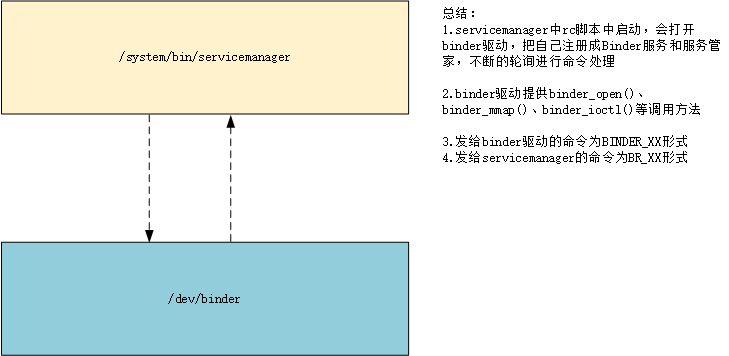
《Android系统启动流程》中,我们已经分析知道ServiceManager在rc脚本中启动,源码位于frameworks\native\cmds\servicemanager,本文基于aosp12,接着看其编译脚本Android.bp:
// frameworks\native\cmds\servicemanager\Android.bp
cc_binary { // 编译成二进制可执行程序
name: "servicemanager", // 程序名称
defaults: ["servicemanager_defaults"], // 引用默认模块
init_rc: ["servicemanager.rc"], // 从哪个rc脚本中启动
srcs: ["main.cpp"], // 源代码
}
cc_defaults {
name: "servicemanager_defaults",
srcs: [
"Access.cpp",
"ServiceManager.cpp",
]
}
从编译脚本Android.bp中可以看出,ServiceManager编译生成一个可执行程序,源代码主要包括main.cpp、Access.cpp、ServiceManager.cpp。接下来看程序入口main函数,主要执行逻辑分为以下几步:
- 打开Binder驱动
- 把自己注册成Binder服务
- 使自己成为“服务大管家”
- 开启轮询
- 解析命令,执行命令
// frameworks\native\cmds\servicemanager\main.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// 从rc脚本可以知道,没有传递过来参数,即driver = "/dev/binder"
const char* driver = argc == 2 ? argv[1] : "/dev/binder";
// 打开Binder驱动
sp<ProcessState> ps = ProcessState::initWithDriver(driver);
ps->setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(0);
ps->setCallRestriction(ProcessState::CallRestriction::FATAL_IF_NOT_ONEWAY);
sp<ServiceManager> manager = sp<ServiceManager>::make(std::make_unique<Access>());
// 把自己注册Binder服务
if (!manager->addService("manager", manager, false /*allowIsolated*/, IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT).isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not self register servicemanager";
}
// 使自己成为“服务大管家”
IPCThreadState::self()->setTheContextObject(manager);
ps->becomeContextManager();
// 开启循环
sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare(false /*allowNonCallbacks*/);
BinderCallback::setupTo(looper);
ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager);
while(true) {
looper->pollAll(-1);
}
// should not be reached
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
下面逐一分析每个步骤。
步骤一:打开Binder驱动
通过单例模式创建ProcessState对象,在其构造方法中打开Binder驱动,并初始化一些默认设置
// frameworks\native\libs\binder\ProcessState.cpp
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::initWithDriver(const char* driver)
{
return init(driver, true /*requireDefault*/);
}
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::init(const char *driver, bool requireDefault)
{
// driver为"/dev/binder",不为null,这个判断不执行
if (driver == nullptr) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(gProcessMutex);
if (gProcess) {
verifyNotForked(gProcess->mForked);
}
return gProcess;
}
// 通过单例模式创建ProcessState对象
[[clang::no_destroy]] static std::once_flag gProcessOnce;
std::call_once(gProcessOnce, [&](){
// 判断"/dev/binder"节点读写是否正常
if (access(driver, R_OK) == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder driver %s is unavailable. Using /dev/binder instead.", driver);
driver = "/dev/binder";
}
// pthread_atfork():linux内核函数,用于多线程时创建进程
int ret = pthread_atfork(ProcessState::onFork, ProcessState::parentPostFork,
ProcessState::childPostFork);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(gProcessMutex);
gProcess = sp<ProcessState>::make(driver);
});
if (requireDefault) {
// 打印异常log
}
verifyNotForked(gProcess->mForked);
return gProcess;
}
// 可以看到ProcessState构造函数中open_driver(),打开了binder驱动
ProcessState::ProcessState(const char* driver)
: mDriverName(String8(driver)),
mDriverFD(-1),
mVMStart(MAP_FAILED),
mThreadCountLock(PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER),
mThreadCountDecrement(PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER),
mExecutingThreadsCount(0),
mWaitingForThreads(0),
mMaxThreads(DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS),
mCurrentThreads(0),
mKernelStartedThreads(0),
mStarvationStartTimeMs(0),
mForked(false),
mThreadPoolStarted(false),
mThreadPoolSeq(1),
mCallRestriction(CallRestriction::NONE) {
base::Result<int> opened = open_driver(driver);
if (opened.ok()) {
// 进行内存映射
mVMStart = mmap(nullptr, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE,
opened.value(), 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
close(opened.value());
opened = base::Error()
<< "Using " << driver << " failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.";
mDriverName.clear();
}
}
// 保存fd值
if (opened.ok()) {
mDriverFD = opened.value();
}
}
static base::Result<int> open_driver(const char* driver) {
// 通过linux内核open(),打开binder驱动
int fd = open(driver, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd < 0) {
return base::ErrnoError() << "Opening '" << driver << "' failed";
}
// 下面是通过ioctl()命令来发送一些初始化设置给binder驱动
int vers = 0;
status_t result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers);
if (result == -1) {
close(fd);
return base::ErrnoError() << "Binder ioctl to obtain version failed";
}
if (result != 0 || vers != BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION) {
close(fd);
return base::Error() << "Binder driver protocol(" << vers
<< ") does not match user space protocol("
<< BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION
<< ")! ioctl() return value: " << result;
}
size_t maxThreads = DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to set max threads failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
uint32_t enable = DEFAULT_ENABLE_ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_ENABLE_ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION, &enable);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE_IF(ProcessState::isDriverFeatureEnabled(
ProcessState::DriverFeature::ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION),
"Binder ioctl to enable oneway spam detection failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
return fd;
}
步骤二:把自己注册成Binder服务
将ServiceManager这个服务保存中mNameToService中,回调服务onRegistration()方法。其实ServiceManager也是一个服务,用来管理其他服务,在其他服务启动注册前就已经就绪了。
// frameworks\native\libs\binder\ProcessState.cpp
Status ServiceManager::addService(const std::string& name, const sp<IBinder>& binder, bool allowIsolated, int32_t dumpPriority) {
...// 前面是一些异常检查
mNameToService[name] = Service {
.binder = binder,
.allowIsolated = allowIsolated,
.dumpPriority = dumpPriority,
.debugPid = ctx.debugPid,
};
auto it = mNameToRegistrationCallback.find(name);
if (it != mNameToRegistrationCallback.end()) {
for (const sp<IServiceCallback>& cb : it->second) {
mNameToService[name].guaranteeClient = true;
cb->onRegistration(name, binder);
}
}
return Status::ok();
}
// frameworks\native\cmds\servicemanager\ServiceManager.h
using ServiceMap = std::map<std::string, Service>;
步骤三:使自己成为“服务大管家”
代码比较简单,就是给binder驱动发送BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR命令
// frameworks\native\libs\binder\ProcessState.cpp
bool ProcessState::becomeContextManager()
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
flat_binder_object obj {
.flags = FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_TXN_SECURITY_CTX,
};
int result = ioctl(mDriverFD, BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR_EXT, &obj);
// fallback to original method
if (result != 0) {
android_errorWriteLog(0x534e4554, "121035042");
int unused = 0;
result = ioctl(mDriverFD, BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR, &unused);
}
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to become context manager failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return result == 0;
}
步骤四:开启轮询
开启了死循环,通过Looper不停的pull,回调给相应的LooperCallback
// frameworks\native\cmds\servicemanager\main.cpp
// 开启轮询
sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare(false /*allowNonCallbacks*/);
BinderCallback::setupTo(looper);
ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager);
while(true) {
looper->pollAll(-1);
}
// -----------------------------轮询读取命令-----------------------------
class BinderCallback : public LooperCallback {
public:
static sp<BinderCallback> setupTo(const sp<Looper>& looper) {
sp<BinderCallback> cb = sp<BinderCallback>::make();
int binder_fd = -1;
IPCThreadState::self()->setupPolling(&binder_fd);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(binder_fd < 0, "Failed to setupPolling: %d", binder_fd);
int ret = looper->addFd(binder_fd,
Looper::POLL_CALLBACK,
Looper::EVENT_INPUT,
cb,
nullptr /*data*/);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(ret != 1, "Failed to add binder FD to Looper");
return cb;
}
int handleEvent(int /* fd */, int /* events */, void* /* data */) override {
IPCThreadState::self()->handlePolledCommands();
return 1; // Continue receiving callbacks.
