A,B,C,D,E,F存入一个字符数组,循环完后逆序输出该字符数组即可。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo34{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
int num=scanner.nextInt();
int i=0;
//定义一个字符数组存放16进制字符
char[] ch=new char[100];
//为0就直接输出
if (num==0) {
System.out.println(0);
}else{
while(num!=0){
//循环对16取余数,如果小于10就将其变为字符,大于10就加上A字符后减10,将其变为16进制字符
int n=num % 16;
if(n < 10){
ch[i++]=(char) (n+'0');
}
else{
ch[i++]=(char) (n+'A'-10);
}
num /= 16;
}
}
//逆序输出该字符数组
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){
System.out.print(ch[j]);
}
}
}

思路: 先定义正数,负数,输入数字的数量,总和,平均值初始为0,循环获取用户输入的数字,与0判断>0正数加一,加入总和,输入数字的数量加1,<0负数加一,加入总和,输入数字的数量加1,循环完后,求平均,输出结果。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo37{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
//定义初始值为0
int temp=0,positNum=0,negatNum=0,total=0,sum=0;
System.out.print("Enter an interger, the input ends if it is 0:");
//判断输入的数字大小,计入总和
while((temp=scanner.nextInt())!=0){
if(temp > 0){
positNum++;
}
if(temp < 0){
negatNum++;
}
sum += temp;
total++;
}
//输出结果
if(total==0){
System.out.println("No numbers are entered except 0");
}else{
double avg=sum / total;
System.out.println("The number of positives is "+positNum);
System.out.println("The number of negatives is "+negatNum);
System.out.println("The total is "+sum);
System.out.println("The average is "+avg);
}
}
}

思路: 循环判断能被5和6整除的数,并计数,每10个换一次行。
public class Demo38{
public static void main(String[] args){
//计数器每行10就换行
int j=0;
//循环判断找出即能被5和6整除的数
for(int i=100;i <=1000;i++){
if(i % 5==0 && i % 6==0){
System.out.print(i+" ");
j++;
}
if(j % 10 ==0){
j=0;
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}

思路: 定义一个字符串来保存输入数的因子,判断输入数是否为1,是就输出空字符串,否则就对该数从2开始取余,如若余数为0,则将该因子存放到字符串中,并将该数赋以/2的数继续循环,否则就自增遍历。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo40{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("输入一个整数:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String result="";
int num=input.nextInt();
//因子数从2开始,输入的数不为1
for(int i = 2;num != 1;) {
if(num % i == 0) {
num /= i;
result += i + ", ";
}else {
i++;
}
}
//输出结果
System.out.println("最小因子数为: "+result);
}
}

思路: 第4行
4 3 2 1 2 3 4
3 2 1 0 1 2 3
y = |x| + 1 x∈[-3,3]
第5行
5 4 3 2 1 2 3 4 5
4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4
y = |x| + 1 x∈[-4,4]
第i行 y = |x| + 1 x∈[-(i-1),i-1]

public class Demo41 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 7 - i ;k++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = -(i - 1); j <= i - 1; j++) {
System.out.print(Math.abs(j) + 1 + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
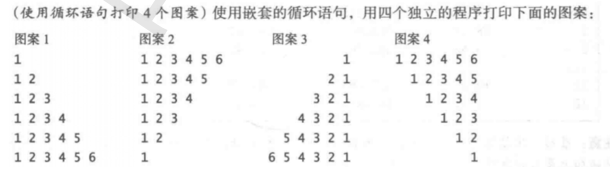
思路: 图案1:从1到6每行打印当前循环的数字
图案2: 就是图案1的倒序
图案3: 打印行时先打印|i-6|个空格
图案4:在图案3的基础上,内循环从1开始到外循环的数结束
public class Demo42{
public static void main(String[] args){
//循环6行每行打印i个数字
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("----------------");
//倒序输出
for(int i=6;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("----------------");
//每行打印|i-6|个空格
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++){
for(int k=1;k<=Math.abs(i-6);k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j=i;j>0;j--){
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("----------------");
//内循环从1开始到i的倒序
for(int i=6;i>=0;i--){
for(int k=1;k<=Math.abs(i-6);k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

思路: 每行为2的从0开始的升序次幂,根据规律找出内循环的范围
第1行 0
第2行 0 1 0
第3行 0 1 2 1 0
第4行 0 1 2 3 2 1 0
第i行:f(x) = i - 1 - |x| x∈[-(i-1),i-1]
public class Demo43{
public static void main(String[] args){
//循环8次每次打印8-i个空格
for(int i=1; i<=8; i++) {
for(int k=1; k<=8-i; k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j=1 - i; j<= i-1;j++) {
int num=(int) Math.pow(2,i -1 -Math.abs(j));
//每个数字占四个空,并右对齐
System.out.printf("%4d",num);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

