MVP是什么
MVP简介
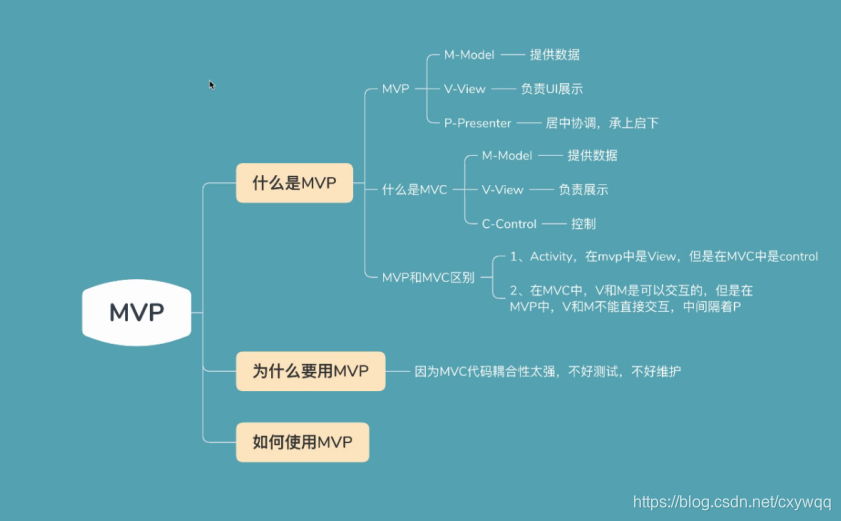
MVP(Model-View-Presenter)是MVC模式的改良,由IBM的子公司Taligent提出。
和MVC的相同之处在于:Controller/Presenter负责业务逻辑,Model管理数据,View负责显示。
1.各部分之间的通信,都是双向的.
View <- (双向) -> Presenter <- (双向) ->Model
2.View 与 Model不发生练习,都通过Presenter传递.
3.View非常薄,不部署任何业务逻辑,被称为"被动视图"(Prassive).既没有任何主动性, 而Presenter非常厚,所有逻辑部署都在这里。
一 MVP使用
1.需要的依赖整理
//异步线程
api 'io.reactivex.rxjava2:rxjava:2.2.6'
api 'io.reactivex.rxjava2:rxandroid:2.1.1'
//网络框架
api 'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.12.1'
//日志拦截器
api 'com.squareup.okhttp3:logging-interceptor:3.11.0'
//网络请求封装框架
api 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.6.2'
//网络请求对象解析器
api 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.6.2'
//线程异常任务调度
api 'com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-rxjava2:2.6.2'
//工具类
api 'com.blankj:utilcodex:1.26.0'
2. 一般三步走
mvp层
(1) m层
定义接口
public interface Imodel {
void destroy();
}
引用接口
调用销毁方法
public class BaseModel implements Imodel {
/**
* 销毁
*/
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
(2) v层
定义接口view三个方法
public interface Iview {
void showLoading();
void hideLoading();
void showToast();
}
定义接口IActicity三个方法
public interface IActivity {
int banLoutler();
void initView();
void initData();
}
定义接口Ifragment接口
public interface Ifragment<T> extends IActivity {
<T extends View> T findViewBayId(int id);
}
base
*[因为我一直写fragment 我这里就先介绍fragment的使用方法,如有需要请联系我]:
public abstract class BaseFragment extends Fragment implements Ifragment,Iview {
*[这里面就是实现的一些方法 大家自行实现吧,都有提示,abstract 抽象 ,里面有的方法用不到 我们要使用抽象方法进行]:
}
(3) p层
(1) 定义接口
public class Basepresenter<M extends Imodel ,V extends Iview> implements Ipresenter {
protected M mModel;
protected V mView;
public Basepresenter(M mModel, V mView) {
this.mModel = mModel;
this.mView = mView;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
if (mModel == null){
mModel.destroy();
mModel = null;
}
}
}
(2) 引用接口
public class Basepresenter<M extends Imodel ,V extends Iview> implements Ipresenter {
protected M mModel;
protected V mView;
public Basepresenter(M mModel, V mView) {
this.mModel = mModel;
this.mView = mView;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
if (mModel == null){
mModel.destroy();
mModel = null;
}
}
}
网络获取层
(1) okhttp获取
单例模式
public class RetrofitManager {
private Retrofit retrofit;
public Retrofit getRetrofit() {
if (retrofit == null){
HttpLoggingInterceptor httpLoggingInterceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
httpLoggingInterceptor.setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY);
OkHttpClient OKbuilder = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.writeTimeout(60*1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.readTimeout(60*1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.connectTimeout(60*1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.addInterceptor(httpLoggingInterceptor)
.build();
retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("需要获取的地址")
.client(OKbuilder)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJava2CallAdapterFactory.create())
.build();
}
return retrofit;
}
private static RetrofitManager retrofitManager;
public static RetrofitManager getRetrofitManager() {
if (retrofitManager == null){
retrofitManager = new RetrofitManager();
}
return retrofitManager;
}
}
okgo获取
(1) 进入
*[皮一下 身为程序员 okgo这么简单的方法还要来看吗 嘻嘻嘻]:
CallOberver
定义接口 自己来看吧
public interface Icalloberver<T> {
void suesse(T t);
void fail(String msg);
}
需要进来看
public abstract class CallOberver<T> extends DisposableObserver<T> implements Icalloberver<T> {
@Override
public void fail(String msg) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) Log.d("CallOberver", msg);
}
@Override
public void onNext(T t) {
suesse(t);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
fail(e.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
}
}
二 使用方法需要记得联系我 下一期继续
记得联系我
私信我
看到这了继续看一下吧 祝您心情好
锲而不舍?
祝你开心 心想事成 步步高升
*[相信自己 努力总会成功 加油 程序员这条路不好走 我们大家一起努力]: