题目贴上
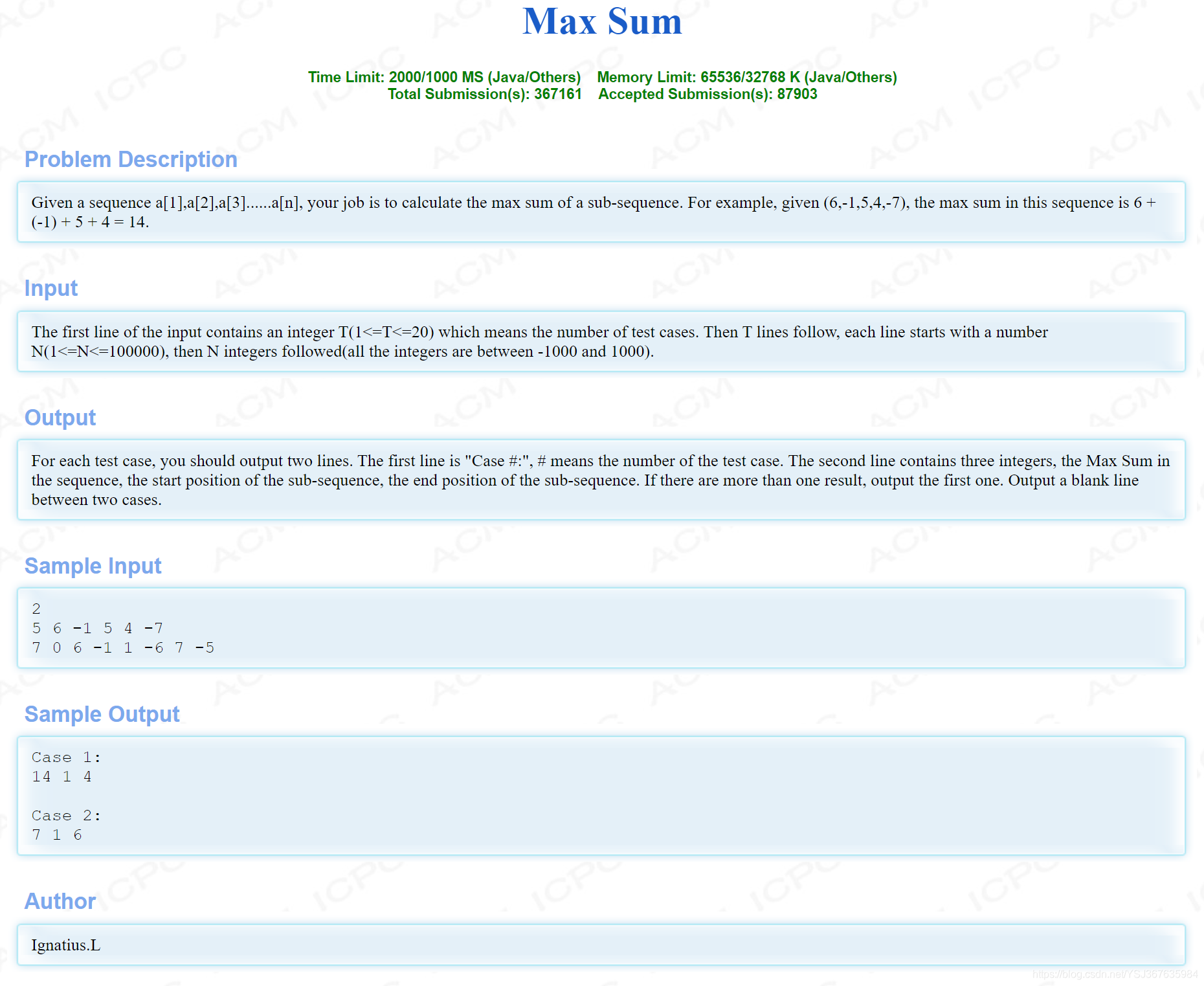
题目大意相信应该都知道了
这里借助动态规划进行状态转移
dp[i] 表示以 a[i] 结尾的最大子段和
为了节省空间,可以将dp[i] 当 a[i] 来用
最后考虑两种情况
- 如果 dp[i-1] 小于0,说明上一个状态是一个结束状态,那么此时的dp[i],我们需要更新新的左端点索引值
- 如果dp[i] 大于当前最大的子段和,将最大左,右端点索引值和最大有效值更新即可,千万不要写大于等于,因为如果你写了大于等于,而当前测试用例如果有多个解,就会被后面的值覆盖,这样子就不符合题目中输出最开始的左右端点索引值的要求了
- 这是一个很经典的动态规划,希望各位认真对待,一定要搞懂昂
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define endl '\n'
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
typedef __int64 bi;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 1e6+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){
return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){
if(!b){
d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{
ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){
ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){
if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){
return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){
ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){
ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {
if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = {
{
1,0}, {
-1,0},{
0,1},{
0,-1} };
int dp[maxn];
signed main(void)
{
int t,n,c=0;
t = read();
while(t--){
n = read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) dp[i] = read();
int l = 1,r = 1,maxn = dp[1] ,curl = 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i){
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+dp[i],dp[i]);
if(dp[i-1] < 0) curl = i;
if(dp[i] > maxn){
// 更新最大子段和
maxn = dp[i];
// 更新最大结果区间的左端点和右端点
l = curl;
r = i;
}
}
printf("Case %d:\n%d %d %d\n",++c,maxn,l,r);
if(t) cout<<endl;
}
}