思路: 根据公式,循环求值即可。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo46{
public static void main(String[] args){
double pai=0;
double s=0;
//循环求值
for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++){
double temp=Math.pow(-1.0, i + 1) / ( 2 * i - 1);
s+=temp;
}
pai=4 * s;
System.out.println(pai);
}
}
四、常用类
4.1 Math类
Java 的 Math 包含了用于执行基本数学运算的属性和方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。
Math 的方法都被定义为 static 形式,通过 Math 类可以在主函数中直接调用。
自然常量:
| 常量名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Math.E | 自然对数(返回double) |
| Math.PI | 圆周率 (返回double) |
取整方法:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Math.ceil(double a) | 向上取整 |
| Math.floor(double a) | 向下取整 |
| Math.round(double a) | 四舍五入 |
三角函数:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Math.sin(double a) | 正弦函数 参数是弧度值 |
| Math.cos(double a) | 余弦 |
| Math.tan(double a) | 正切 |
| Math.toDegrees(double a) | 将弧度转角度 |
| Math.toRadians(double a) | 将角度转弧度 |
| Math.asin(double a) | 反正弦函数 |
| Math.acos(double a) | 反余弦函数 |
| Math.atan(double a) | 反正切函数 |
指数函数:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Math.pow(double a,double b) | a^b |
| Math.sqrt(double a) | a的平方根 |
| Math.cbrt(double a) | a的立方根 |
其他:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Math.hypot(double a,double b) | 求a,b两点间的距离 |
| Math.abs(double a) | a的绝对值 |
| Math.max(a,b) | 返回a和b之间的最大值 |
| Math.min(a,b) | 返回a和b之间的最小值 |
| Math.random() | 产生[0,1)之间的一个小数 |
4.2 Scanner类
用于负责数据输入的类,底层是和IO流相关。
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| String next() | 获取直到遇到空格为止的一个字符串 |
| String nextLine() | 获取直到遇到回车为止的一个字符串 |
| int nextInt() | 获取一个整数空格结束 |
| double nextDouble() | 获取一个小数空格结束 |
| float nextFloat() | 获取一个小数空格结束 |
| boolean nextBoolean() | 获取一个布尔类型空格结束 |
4.3 Random类
用于产生随机数
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| int nextInt() | 随机生成一个整数0~2^32的整数 |
| int nextInt(n) | 随机产生一个[0,n)的整数 |
| double nextDouble() | 随机产生一个[0,1)的小数 |
| boolean nextBoolean() | 随机产生一个布尔类型值 |
4.4 String类
String 类是不可改变的,所以你一旦创建了 String 对象,那它的值就无法改变了, 不可修改其长度,不可修改其内容 。所以将来对字符串内容的改变,不能在原地改,只能重新创建一个字符串。
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "ab" + "dc";
//上述代码一共有几个字符串?
//四个"abc" "ab" "dc" "abdc"
}
}
获取:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| char charAt(int index) | 获取指定角标index处的字符 |
| int indexOf(int ch) | 获取指定字符(编码)在字符串中第一次(从左到右)出现的地方反回的是角标。-1 表示不存在 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 获取指定字符(编码)在字符串中第一次(从右到做)出现的地方返回的是角标 |
| int indexOf(String str) | 获取指定字符串在本字符串中第一次(从左到右)出现的地方返回的是角标 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str) | 获取指定字符串在本字符串中第一次(从右到左)出现的地方返回的是角标 |
| int length() | 获取字符串的长度 |
| String[] split(String regex) | 将字符串按照regex的定义进行分割 |
| String substring(int beginIndex) | 截取一段子字符串,从beginIndex开始到结尾 |
| String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 截取一段子字符串,从beginIndex开始到endIndex(不包含) |
修改:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| String toLowerCase() | 将字符串中所有的英文字母全部变为小写 |
| String toUpperCase() | 将字符串中所有的英文字母全部变为大写 |
| String trim() | 移除字符串两端的空格 |
| String replace(char oldCh,char newCh) | 将字符串中oldCh字符替换成newCh字符 |
判断:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| int compareTo(String anotherString) | 按照字典顺序比较两个字符串的大小 |
| boolean contains(String another) | 判断当前字符串中是否包含指定字符串another |
| boolean equals(String another) | 比较当前字符串与指定字符串的内容是否相同 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断当前字符串是否为空 |
| boolean startsWith(String prefix) | 判断该字符串是否以prefix开头 |
| boolean endsWith(String suix) | 判断该字符串是否已suix结尾 |
案例1
如何删除字符串中左右两端出现的空格,不用trim?
思路:从字符串两端开始,只要遇到字符就记下该下标,最后用两端的下标截取字符串,就可以去除两边的空格。
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " 123123123 12123 ";
//去空格后"123123123 12123"
//定义两端的下标
int l = 0;
int r = str.length() - 1;
while (str.charAt(l) == ' ') {
l++;
}
while (str.charAt(r) == ' ') {
r--;
}
//用下标截取字符串
System.out.println("[" + str.substring(l,r + 1) + "]");
}
}
案例2
在字符串"abcbcbcbcbcbc"中统计"bcb"出现的次数?
思路:
非贪心算法:每次获取子串在父串的第一个索引,计数后,截取该索引处的字符串,并循环,直到找不到索引为止。
贪心算法:循环长度较长的字符串,次数为较长字符串-较短字符串,每次判断较长字符串的首字母是否和要匹配的字符串的首字符匹配,相匹配,就截取较长字符串(匹配字符串的长度)与要匹配的字符串比较计数。
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcbcbcbcbcbc";
String s2 = "bcb";
//贪心算法 5个
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length() - s2.length() + 1; i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(0)) {
if (s2.equals(s1.substring(i,i + s2.length()))) {
count++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
//非贪心算法 3个
/*
String temp = s1;
int count = 0;
while (true) {
int index = temp.indexOf(s2);
if (index == -1) {
break;
}
count++;
temp = temp.substring(index + s2.length());
}
System.out.println(count);
*/
}
}
案例3
查找两个字符串中最长的公共子串?
思路:在较短的字符串,定义左右角标每次循环截取较短字符串,与比较字符串比较是否包含关系,是就输出,否则就继续循环遍历。
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "c is a program but is diffcult";
String s2 = "Java is a program but is slow";
for (int len = s2.length(); len > 0; len--) {
for (int l = 0,r = len - 1; r < s2.length(); l++,r++) {
String temp = s2.substring(l,r + 1);
if (s1.contains(temp)) {
System.out.println(temp);
return;//直接结束程序
}
}
}
}
}
4.5 Character类
字符工具类
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Character.isDigit(char ch) | 判断字符是否是数字 |
| Character.isLetter(char ch) | 判断字符是否是字母 |
| Character.isLetterOrDigit(char ch) | 判断字符是否是数字或字母 |
| Character.isLowerCase(char ch) | 判断是否是小写字母 |
| Character.isUpperCase(char ch) | 判断是否是大写字母 |
| Character.isSpaceChar(char ch) | 判断是否空白字母(空格 制表符 回车) |
案例1
将十六进制数字转为十进制?
思路: 用户输入十六进制字符,循环用字符串工具类判断该字符是否为数字和字母,是字母就判断该字母是否在A-F的范围内,否则就输出非法字符,如果不是非法字符就循环计数十六进制对应的十进制数字。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Sample{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("请输入一个十六进制数字: ");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String hex = input.nextLine().toUpperCase();
//输入长度为0则无输入
if(hex.length() == 0){
System.out.println("无输入!");
return;
}
//循环判断输入的字符是否为非法字符
//排除非数字,字母和非A-F字符
for(int i=0; i<hex.length(); i++) {
char ch = hex.charAt(i);
if(Character.isDigit(ch) || Character.isLetter(ch)) {
if(Character.isLetter(ch) && (ch < 'A' || ch > 'F')) {
System.out.println("非法字符:"+ch);
return;
}
}else {
System.out.println("非法字符:"+ch);
return;
}
}
//循环计数16进制的十进制数
int sum=0;
for(int i=hex.length() - 1; i>=0; i--) {
char ch = hex.charAt(i);
//如果为数字则就字符-48得当前数字
if(Character.isDigit(ch)) {
sum += (int) Math.pow(16, hex.length()-i-1) * (ch - 48);
}else {
//字符就-65+10获得字符对应的十进制数
sum += (int) Math.pow(16,hex.length()-i-1) * (ch - 55);
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
4.6 编程练习题

