题目
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3884
分析
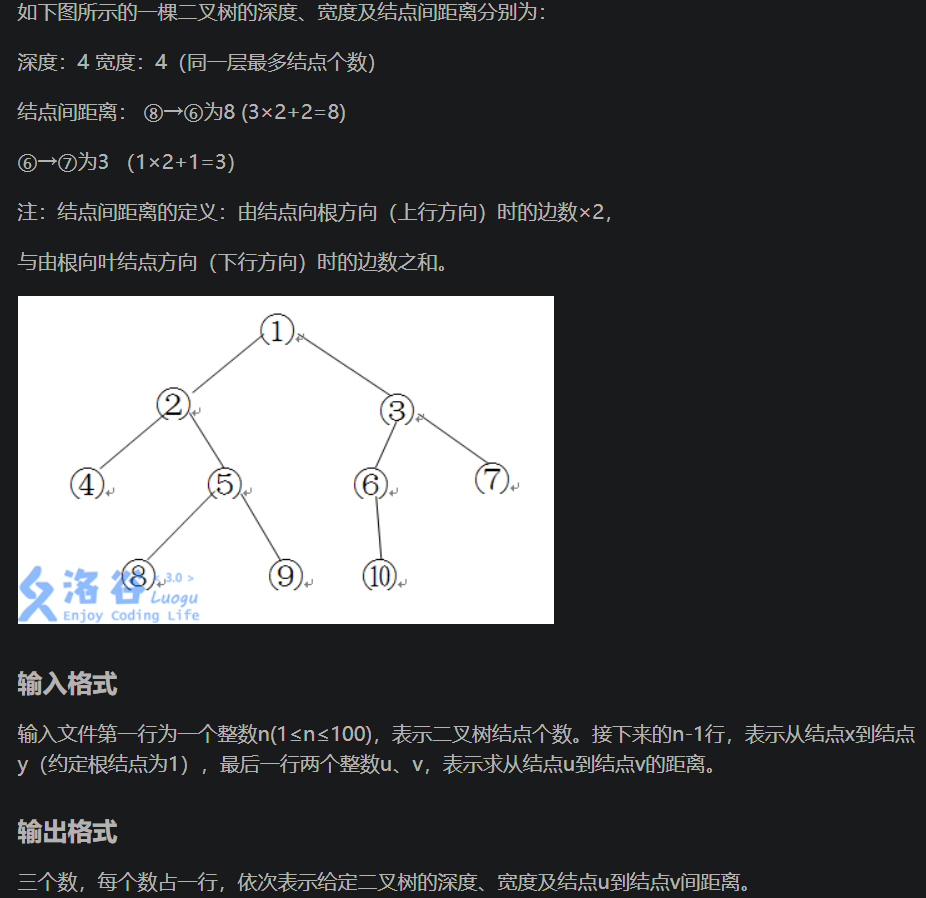
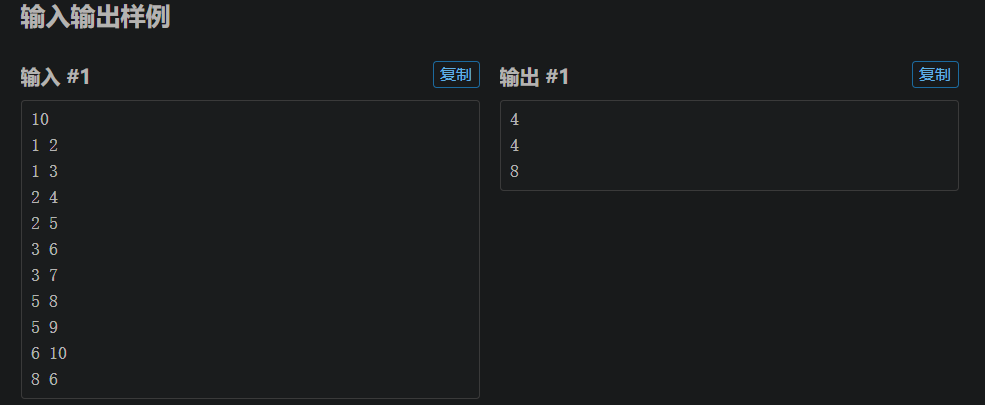
二叉树的深度、宽度:我们可以使用链式前向星在进行dfs遍历的时候为节点的深度赋值,同时对记录深度的数组的个数加一最后选择深度的最大值,宽度的最大值
U 到V的距离:这里一般的算法就是使用LCA来寻找这两个节点的共同公共祖先,通过公共祖先的路径就是二者的最短路径
于是我们可以使用离线的tarjan算法寻找公共祖先,但是本题的特殊性是题目的图是一个有根树而不是一个无根树,所以我们可以通过记录每一个节点的父亲来寻找公共祖先
方法一
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; int deep[200], amount[200],head[200],head2[200],vis[200],father[200],answer[200]; int n,cnt=0,cnt2=0; #define maxn 200 #define maxm 4000 struct edge { int to; int next; }e[maxm*2]; struct edge2 { int to; int next; int num; }e2[maxm * 2]; void addedge(int u,int v) { cnt++; e[cnt].to = v; e[cnt].next = head[u]; head[u] = cnt; } void addedge2(int u, int v,int w) { cnt2++; e2[cnt2].to = v; e2[cnt2].num = w; e2[cnt2].next = head2[u]; head2[u] = cnt2; } int maxdepth = -1, maxwidth = -1; void dfs(int p, int fa,int depth) { deep[p] = depth; if (depth > maxdepth)maxdepth = depth; amount[depth]++; if (amount[depth] > maxwidth)maxwidth = amount[depth]; for (int i = head[p]; i; i = e[i].next) { int y = e[i].to; if (y == fa)continue; dfs(y, p, depth + 1); } } int find(int x) { if (father[x] == x)return x; return father[x] = find(father[x]); } void tarjan(int root) { vis[root] = 1; for (int i = head[root]; i; i = e[i].next) { int y = e[i].to; if (vis[y])continue; tarjan(y); father[y] = root; } for (int i = head2[root]; i; i = e2[i].next) { int y = e2[i].to; if (vis[y])answer[e2[i].num] = find(y); } } int main() { scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { int a, b; scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); addedge(a, b); addedge(b, a); } dfs(1, 0, 1); int u, v; scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); addedge2(u,v,0); addedge2(v, u, 0); for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)father[i] = i; tarjan(1); printf("%d\n", maxdepth); printf("%d\n", maxwidth); printf("%d", (deep[u]-deep[answer[0]]) * 2 + deep[v]-deep[answer[0]]); }
方法二
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int deep[200], amount[200],head[200], father[200]; int n, cnt = 0; #define maxn 200 #define maxm 4000 struct edge { int to; int next; }e[maxm * 2]; void addedge(int u, int v) { cnt++; e[cnt].to = v; e[cnt].next = head[u]; head[u] = cnt; } int maxdepth = -1, maxwidth = -1; void dfs(int p, int fa, int depth) { father[p] = fa; deep[p] = depth; if (depth > maxdepth)maxdepth = depth; amount[depth]++; if (amount[depth] > maxwidth)maxwidth = amount[depth]; for (int i = head[p]; i; i = e[i].next) { int y = e[i].to; if (y == fa)continue; dfs(y, p, depth + 1); } } int main() { scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { int a, b; scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); addedge(a, b); addedge(b, a); } dfs(1, 0, 1); int u, v; scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); printf("%d\n", maxdepth); printf("%d\n", maxwidth); int uu = u, vv = v; while (deep[u]!=deep[v]) { if (deep[u] > deep[v]) { u = father[u]; } else { v = father[v]; } } if (u == v) { if (deep[uu] < deep[vv])printf("%d", abs(deep[uu] - deep[vv])); else printf("%d", abs(deep[vv] - deep[uu]) * 2); return 0; } while (father[u] != father[v]) { u = father[u]; v = father[v]; } printf("%d", (deep[uu] - deep[father[u]]) * 2 + deep[vv] - deep[father[u]]); }
第二种的方法注意要区别两个节点在同一侧还是在不同的两侧