}
};
步骤五:解析命令,执行命令
从上面可以看到,处理命令是调用了IPCThreadState::self()->handlePolledCommands();,下面分析具体逻辑。
解析命令:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
15204284 查看本文章


// `self()`主要获取IPCThreadState对象
// 读取Parcel中的数据,执行命令
status_t IPCThreadState::handlePolledCommands()
{
status_t result;
do {
result = getAndExecuteCommand();
} while (mIn.dataPosition() < mIn.dataSize());
processPendingDerefs();
flushCommands();
return result;
}
status_t IPCThreadState::getAndExecuteCommand()
{
status_t result;
int32_t cmd;
// 通过给binder驱动发送ioctl(BINDER_WRITE_READ)
result = talkWithDriver();
if (result >= NO_ERROR) {
size_t IN = mIn.dataAvail();
if (IN < sizeof(int32_t)) return result;
cmd = mIn.readInt32(); // 读取命令
...
result = executeCommand(cmd); // 执行命令
...
}
return result;
}
执行命令:
BR_TRANSACTION这个命令比较重要,可以看到里面有对oneway标识的处理,没有加oneway标识时会对binder驱动回复。
// 执行命令
status_t IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int32_t cmd)
{
BBinder* obj;
RefBase::weakref_type* refs;
status_t result = NO_ERROR;
switch ((uint32_t)cmd) {
case BR_TRANSACTION_SEC_CTX:
case BR_TRANSACTION:
{
binder_transaction_data_secctx tr_secctx;
binder_transaction_data& tr = tr_secctx.transaction_data;
if (cmd == (int) BR_TRANSACTION_SEC_CTX) {
result = mIn.read(&tr_secctx, sizeof(tr_secctx));
} else {
result = mIn.read(&tr, sizeof(tr));
tr_secctx.secctx = 0;
}
if (result != NO_ERROR) break;
Parcel buffer;
buffer.ipcSetDataReference(
reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast<const binder_size_t*>(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(binder_size_t), freeBuffer);
const void* origServingStackPointer = mServingStackPointer;
mServingStackPointer = &origServingStackPointer; // anything on the stack
const pid_t origPid = mCallingPid;
const char* origSid = mCallingSid;
const uid_t origUid = mCallingUid;
const int32_t origStrictModePolicy = mStrictModePolicy;
const int32_t origTransactionBinderFlags = mLastTransactionBinderFlags;
const int32_t origWorkSource = mWorkSource;
const bool origPropagateWorkSet = mPropagateWorkSource;
// Calling work source will be set by Parcel#enforceInterface. Parcel#enforceInterface
// is only guaranteed to be called for AIDL-generated stubs so we reset the work source
// here to never propagate it.
clearCallingWorkSource();
clearPropagateWorkSource();
mCallingPid = tr.sender_pid;
mCallingSid = reinterpret_cast<const char*>(tr_secctx.secctx);
mCallingUid = tr.sender_euid;
mLastTransactionBinderFlags = tr.flags;
Parcel reply;
status_t error;
if (tr.target.ptr) {
// We only have a weak reference on the target object, so we must first try to
// safely acquire a strong reference before doing anything else with it.
if (reinterpret_cast<RefBase::weakref_type*>(
tr.target.ptr)->attemptIncStrong(this)) {
error = reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->transact(tr.code, buffer,
&reply, tr.flags);
reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->decStrong(this);
} else {
error = UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION;
}
} else {
error = the_context_object->transact(tr.code, buffer, &reply, tr.flags);
}
if ((tr.flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0) {
// 没有加oneway标识,直接进行回复
if (error < NO_ERROR) reply.setError(error);
constexpr uint32_t kForwardReplyFlags = TF_CLEAR_BUF;
sendReply(reply, (tr.flags & kForwardReplyFlags));
} else {
// 打印log
}
mServingStackPointer = origServingStackPointer;
mCallingPid = origPid;
mCallingSid = origSid;
mCallingUid = origUid;
mStrictModePolicy = origStrictModePolicy;
mLastTransactionBinderFlags = origTransactionBinderFlags;
mWorkSource = origWorkSource;
mPropagateWorkSource = origPropagateWorkSet;
}
break;
case BR_DEAD_BINDER:
{
BpBinder *proxy = (BpBinder*)mIn.readPointer();
proxy->sendObituary();
mOut.writeInt32(BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE);
mOut.writePointer((uintptr_t)proxy);
} break;
......
return result;
}