思路: 循环对16取余数,得余数后判断余数是否大于10,将大于等于10的部分+55并将其转换为A-F的字符,小于10的部分直接拼接到字符串即可,在对当前循环的数除以16,进行下一次循环。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo59{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("请输入一个十进制数:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = input.nextInt();
String hex = "";
//循环遍历对16取余数
while(number != 0) {
int i = number % 16;
//如果余数大于等于10将其转换为相应的A-F,否则就直接拼接到字符串的首部
if(i >=10) {
hex = (char)(i + 55) + hex;
}else {
hex = i + hex;
}
number /= 16;
}
System.out.println(hex);
}
}

思路: 对输入的字符串判断其长度和字符是否符合要求,不符合就退出程序,符合要求的就将字符串的奇数位求幂的3次方,加入总和,偶数位直接加入总和,在根据公式求isbn的第十三为数,最后拼接字符串返回输出。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo63{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter ISBN-12:");
String isbn = input.nextLine();
//判断输入的字符串长度是否为12为,每个字符是否为数字,不符合就结束程序
if(isbn.length() != 12) {
System.out.println(isbn+" is an invalid input ");
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<isbn.length(); i++) {
if(!Character.isDigit(isbn.charAt(i))) {
System.out.println(isbn+" is an invalid input");
return;
}
}
int sum = 0;
//符合要求的就对字符串中奇数为取幂的3次加入总和,偶数位直接加入总和,带入公式计算isbn码
for(int i=0; i<isbn.length(); i++) {
if(i % 2 == 0) {
sum = sum + isbn.charAt(i) - 48;
}else {
sum = sum + 3 * (isbn.charAt(i) - 48);
}
}
int d13 = 10 - sum % 10;
if(d13 == 10) {
d13 = 0;
}
System.out.println("The ISBN-13 number is "+isbn+d13);
}
}

思路: 首先判断首字符是否相等,不相等就结束程序,否则就循环判断两个字符串的第一个字符是否相等,相等就判断下一个字符,不相等就截取0到当前下标的字串,默认为str2为最大公共前缀。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo66{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a s1: ");
String str1 = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter a s2: ");
String str2 = input.nextLine();
/*
判断首字符是否相等,不相等就返回无相等的前缀
*/
if(str2.charAt(0) != str1.charAt(0)) {
System.out.println(str1 +" and "+str2+" have no common prefix");
return;
}
//否则就循环str2(默认str2最短),逐一比较两个字符串的字符是否相等,不相等就截取该字符,默认为str2
boolean flag = true;
for(int i=0; i<str2.length(); i++) {
if(str1.charAt(i) != str2.charAt(i)) {
flag = false;
System.out.println(str2.substring(0,i));
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println("The common prefix is: "+str2);
}
}
}
五、函数
5.1 函数的概念
函数的定义: 函数的定义就是指一段具有独立功能的代码,减少代码冗余,提高程序的利用率和效率。
函数的组成部分:
- 函数名
- 函数体
- 函数参数(形式参数)
- 函数返回值类型
基本个数如下:
修饰符 函数类型 返回值类型 函数名(数据类型 数据1,数据类型 数据2,...) {
独立功能的代码片段(函数体);
return 函数的计算结果;
}
- 修饰符:指的是函数的访问权限,public private 默认 protected
- 函数类型:函数的分类,本地函数native,静态函数static,同步函数 synchronized
- 返回值类型:指的就是函数计算结果的数据类型 如果函数没有返回值 则为void
- 函数名:就是函数的名称
- 参数列表:指的是外界向函数传入的数据(实际参数),由这些参数变量进行接收(形式参数)
- 函数体:具有独立功能的代码片段
- return:仅仅表示函数结束!如果函数有返回值,则return后跟返回值;如果没有返回值,则return可以不写,但是是存在的(隐藏的 在最后一行)
根据形参和返回值来看,函数有如下几个分类:
- 有参数有返回值
- 有参数没返回值
- 没参数有返回值
- 没参数没返回值
5.2 函数的运行原理
函数的运行是基于栈运行的
栈:是一种先进后出的容器,我们这里面所说的栈是指JVM中的栈内存空间。
每一个函数,叫做栈帧,栈帧中所包含的内容有函数的定义,参数列表,函数的执行内容代码。
每一个函数要运行,就相当于这个栈帧进入到栈内存中-入栈
如果一个函数即将结束,将这个栈帧从栈顶移出-出栈。
如果栈内存中有多个栈帧,运行的是最上面的栈帧,底下的栈帧暂停运行,直到该栈帧为栈顶元素。
比如:主函数先进栈,开始逐行运行,如果执行到第n行,调用另外一个函数A,则主函数在第n行暂停运行,将另一个函数A的栈帧入栈,再继续逐行运行,直到函数A的内容执行完毕,函数A出栈,主函数接着从第n行继续向下执行。以此类推。
例子如下:
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
String s1 = "123";
String s2 = "456";
int c = test1(a,b);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
String s3 = test2(s1,s2);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
}
public static int test1(int a, int b) {
a = 20;
b = 30;
return a + b;
}
public static String test2(String s1, String s2) {
s1 = s1.replace("1","hehe");
s2 = s2.replace("4","heihei");
return s1 + s2;
}
}

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo68{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = input.nextInt();
System.out.println(isPalindrome(number));
}
public static boolean isPalindrome(int number) {
int revNumber = reverse(number);
return revNumber == number;
}
public static int reverse(int num) {
int result = 0;
while(num != 0) {
result = result * 10 + num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
return result;
}
}

