1053 Path of Equal Weight (30分)
Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
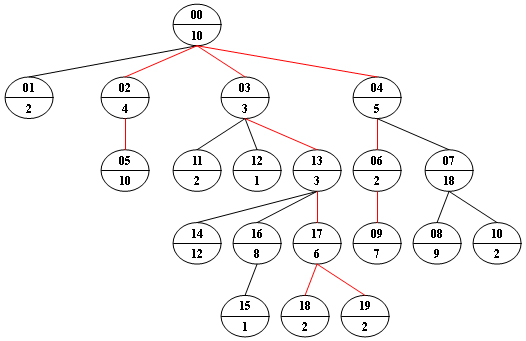
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let's consider the tree showed in the following figure: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in the figure.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N≤100, the number of nodes in a tree, M (<N), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0<S<230, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<1000) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence {A1,A2,⋯,An} is said to be greater than sequence {B1,B2,⋯,Bm} if there exists 1≤k<min{n,m} such that Ai=Bi for i=1,⋯,k, and Ak+1>Bk+1.
Sample Input:
20 9 24
10 2 4 3 5 10 2 18 9 7 2 2 1 3 12 1 8 6 2 2
00 4 01 02 03 04
02 1 05
04 2 06 07
03 3 11 12 13
06 1 09
07 2 08 10
16 1 15
13 3 14 16 17
17 2 18 19Sample Output:
10 5 2 7
10 4 10
10 3 3 6 2
10 3 3 6 2AC代码(算法笔记):
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
const int maxn = 110;
int n, m, s, path[maxn];
struct Node {
int weight;
vector<int> child;
}node[maxn];
bool cmp(int x, int y) { return node[x].weight > node[y].weight; }
void dfs(int index, int nowsum, int total) {
if (nowsum > s)return;
if (nowsum == s) {
if (node[index].child.size() != 0)return;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
printf("%d%c", node[path[i]].weight, (i == total - 1) ? '\n' : ' ');
return;
}
if (nowsum < s) {
for (int i = 0; i < node[index].child.size(); i++) {
path[total] = node[index].child[i];
dfs(node[index].child[i], nowsum + node[node[index].child[i]].weight, total + 1);
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &s);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d", &node[i].weight);
int k, id, childnum;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &id, &k);
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
scanf("%d",&childnum);
node[id].child.push_back(childnum);
}
sort(node[id].child.begin(), node[id].child.end(), cmp);
}
path[0] = 0;
dfs(0, node[0].weight, 1);
return 0;
}