1玩转单例模式
饿汉式、DCL懒汉式
1饿汉式
/**
* 饿汉式单例
*/
public class Hungry {
/**
* 可能会浪费空间
*/
private byte[] data1=new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data2=new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data3=new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data4=new byte[1024*1024];
// 私有化构造器
private Hungry(){
}
private final static Hungry hungry = new Hungry();
public static Hungry getInstance(){
return hungry;
}
}
2懒汉式
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 多进程并发
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
lazyMan.getInstance();
}).start();
}
}
}
这样做是有问题的
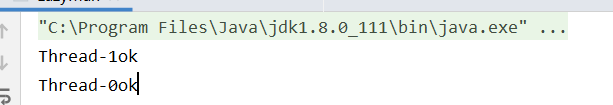
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 双重检测锁模式 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是原子性操作
/**new
* 1 分配内存空间
* 2 执行构造方法 初始化对象
* 3 把这个对象指向这个空间
* 可能出现的问题?
* 可能会出现指令重排
*/
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 多进程并发
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
lazyMan.getInstance();
}).start();
}
}
}
3静态内部类 反射会破坏单例
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 双重检测锁模式 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是原子性操作
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
// 反射会破坏单例
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor =
LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //无视私有的构造器
LazyMan instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}

4解决反射破坏单例方案一
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan() {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射破坏异常!");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 双重检测锁模式 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是原子性操作
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
// 反射会破坏单例
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor =
LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //无视私有的构造器
LazyMan instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}

5两个实例都使用反射构建
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan() {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射破坏异常!");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 双重检测锁模式 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是原子性操作
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
// 反射会破坏单例
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
// LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor =
LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //无视私有的构造器
LazyMan instance = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
LazyMan instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
又会出现问题

5标志位解决方案反射破坏单例的问题方案二
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private static boolean zs = false; // 标志位
private LazyMan() {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (zs == false) {
zs = true;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射破坏异常!");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 双重检测锁模式 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是原子性操作
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
// 反射会破坏单例
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
// LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor =
LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //无视私有的构造器
LazyMan instance = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
LazyMan instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
6再次破坏单例
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//懒汉式单例模式
// 单线程是ok的
public class LazyMan {
private static boolean zs = false; // 标志位
private LazyMan() {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (zs == false) {
zs = true;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射破坏异常!");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 双重检测锁模式 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是原子性操作
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
// 反射会破坏单例
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
// LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Field zs = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredField("zs");
zs.setAccessible(true);
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor =
LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //无视私有的构造器
LazyMan instance = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
zs.set(instance,false);
LazyMan instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
再次破坏

单例不安全, 因为反射
4枚举
反射是不能破坏枚举的
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//enum 是什么? enum本身就是一个Class 类
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
EnumSingle instance = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
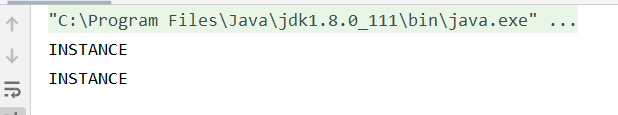
加入反射机制之后
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//enum 是什么? enum本身就是一个Class 类
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
EnumSingle instance = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
EnumSingle instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoSuchMethodException
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}


这就出现了问题 报的错是不一样的! 我们的探究失败了 ! ieda欺骗了我们!!!
java -p反编译
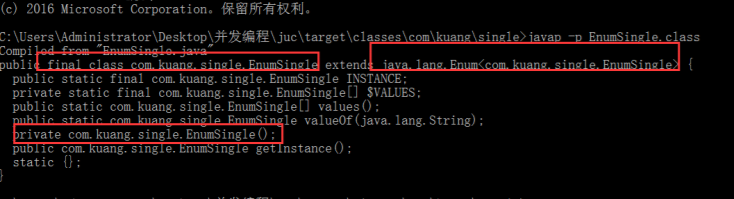
public final class EnumSingle extends Enum
{
public static EnumSingle[] values()
{
return (EnumSingle[])$VALUES.clone();
}
public static EnumSingle valueOf(String name)
{
return (EnumSingle)Enum.valueOf(com/ogj/single/EnumSingle, name);
}
private EnumSingle(String s, int i)
{
super(s, i);
}
public EnumSingle getInstance()
{
return INSTANCE;
}
public static final EnumSingle INSTANCE;
private static final EnumSingle $VALUES[];
static
{
INSTANCE = new EnumSingle("INSTANCE", 0);
$VALUES = (new EnumSingle[] {
INSTANCE
});
}
}

import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
//enum 是什么? enum本身就是一个Class 类
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
EnumSingle instance = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
EnumSingle instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoSuchMethodException
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