5.3 函数重载
同一个类中可以出现多个同名函数,这个现象就叫做函数的重载(overload)
如何来区分同名函数是否是重载关系呢?前提必须是同名,和返回值类型无关(返回值类型只和函数的计算功能相关),和权限也没有关系,和形式参数的名称也无关!只和形式参数的数据类型有关(数量,排列组合)。
public static void show(int a ,float b ,char c){
}
下列哪些是该函数的重载:
- int show(int x, float y, char z) :不算重载 数据类型都是int float char
- void show(float b,int a,char c):算重载,顺序不一样float int char
- void show(int a,int b,int c):算重载,顺序不一样int int int
- double show():算重载,参数不一样
寻找重载函数的流程:
- 看是否有确切的参数定义匹配,int int 找 int int
- 看是否有可兼容的参数定义匹配,int int找double double或int double或double int
- 如果可兼容的参数定义匹配较多,会报引用确定报错 引用不明确
5.4 函数的递归
函数的递归就是指函数自身调用自身。
- 但凡迭代能够解决的问题,递归都可以解决;递归能够解决的问题,迭代就不一定了
- 相对而言,从内存的角度而言,函数如果过多的自我调用,势必会对内存不友好,占用过多
- 通常来讲,同样的问题用递归写要比用迭代写代码量较少
写递归时,一定要先确定递归结束条件-递归边界
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//show(); //无限递归
test(10);
}
public static void test(int n) {
System.out.println(n);
if (n == 1) {
return;
} else {
test(n - 1);
}
}
public static void show() {
System.out.println("Hello!");
show();
}
}
用递归实现1+2+…+99+100
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(f(100));
//System.out.println(f(10000000));//StackOverflowError
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000000; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
/*
求1+2+...+99+100
设函数f(x) = 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + x-3 + x-2 + x-1 + x
f(3) = 1 + 2 + 3
f(2) = 1 + 2
f(3) = f(2) + 3
=>
1 ,x = 1
f(x) =
f(x-1) + x , x>1
递归实现斐波那契数列
f(x) = f(x- 1) + x
f(100) = f(99) + 100 1+2+3+...+99 + 100
f(99) = f(98) + 99 1+2+3+...+98 + 99
.....
f(4) = f(3) + 4 1+2+3 + 4
f(3) = f(2) + 3 1+2 + 3
f(2) = f(1) + 2 1 + 2
f(1) = 1 递归的边界
*/
public static int f(int x) {
if (x == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return f(x - 1) + x;
}
}
}
递归实现斐波那契数列
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 ...
1 x=1,x=2
f(x) =
f(x-1) + f(x-2) x>2
f(5)
f(4) f(3)
f(3) f(2) f(2) f(1)
f(2) f(1)
*/
//递归O(2^n)
System.out.println(f(35));
//迭代O(n)
System.out.println(fibo_it(35));
}
public static int fibo_it(int x) {
if (x == 1 || x == 2) {
return 1;
}
/*
1 1 2 3
c
a b
*/
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
int c = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= x; i++) {
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return c;
}
public static int f(int x) {
if (x == 1 || x == 2) {
return 1;
}else {
return f(x-1) + f(x-2);
}
}
}
5.5 编程练习题
汉诺塔问题
public class Demo81 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String x = "x";
String y = "y";
String z = "z";
hano(3,x,y,z);
//前3层从 x->z
//前2层从 x->y
}
/// <param name="begin">承载最初圆盘的柱子</param>
/// <param name="mid">起到中转作用的柱子</param>
/// <param name="end">移动到的目标柱子</param>
public static void hano(int level,String begin,String mid,String end) {
if (level == 1) {
System.out.println(begin+"->"+end);
} else {
//将begin柱子上的从上到下n-1个盘移到mid柱子上
hano(level - 1,begin,end,mid);
//将最大的盘子一到end上面
System.out.println(begin+"->"+end);
//将mid柱子上的n-1个盘子移到end柱子上
hano(level - 1,mid,begin,end);
}
}
}
六、数组
6.1 数组的概念及定义
数组主要用于解决大量数据计算与存储的问题。
定义:数组是Java提供的一种最简单的数据结构,可以用来存储一个元素 个数固定 且 类型相同 的有序集。
数组在内存中的情况
栈:主要用于运行函数的内存
堆:主要用于存储数据对象的内存
对每一个数组而言,都是存在堆内存当中,每一个数组都是一个对象。

1.数组本质上就是在堆内存中一系列地址连续且空间大小相等的存储空间(变量),每一个存储空间用来存储数据(基本,引用)。
2.数组是在堆内存中存储,称之为是一个数组对象,并且在堆内存中存储的数据都有默认初始化的流程。所以数组创建之初,每一个存储空间里面都会被JVM初始化该数据类型对应的零值。
2.数组的地址是连续的,所以通过公式:An=A1+(n-1)*d可以快速访问到其他的元素,所以对于数组而言查找元素比较快的。将元素的真实物理地址转换成对应的角标获取元素。
3.如何来调用数组呢?通过一个变量存储该数组在堆内存当中的首元素的地址。
4.当数组一旦定义出来,其长度不可变,存储空间的内容是可变的。
5.所以我们在定义数组的时候,要么把长度固定,要么直接输入相关的元素。
数组的定义方式
//创建一个指定长度且指定数据类型的一维数组,名称为数组名,虽然没有指定元素,但是会有默认值
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[长度];
//创建一个指定元素且指定数据类型的一维数组,名称为数组名,虽然有指定元素,还是有默认初始化这个步骤的!
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[]{
数据1,数据2,...,数据n};
数据类型[] 数组名 = {
数据1,数据2,...,数据n};
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println(arr[0]);
//System.out.println(arr[5]);
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
arr[2] = 10;
int[] arr2 = arr;
System.out.println(arr2[2]);
arr2 = null;
//System.out.println(arr2[2]);
//NullPointerException
/*
String s = null;
s.length();
*/
arr = null;
}
}

6.2 常用数组操作
数组遍历问题
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
//String str str.length()-函数
//int[] arr arr.length-属性
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] * 10;
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
//通过角标遍历 可以在遍历的过程中对指定的元素进行修改
//foreach遍历 主要针对的是一些可迭代对象 Iterable
/*
for (数据类型 变量名 : 可迭代容器) {
}
*/
for (int num : arr) {
//num -> arr[i]
num = num / 10;
System.out.println(num);
}
//这种遍历方式 只能获取元素,不能修改元素
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
数组最值问题
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{
3,6,8,2,9,4,5,1,7};
int min = arr[0];
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(min);
}
}
数组扩容问题
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{
1,2,3,4,5};
arr = add(arr,6);
arr = add(arr,6);
arr = add(arr,6);
arr = add(arr,6);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
//在指定的数组arr中添加元素element
public static int[] add(int[] arr, int element) {
int[] newArr = new int[arr.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
newArr[newArr.length - 1] = element;
return newArr;
}
}

选择排序算法
思路: 每次将首位数字与后面的所有数字比较,找出其中的最小值放到第一位,在将首位数字移到第二位,在循环比较剩下的数字,找出第二小的数字,以此类推。
public class Sample {
//选择排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
8,9,2,6,7,1,4,5,3};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
//-1 n个数字没有第n轮
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
swap(arr,i,j);
}
}
}
print(arr);
}
//[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
public static void print(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
System.out.println("]");
} else {
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}

冒泡排序算法
思路: 每次将第一个数字,与后面的数字比较,比后面的大就交互位置,反之不交换,一直两两比较,冒出最大值到最后一位,下一次循环减少一次,因为每一次循环比较都会找到当前的最大值,以此类推循环,得出升序。
public class Sample {
//冒泡排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
8,9,2,6,7,1,4,5,3};
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) {
//-1 表示n个数字只有n-1轮
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
//-1 避免重复比较(当前最大和上一
轮最大)
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
swap(arr,j,j+1);
}
}
}
print(arr);
}
public static void print(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
System.out.println("]");
} else {
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}

插入排序算法
思路:
1.从数组的第二个数据开始往前比较,即一开始用第二个数和他前面的一个比较,如果 符合条件(比前面的大或者小,自定义),则让他们交换位置。
2.然后再用第三个数和第二个比较,符合则交换,但是此处还得继续往前比较,比如有 5个数8,15,20,45, 17,17比45小,需要交换,但是17也比20小,也要交换,当不需 要和15交换以后,说明也不需要和15前面的数据比较了,肯定不需要交换,因为前 面的数据都是有序的。
3.重复步骤二,一直到数据全都排完。
public class Sample {
//插入排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
8,9,2,6,7,1,4,5,3};
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int e = arr[i];
int j = 0;
for (j = i; j > 0 && arr[j - 1] > e; j--) {
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
}
arr[j] = e;
}
print(arr);
}
public static void print(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
System.out.println("]");
} else {
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}
}
二分查找算法
思路: 在有序数组中,每次找到最小值,最大值,中间值,比较中间值和当前寻找值的大小,大于则在有序数组的右边,重新定义最大值,最小值,中间值为右边部分,小于则重复上述步骤(定义与左边),找到就返回下标,当最小值的下标大于最大值的下标时表示没找到返回-1.
public class Sample {
//二分查找
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int min = 0;
int max = arr.length - 1;
int mid = (min + max) / 2;
int key = 10;
while (arr[mid] != key) {
if (key < arr[mid]) {
max = mid - 1;
}
if (arr[mid] < key) {
min = mid + 1;
}
if (min > max) {
mid = -1;
break;
}
mid = (min + max) / 2;
}
System.out.println(mid);
}
}
计数排序:
public class Sample {
//计数排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
-2,9,-1,12,8,-3,6,7,4,5,2,1,0,8,6,7,4,-3,-2,-1,-1,7};
int min = arr[0];
int max = arr[0];
//O(n)
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
int[] temp = new int[max - min + 1];
//对应关系 index = number - min number = index + min
//O(n)
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
temp[arr[i] - min]++;
}
//temp[index] 表示index对应的数字number出现的次数
int k = 0;
//O(n)
for (int index = 0; index < temp.length; index++) {
while (temp[index] != 0) {
arr[k] = index + min;
k++;
temp[index]--;
}
}
print(arr);
}
public static void print(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
System.out.println("]");
} else {
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}
}

基数排序:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Sample {
//基数排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
102,203,321,13,12,78,96,34,37,28,6,8,5,6};
//1.先找到最大值 决定轮数
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
int radex = (max + "").length();
//2.创建十个桶 每一个桶是LinkedList
LinkedList<Integer>[] queues = new LinkedList[10];
for (int i = 0; i < queues.length; i++) {
queues[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
//3.进行数字分类和规整
//r=0个位 r=1十位 r=2百位...
for (int r = 0; r < radex; r++) {
//先按照r进行分类
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int index = getIndex(arr[i],r);//获取数字的r位 返回该数字要去的桶的角标0~9
queues[index].offer(arr[i]);
}
//然后在重新规整到arr里
int k = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < queues.length; index++) {
while(!queues[index].isEmpty()) {
arr[k++] = queues[index].poll();
}
}
}
print(arr);
}
public static int getIndex(int number, int r) {
//123 r=0
//123 r=1
//123 r=2
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= r; i++) {
index = number % 10;
number /= 10;
}
return index;
}
public static void print(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
System.out.println("]");
} else {
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}
}

6.3 二维数组
二维数组,在表现形式上就是一个表格,在操作表格的时候以行列来操作
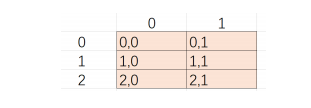
所谓的二维数组,本质上就是一个一维数组,只不过该一维数组里面的元素是另一个一维数组而已

二维数组的定义:
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数据类型[][] 矩阵名 = new 数据类型[row][col];
int[][] matrix = new int[3][2];
/*
数据类型[][] 矩阵名 = new 数据类型[][] {
{...},
{...},
{...}
};
数据类型[][] 矩阵名 = {
{...},
{...},
{...}
};
*/
int[][] matrix2 = {
{
1,2,3},
{
4,5,6},
{
7,8,9}
};
for (int i = 0; i < matrix2.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix2[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix2[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
int[][] matrix3 = {
{
1},
{
1,2,3},
{
1,2,3,4},
{
7,6,5,4,3,2,1}
};
for (int i = 0; i < matrix3.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix3[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix3[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
案例1
输入8个点坐标,然后计算这些点中,那两个点的距离是最近的?
思路: 定义一个二维数组,来接受用户输入的八个点的坐标,在循环判断两个坐标的距离,从而获取两点间的最短距离。

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//定义一个8行两列的二维数组
double[][] points = new double[8][2];
//1.获取输入的点坐标
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
System.out.print("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "个点坐标:");
points[i][0] = input.nextDouble();
points[i][1] = input.nextDouble();
}
//默认最短距离为点0和点1
double shortestDistance = getDistance(points,0,1);
int p1 = 0;
int p2 = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; j++) {
double distance = getDistance(points,i,j);
//比较判断最短距离,小于就获取该下标
if (distance < shortestDistance) {
shortestDistance = distance;
p1 = i;
p2 = j;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("(%.1f,%.1f)和(%.1f,%.1f)的距离为最短%.1f",points[p1]
[0],points[p1][1],points[p2][0],points[p2][1],shortestDistance);
}
public static double getDistance(double[][] m , int p1 , int p2) {
//用函数计算两点间的距离
return Math.hypot(m[p1][0] - m[p2][0] , m[p1][1] - m[p2][1]);
}
}
6.4 编程练习题

思路: 计数排序思路,根据下标来对对应出现的数字计数,最后在输出。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo82{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Enter the number between 1 and 100:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//数组保存用户输入的数字0表示输入结束
int[] array = new int[101];
while(true) {
int num = input.nextInt();
if(num == 0){
break;
}
//输入数字的对应数组下标加1
array[num]++;
}
//循环输出数组中角标出现的次数,次数为0不管,1次输出time,否则输出times
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(array[i] != 0){
if(array[i] == 1){
System.out.println(i+" occurs "+array[i]+" time");
}else{
System.out.println(i+" occurs "+array[i]+" times");
}
}
}
}
}

思路:
思路1:动态扩容数组,定义一个长度为0的数组,从0开始循环10次,每次都判断数组中是否包含用户输入的数组,包含则跳过,否则,就扩容定义的数组,没次扩容一个数字。
思路2:固定数组长度 用标记表示有效数据,定义数组长度为10,在定义一个变量size来标记有效数字的个数和角标。
import java.util.*;
public class Demo83{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//思路1:动态扩容数组
// int[] array = new int[0];
// System.out.print("Enter ten numbers:");
// Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// for(int i=0;i<10; i++) {
// int num = input.nextInt();
// if(!container(array,num)){
// array = add(array,num);
// }
// }
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
//思路2:固定数组长度,用标记表示数据
int[] array = new int[10];
//即表示有效数字的个数,也表示当前数组的角标
int size = 0;
System.out.print("Enter ten numbers:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<10; i++) {
int num = input.nextInt();
if(!container(array,num,size)){
array[size++] = num;
}
}
System.out.println(toString(array,size));
}
//自定义Arrays.toString();方法
public static String toString(int [] arr,int size){
String s="[";
for(int i=0;i<size; i++) {
if(arr[i] !=0){
if(i == size-1){
s += arr[i]+"]";
}else{
s += arr[i]+",";
}
}
}
return s;
}
//重载方法(思路2)
public static boolean container(int[] arr,int num,int size){
for(int i=0;i<size; i++) {
if(arr[i] == num){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//动态扩容该数组,每次扩容一个数字
public static int[] add(int[] arr,int num){
int[] newArr = new int[arr.length+1];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length; i++) {
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
newArr[arr.length] = num;
return newArr;
}
//循环遍历数组当期数字是否已经在该数组中
public static boolean container(int[] arr,int num){
for(int i=0;i<arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i] == num){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}

思路: 获取数组中的最小值,从改值倒序遍历,查找一个可以整除数组中的所有数字,找到就返回输出该数,即可。
import java.util.*;
public class Demo85{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(gcd(35,40,20,55));
System.out.println(gcd(28,16));
}
//返回最大公约数方法
public static int gcd(int ... numbers) {
int min = getMin(numbers);
//每次从最小值遍历,循环判断该数是否可以整除数组中的每一个数,可以就返回输出
for(int i=min; i>=1; i--) {
boolean flag = true;
for(int j=0; j<numbers.length; j++){
if(numbers[j] % i != 0){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
return i;
}
}
return 1;
}
//获取输入数组中的最小值
public static int getMin(int[] array) {
int min = array[0];
for(int i=1; i<array.length;i++) {
if(array[i] < min){
min = array[i];
}
}
return min;
}
}


思路: 随机数来模拟小球的路径,1表示R,0表示L,每次产生输入小球的个数个路径,并统计其中R的个数,根据R的个数来判读小球落进那个槽子,对应的槽子的个数加1,在打印槽子的数组即可。
import java.util.*;
public class Demo88{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//随机数1表示R,0表示L
Random random = new Random();
System.out.print("请输入球的个数:");
int balls = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入槽子的个数:");
int slots = input.nextInt();
//定义一个槽子的数组,保存的值为落进小球的个数
int[] temp = new int[slots];
//定义一个路径的个数,随机产生的每个小球的路径
String[] paths = new String[balls];
//循环次数为小球的个数
for(int i=0; i<balls; i++) {
//每一个小球的具体路径
String path = "";
//路径中R出现的个数
int Rcount = 0;
for(int j=0; j<slots-1; j++){
if(random.nextInt(2) == 0) {
path += "L";
}else{
path += "R";
Rcount++;
}
}
paths[i] = path;
System.out.println(path);
temp[Rcount]++;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp));
}
}

思路: 参考代码注释
import java.util.*;
public class Demo90{
public static void main(String[] args){
//获取输入个数据
System.out.print("请输入数字的个数:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入"+num+"个数字:");
int[] arr = new int[num];
//定义一个数字长度为num的一维数组,来保存用户输入的数字
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
arr[i] = input.nextInt();
}
//方法判断该数组中是否有连续出现的四个数字
isConsecutiveFour(arr);
}
public static void isConsecutiveFour(int[] arr) {
//循环判断数组中连续相等的数字,相等计数器就加一,到4就输出true,结束程序运行,否则就从J开始重新循环
for(int i=0; i < arr.length;) {
//count为1,提前去除了一个,用来判断
int count = 1,j=0;
for(j=i+1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if(arr[i] == arr[j]){
count++;
}else {
break;
}
}
if(count >= 4){
System.out.println("true");
return;
}else{
i=j;
}
}
System.out.println("false");
}
}


思路: 如上图比较两个数组中的值,但是每次比较是要先判断两个数组的其中一个下标是否已经越界,对于越界的就直接拼接没有越界数组的后面数字即可,没越界的就进行两数组的比较。
import java.util.*;
public class Demo91{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] list1 = {
1,3,5,7,9,50,90};
int[] list2 = {
2,4,6,8,10};
//调用方法获取拼接两个排序后的最终数组
int[] list3 = merge(list1,list2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(list3));
}
public static int[] merge(int[] arr1,int[] arr2) {
//返回数组的长度为两数组长度的总和
int[] arr3 = new int[arr1.length + arr2.length];
//下标都从0开始
int p1=0,p2=0,p3=0;
//先判断两个下标是否越界(数组的长度)
while(p1 < arr1.length || p2 < arr2.length){
//每次都先判断两个数组中是否有一个下标,越界(如果先直接判断两个值的大小的话,会出现下标越界的异常)
if(p1 >= arr1.length && p2 < arr2.length){
arr3[p3++] = arr2[p2++];
}else if(p2 >= arr2.length && p1 < arr1.length){
arr3[p3++] = arr1[p1++];
}else if(arr1[p1] > arr2[p2]) {
arr3[p3++] = arr2[p2++];
}else{
arr3[p3++] = arr1[p1++];
}
}
return arr3;
}
}

思路: 见代码注释
import java.util.*;
public class Demo92{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串数组,为要猜的单词词库
String[] words = {
"apple","banana","python","computer"};
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
while(true){
//随机从词库中获取一个单词
String word = words[random.nextInt(words.length)];
//定义一个单词的状态数组,true代表明文显示单词,false代表密文显示单词
boolean[] status = new boolean[word.length()];
//统计猜错的次数
int count = 0;
while(!isOver(status)){
//每次根据状态数组显示要密文或明文显示的字符
String password = getPassWord(word,status);
System.out.print("Enter a letter in word "+password+" > ");
//获取用户输入的单词
String letter = input.nextLine();
//判断字母是否在单词中
if(word.contains(letter)){
//在改变状态数组,如该状态已经为true就输出下面的提示
if(!changeStatues(word,letter,status)){
System.out.println("\t" + letter + " is alreay in the word");
}
}else{
//不包含输入的字符就记录输入错误的次数,并打印信息
System.out.println("\t"+letter+" is not in the word.");
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("The word is " + word + ". You missed " + count);
//循环玩游戏
System.out.print("Do you want again?(y/n):");
String choice = input.nextLine();
if(choice.equals("n")){
break;
}
}
}
public static boolean changeStatues(String word,String letter, boolean[] status){
//改变状态数组中的值,先获取相等字符的下标,在判断该状态数组中的该下标是否为true,为true返回false(表示该字符以猜出,去除重复猜),否则返回true
char ch = letter.charAt(0);
for(int i=0; i<word.length(); i++) {
if(word.charAt(i) == ch){
if(status[i]){
return false;
}else{
status[i] = true;
}
}
}
return true;
}
//判断是否继续如果状态数组全为true,就结束游戏了
public static boolean isOver(boolean[] status){
for(int i=0;i<status.length;i++){
if(!status[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static String getPassWord(String word,boolean[] status) {
//判断状态数组为true,明文显示对应下标的字母,为false显示*密文
String password = "";
for(int i=0; i<status.length; i++){
if(status[i]){
password += word.charAt(i);
}else {
password += "*";
}
}
return password;
}
}

思路: (这边直接做五子棋)

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo101 {
//1.定义15 * 15一个棋盘
public static String[][] baord = new String[15][15];
//玩家轮次计数(同样也是棋子的个数)偶数表示黑棋,奇数表示白棋
public static int player = 0;
//黑棋(O)和白棋(X)
public static final String BLACK_CHESS = "O";
public static final String WHITE_CHESS = "X";
public static Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//2.初始化棋盘和打印棋盘
initBoard();
printBoard();
//3.开始下棋
startGame();
}
public static void startGame() {
//只要棋盘没有5子相连就继续下棋
while(!isGameOver()){
if(player % 2 ==0) {
//黑棋下
System.out.println(">>>请黑方下棋");
playChess(BLACK_CHESS);
}else{
//白棋下
System.out.println(">>>请白方下棋");
playChess(WHITE_CHESS);
}
player++;
}
//棋数等于棋盘数则为和棋
if(player == 15 * 15){
System.out.println(">>>和棋,游戏结束!");
}else {
//根据棋数判断哪个棋子赢(-1表示循环出来后加了1所有这里要减去)
if((player-1) % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(">>>黑棋赢,游戏结束!");
}else {
System.out.println(">>>白棋赢,游戏结束!");
}
}
}
//判断棋盘是否有棋子连成5子(游戏是否结束)
public static boolean isGameOver() {
for(int row=0; row<baord.length;row++) {
for(int col=0;col<baord[row].length;col++) {
if(!baord[row][col].equals("+")){
//棋子向右判断(11,为向右的边界值)
if(col < 11){
boolean flag = true;
for(int c=col + 1; c<=col+4; c++){
if(!baord[row][col].equals(baord[row][c])){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
return true;
}
}
//棋子向下判断
if(row < 11){
boolean flag = true;
for(int r=row + 1; r<=row+4; r++){
if(!baord[row][col].equals(baord[r][col])){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
return true;
}
}
//棋子向右上判断
if(row > 3 && col < 11){
boolean flag = true;
for(int r=row - 1,c = col + 1; c <= col+4;r--,c++){
if(!baord[row][col].equals(baord[r][c])){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
return true;
}
}
//棋子向右下判断
if(row < 11 && col < 11){
boolean flag = true;
for(int r=row + 1,c = col + 1; c <= col+4;r++,c++){
if(!baord[row][col].equals(baord[r][c])){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
//下棋方法
public static void playChess(String chess) {
System.out.print("请输入棋子的坐标:");
int x = input.nextInt() - 1;
int y = input.nextInt() - 1;
if(!baord[y][x].equals("+")) {
//判断该处是否有棋子,有的话下棋数--返回上一次
System.out.println("此处已有棋子,请重新下!");
//--回到上一步
player--;
return;
}
//为棋盘下相应的棋子,并重新打印棋盘
baord[y][x] = chess;
printBoard();
}
//格式化打印棋盘以及棋盘上面,和左边对应的序号
public static void printBoard(){
System.out.print(" ");
for(int i=1; i<=baord[0].length; i++){
System.out.printf("%-3d",i);
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0;i<baord.length;i++){
System.out.printf("%2d ", i + 1);
for(int j=0;j<baord[i].length;j++) {
System.out.print(baord[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//初始化棋盘
public static void initBoard(){
//循环棋盘为棋盘赋值(+)
for(int i=0;i<baord.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<baord[i].length;j++) {
baord[i][j]="+";
}
}
}
}
八皇后问题
思路: 简单理解递归就是循环嵌套循环,循环完就返回执行上一个,直到顶部最外层的循环执行完毕才结束,整个循环,输出的话,就是根据具体的条件,输出结果即可。

public class NQueen{
//N皇后
public static int N = 8;
//棋盘
public static int[][] board = new int[N][N];
//统计有几种解法
public static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
nqueen(0);
}
public static void nqueen(int row) {
//如果行增到和N相等表示,该组合就是一种解法,直接打印输出即可
if(row == N){
count++;
System.out.printf("这是第%d种解法:\n",count);
for(int i=0; i<board.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<board[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(board[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}else{
//否则就从第一行每个格开始下
for(int col=0; col<N; col++) {
//如果该空可以下就先清空该行,在将皇后放在对应的坐标上
if(!isDangerous(row,col)){
for(int c=0; c<N; c++){
board[row][c] = 0;
}
board[row][col] = 1;
//递归到下一行(循环的嵌套)
nqueen(row+1);
}
}
}
}
//判断当期空格是否可以放皇后
public static boolean isDangerous(int row,int col) {
//向上判断,行递减
for (int r = row - 1;r >= 0; r--) {
if (board[r][col] == 1) {
return true;
}
}
//向左上判断,行列都递减
for (int r = row - 1,c = col - 1; r >= 0 && c >= 0;r--,c--) {
if (board[r][c] == 1) {
return true;
}
}
//向右上判断,行递减,列递增
for (int r = row - 1,c = col + 1; r >= 0 && c < N; r--,c++) {
if (board[r][c] == 1) {
return true;
}
}
//可以就返回false
return false;
}
}
6.4 LeetCode题

思路: 倒序循环判断是否产生进位,产生进位就继续循环,没进位就直接退出,如果循环完还有进位,就对数组进行扩容,将首位赋值为1即可。
class Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
//进位符,默认为1表示加1
int carry = 1;
//倒序循环
for(int i=digits.length-1; i>=0; i--) {
//末尾数字加一,取余赋值,除10取进位符
int num = digits[i] + 1;
digits[i] = num % 10;
carry = num / 10;
//进位符为0退出程序
if(carry == 0){
break;
}
}
//循环完还有进位,就对数组进行扩容
if(carry == 1){
int[] arr = new int[digits.length+1];
arr[0] = 1;
return arr;
}
return digits;
}
}
扩展两个数组相加
import java.util.*;
public class LeetCode66{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1 = {
9,9,9};
int[] arr2 = {
9,9,9,9,9};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(plus(arr1,arr2)));
}
public static int[] plus(int[] digits1,int[] digits2) {
//将两个数组扩容到长度相等,比较谁小就扩谁
if(digits1.length < digits2.length) {
digits1 = kuorong(digits1,digits2.length);
}else if(digits1.length > digits2.length) {
digits2 = kuorong(digits2,digits1.length);
}
//进位符
int carry = 0;
//数组从后开始加
for(int i=digits1.length-1; i>=0; i--){
//两个数组中每两个数相加,并加上进位符,第一次为0,每次加后要对进位符进行重新赋值
int num = digits1[i] + digits2[i] + carry;
//判断当前相加的两个数字是否产生进位
carry = num / 10;
//将相加结果赋值给数组1
digits1[i] = num % 10;
}
//循环完后进位符为1则表示要对数组扩容,产生进位
if(carry == 1){
//定义一个新数组,第一位为1,后面的位数遍历digits1来赋值,最后返回digits3
int[] digits3 = new int[digits1.length + 1];
digits3[0] = 1;
for(int i=0;i<digits1.length;i++){
digits3[i+1] = digits1[i];
}
return digits3;
}
//循环完没产生进位返回digits1
return digits1;
}
//数组扩容num 为要扩容的长度
public static int[] kuorong(int[] arr, int num) {
int[] newArr = new int[num];
//定义两个下标都从数组的最后一位开始递减
int i = arr.length - 1,k = newArr.length - 1;
//为新的数组赋值,从后往前赋,角标低的为0
while(i >= 0){
newArr[k--] = arr[i--];
}
return newArr;
}
}

思路: (见代码注释)
public class LeetCode283{
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
//思路1:选择排序思路
// for(int i=0; i<nums.length - 1; i++) {
// for(int j=i+1; j<nums.length; j++){
// //左边为0右边不为0就交换
// if(nums[i] == 0 && nums[j] != 0){
// int temp = nums[i];
// nums[i] = nums[j];
// nums[j] = temp;
// break;
// }
// }
// }
//思路2:插入排序思路
// for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++) {
// //为0就跳过这次循环
// if(nums[i] == 0){
// continue;
// }
// //只要j-1为0的话就交换位置
// for(j=i; j>0 && nums[j-1] == 0; j--){
// int temp = nums[i];
// nums[j] = nums[j-1];
// nums[j-1] = temp;
// }
// }
//思路3:双指针做法 k一直卡着第一个0
//数组为空直接结束程序
if(nums == null){
return;
}
//定义一个k始终指向数组中的第一0
int k = 0;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
//如果当前元素不为0就交换i和k角标对应的值(不为0就自己交互自己),为0就不管直接到下一个不为0的数字
if(nums[i] != 0){
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[k];
nums[k] = temp;
k++;
}
}
}
}

思路: 对数组排序,排序后取出n/2位置的数即是该数组的多数元素。
思路2,正负相消。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
//思路1:插入排序做 排序之后中间的位置一定是众数
/*
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int e = nums[i];
int j = 0;
for (j = i; j > 0 && nums[j - 1] > e; j--) {
nums[j] = nums[j - 1];
}
nums[j] = e;
}
return nums[nums.length / 2];
*/
//思路2:正负相消
//默认出现数组中第一个数,出现次数为1
int num = nums[0];
int count = 1;
//从数组中第二个数开始循环判断,等于出现的数就次数加1
//不等于就次数减1,抵消一个数,如果次数小于0,表示出现了另外一个数,将另外一个数赋值,将次数赋为1
for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] == num){
count++;
}else{
if(count > 0){
count--;
}else{
num = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
}
}
return num;
}
}

思路: 定义左右指针,判断左右奇偶情况,根据情况来替换,或移动指针。
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParity(int[] A) {
int l = 0;
int r = A.length - 1;
while(l < r){
//左奇右偶
if(A[l] % 2 == 1 && A[r] % 2 == 0) {
int temp = A[l];
A[l] = A[r];
A[r] = temp;
//左偶右奇
}else if(A[l] % 2 == 0 && A[r] % 2 == 1){
l++;
r--;
//左奇右奇
}else if(A[l] % 2 == 1 && A[r] % 2 == 1){
r--;
//右偶右偶
}else{
l++;
}
}
return A;
}
}

思路: 对数组求和,对求和数除三,分为三组,循环数组,用求和除三的数对每个数组的值进行相减,如果求和除三的数减到0则为一组,对组计数,并对求和除三的数重新赋值,在继续循环判断,返回判断组计数是否为3。
class Solution {
public boolean canThreePartsEqualSum(int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
//求和数组
for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++){
sum += arr[i];
}
//对求和数分三份
int key = sum / 3;
//组计数器
int group = 0;
for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++){
key -= arr[i];
//如果key为0则为一组,并对key出现赋值
if(key == 0){
group++;
key = sum / 3;
}
}
//返回结果,如果总和为0,且组数大于3,则可以自由组合为三组返回true
return group == 3 || sum == 0 && group >=3;
}
}

思路: 定义左右指针,用数组总和计算左右的和,并判断左右的和是否相等,相等就返回角标,结束程序的运行,循环完,没有结果,就返回-1。
class Solution {
public int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
//对数组求和
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
}
//定义数组左右两边的总和
int leftSum=0,rightSum=0;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
if(i == 0){
leftSum = 0;
}else{
//对数组左边求和累加
leftSum += nums[i-1];
}
//对数组右边求和,总和减左边的和,在减当前角标对应的数值
rightSum = sum - leftSum - nums[i];
//左右两边相等就结束程序,返回下标
if(rightSum == leftSum) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}

思路: 滑动窗口机制(见代码)
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int s, int[] nums) {
int len = 0, i = 0, sum = 0;
for(int j=0; j<nums.length; j++){
//总数相加
sum += nums[j];
//总数大于s的话就先判断该长度是否小于len,小于就为len重新赋值,否则就缩小左边的窗口
//左边弹出一个值,对应的总数将弹出的值,如果总和比s小,就扩大右边的窗口,右边加入一个值总数加一,后面的数依次类推
while(sum >= s) {
len = len == 0 ? j-i+1 : Math.min(len,(j-i+1));
sum -= nums[i++];
}
}
return len;
}
}